In recent years, the worlds of web3 and finance have intertwined in a revolutionary transformation called DeFi (decentralized finance).
DeFi is helping reshape the way we think about traditional financial systems and may offer a more inclusive, open, and transparent approach to managing, lending, and borrowing assets.
The relatively new financial model accounts for over $56 billion TVL (total valued locked), with an all-time high of $177 billion in 2021 when it burst on the scene.
We will delve into the fascinating world of DeFi, providing a comprehensive introduction to what it is, its underlying principles, key components, and its impact on the global financial landscape.
This article outlines some of the key concepts and real world applications in DeFi and explains how it differs from traditional finance (TradFi).
What is DeFi?
DeFi refers to “decentralized finance”, a sector in which all transactions take place without any centralized financial institutions like banks. Instead, self-executing computer codes called smart contracts manage these transactions.
Decentralized finance is built on blockchain technology, just like cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin and Ethereum. And just like those blockchains, decentralized finance stems from the idea that everyone should be in full control of their digital assets, and free to use them as they like.
In DeFi, anyone with an internet connection can participate in applications like decentralized exchanges (DEXs), yield farming, liquidity pools, borrowing and lending platforms, and much more.
History of DeFi and Ethereum
In 2013, Vitalik Buterin first proposed the idea that cryptocurrencies can expand beyond simple transactions to include complex financial services. In the Ethereum white paper, he introduced the concept of smart contracts, which would enable developers to design decentralized apps.
Solidity, the programming language of Ethereum, was conducive to writing the contract code for dApps and deploying them on the blockchain. Ethereum, therefore, inaugurated the decentralized finance movement and is still host to the majority of dApps. Currently, the Ethereum network dominates the DeFi sector with a 54% market share.
This market dominance has some disadvantages, however. The transaction fees (gas) have skyrocketed during periods of high network congestion and led to more transaction processing time.

Moreover, for most of its existence Ethereum has relied on the energy-intensive Proof of Work consensus mechanism that leaves behind a high carbon footprint.
To overcome these shortcomings, Ethereum completed the upgrade to Ethereum 2.0 and a Proof of Stake consensus model. Since the Ethereum mainnet “merged” with the Beacon Chain, the blockchain network has reduced its energy emissions by 99.9%.
Important DeFi concepts you should know
Although decentralized finance may sound complex, its core concepts are relatively simple to understand:
1. Smart contracts
Smart contracts are self-executing agreements written in code that automatically execute when specific, predetermined conditions are met.
In DeFi, smart contracts are used to facilitate lending, borrowing, trading, and other financial services. They replace traditional contracts and centralized intermediaries, making transactions faster and, in many cases, cheaper.
Smart contracts use Oracles to provide external information via trusted data feeds. Oracle networks like Chainlink (LINK) enable DeFi applications to access real-world data, such as market prices, weather conditions, or scores from sporting events, and allow smart contracts to execute with correct information.
2. Yield farming
Yield farming is the process by which digital asset holders generate passive income by providing liquidity to DeFi apps. It is similar to depositing funds in a bank's savings accounts, albeit with much higher interest rates than those offered by banks.

In yield farming, liquidity providers deposit their digital assets in trading protocols to facilitate crypto trading. In return, farmers get Liquidity Provider (LP) tokens to stake in DeFi platforms or participate in initial DEX offerings (IDOs).
Yield farmers also provide capital to smart contract-enabled lending platforms and have the ability to earn interest from lending digital assets.
3. Staking
Staking is the process by which users lock their cryptocurrencies to validate transactions in a Proof of Stake blockchain. Stakers who deposit their crypto in a staking pool may earn rewards for keeping the blockchain safe. Stakers also run the risk of losing some or all of their crypto through a penalty known as ‘slashing’.

The protocol will generally offer a percentage of fees and governance tokens for successfully validating legitimate transactions on the network and may confiscate tokens for illegitimate actions.
Staking is comparatively easier than yield farming but has fixed lock-in periods.
4. Liquidity mining
Liquidity mining is the process by which miners can earn interest by providing digital assets to a liquidity pool on a decentralized exchange (DEX). Some decentralized crypto exchanges like Uniswap (UNI) require an equal proportion of token pairs in the liquidity pool while Balancer allows a customizable pool.
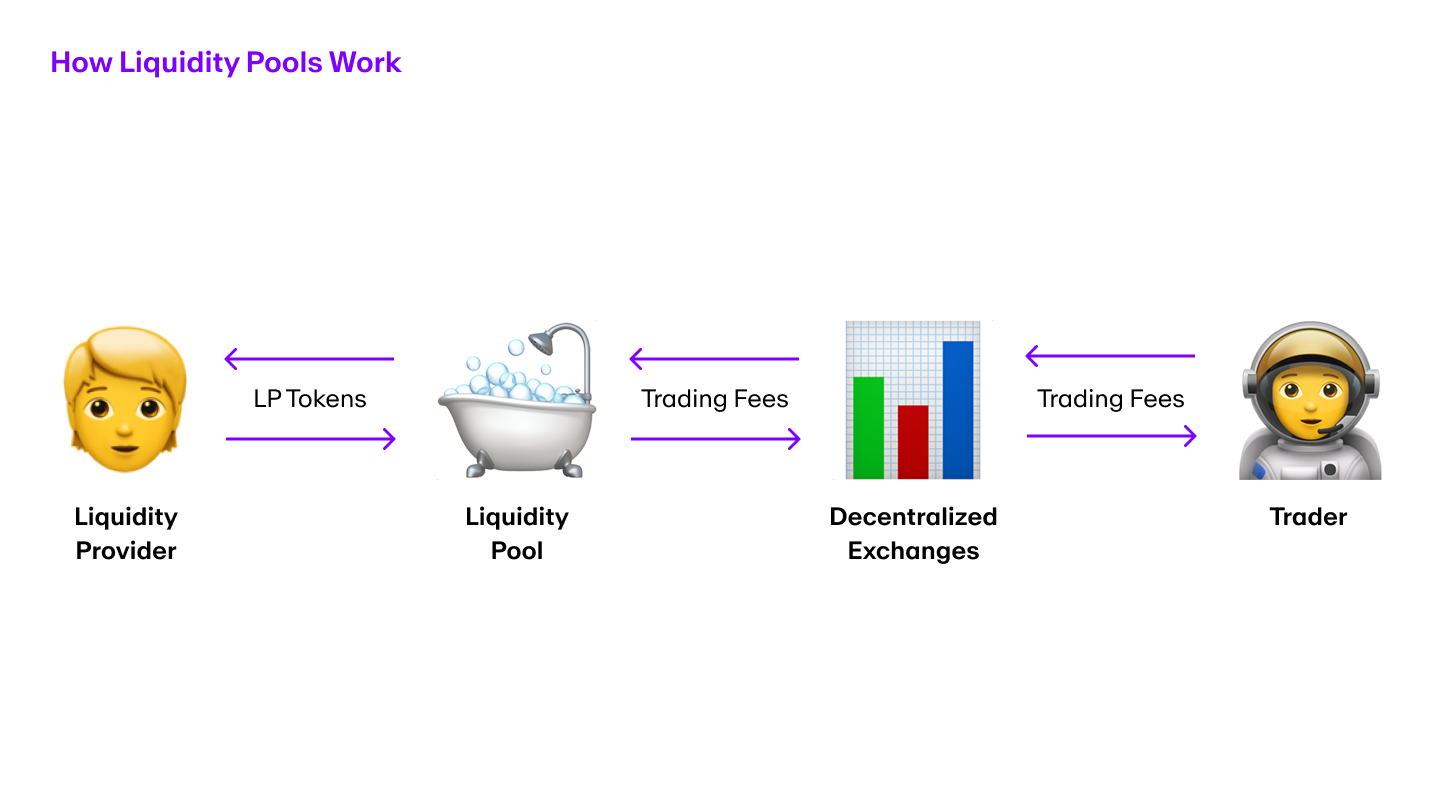
Liquidity mining is another popular passive income strategy for DeFi users. Many platforms offer enticing rewards to users like a percentage of trading fees and governance tokens.
Generally speaking, investing in a liquidity pool with a high Annual Percentage Yield (APY) will generate more returns than one with a lower APY. However, there are always liquidity risks such as impermanent loss, slippage, and smart contract bugs.
Simultaneously, DeFi projects may issue governance tokens for project users, empowering them to directly participate in governance decisions. Governance token holders have voting powers, with each token usually equivalent to one vote.
Users can vote on issues like adjusting transaction fees, adopting new rules, and general upgrades and modification to the protocol.
5. Token swapping
Token swapping is the process by which crypto holders exchange tokens for other cryptocurrencies.
Swapping happens through smart contract-enabled decentralized exchanges that leverage an Automated market maker (AMM) for exchanging tokens. An Automated Market Maker (such as Uniswap) is an underlying protocol in a decentralized exchange that replaces a traditional order book with an automatic pricing algorithm, facilitating trustless trading.
6. Composability
DeFi composability refers to the interoperability of DeFi platforms in which the value locked across different protocols is available for all decentralized applications (dApps). Users can therefore leverage the value locked across protocols like Aave, MakerDAO, and Curve Finance, and use it in other protocols.
Composability enables decentralized finance platforms to unlock new revenue streams as the liquidity no longer remains isolated. Thus, users can trade crypto assets, stake them, deposit tokens in liquidity pools, and lend and borrow cryptos across blockchain networks.
How is DeFi different from traditional finance?
Consider the following example to understand how decentralized finance functions differently from centralized institutions.
When Bob goes grocery shopping, he uses his debit card to pay for the bills. This seemingly simple payment process requires multiple steps.
First, the merchant forwards a request to an acquiring bank. The bank then forwards it to the card network, which requests payment from Bob's bank account. The money is then debited and transferred into the merchant account.
Since each intermediary charges a service fee, financial transactions become costly for the merchant. DeFi aims to bring down the transaction costs by facilitating a direct peer-to-peer payments system without involving traditional banking or other financial institutions.

A peer-to-peer network can also reduce friction points for people applying for loans or buying insurance. Users don't need to visit their local bank branch to submit a loan application and wait for approval.
Instead of relying on their credit score and paying hefty service fees, they can pay collateral and borrow money instantly via DeFi loans.
Popular DeFi applications and use cases
Now that you know the core concepts of DeFi, here are some of its most common use cases:
Decentralized exchange (DEX)
Most crypto users trade cryptocurrency assets on a centralized exchange (CEX) in which a central entity has control over user funds. In Q3 of 2023, for example, centralized exchanges recorded $1.12 trillion in trading volume.
Users are beginning to realize, however, that CEXs require them to trust third parties, which goes against a fundamental principle of crypto. It can also be risky: some CEXs have kept users' funds when facing collapse.

In smart contract-enabled DEXs, however, users can trade a particular digital asset without involving any intermediaries. This peer-to-peer (P2P) trading helps users retain sovereign control of their funds.
Of course, DEXs also carry certain risks, such as smart contract vulnerabilities, liquidity risks, network issues, and more.
The use of decentralized exchanges is thus rising: In 2022, DEXs recorded $854 billion in trading volume. Although this marks a downturn from $1 trillion in 2021, it still marks a steep rise of 642% from 2020. The data still demonstrates that DEX trading grew more in the last year than CEX trading, with DEX vs CEX dominance currently sitting at 15.1%.
Lending and borrowing
Unlike traditional financial systems in which banks manage lending and borrowing, in DeFi, smart contracts facilitate these services. Automating lending and borrowing services may help to reduce application processing time and high overhead charges. A user might be able to instantly get a loan without having to complete any paperwork.
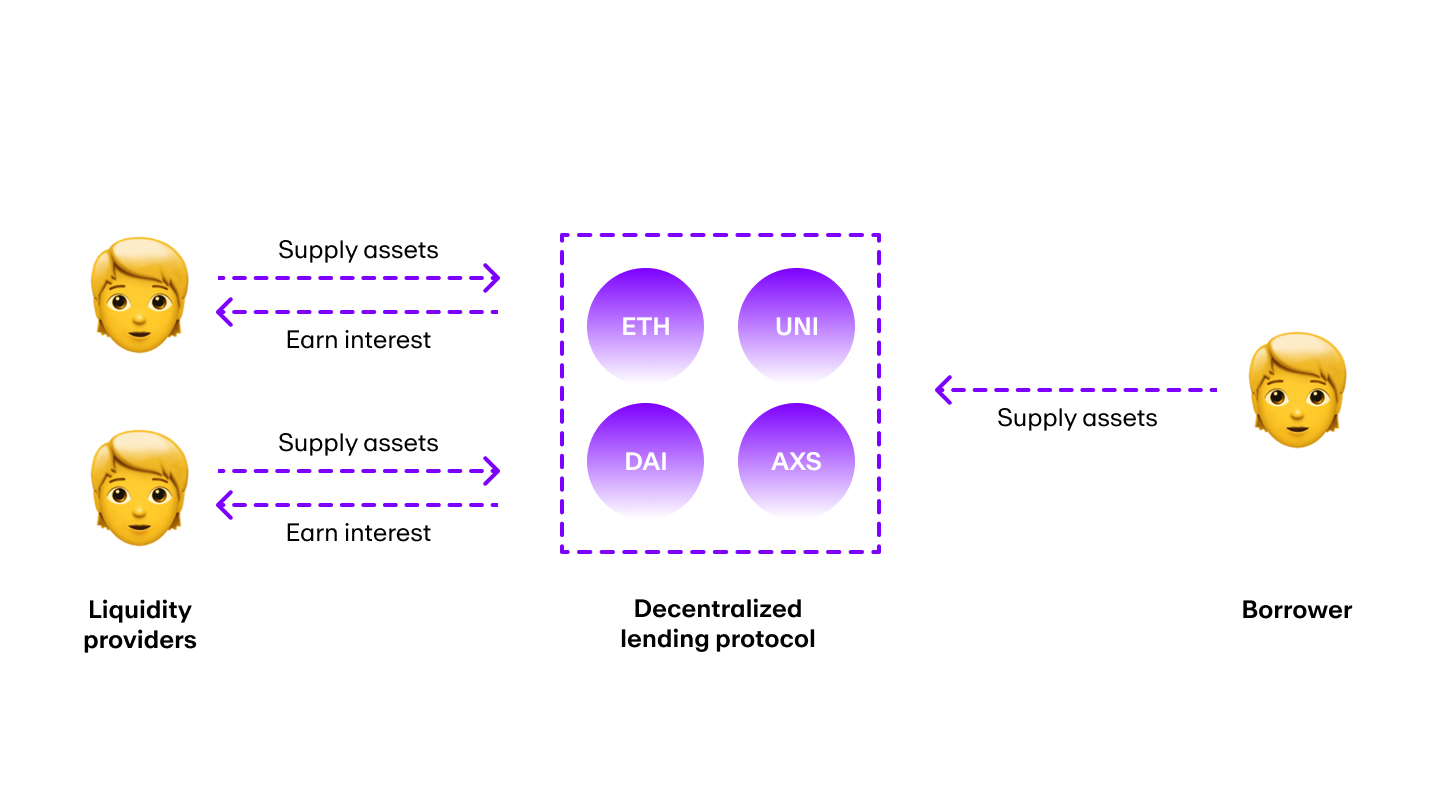
Some DeFi applications also offer flash loans to users. A flash loan is an uncollateralized loan in which traders borrow and return funds instantaneously.
Stablecoins
Stablecoins are a relatively new innovation that addresses the notoriously high crypto market volatility. A stablecoin is a cryptocurrency that attempts to maintain a stable value by pegging it to a fiat currency (US Dollar, Euro) or commodities like gold. Some of the most popular stablecoins include Tether (USDT), USD Coin (USDC), and Dai (DAI).
Stablecoins can be held in a wallet as a hedge against crypto inflation, used in liquidity pools to earn yield, or traded for other cryptocurrency tokens. For instance, MoonPay allows you to trade USDC (SOL) for any Solana SPL token, right in your MoonPay Account.
%20(1)-1.png)
Wrapped cryptocurrencies
Wrapped cryptocurrencies are a unique technology that strengthens DeFi composability. Wrapped cryptocurrencies refer to digital tokens whose value is pegged to another crypto on a different blockchain in a 1:1 ratio, like wrapped Ethereum (WETH) or wrapped Bitcoin (WBTC). Wrapped tokens can work on non-native blockchain networks, making assets more interoperable.

For example, wrapped Bitcoin (wBTC) can function on Ethereum protocols, enabling Bitcoin holders to participate in the DeFi ecosystem. Some companies like DG Labs and Suredbits have even experimented with solutions that incorporate smart contract functionality into the Bitcoin network.
Instead of wrapping BTC, these projects are developing discreet log contracts to facilitate derivatives trading and pay for futures contracts.
Did you know? There are now Bitcoin NFTs
Decentralized banking
DeFi offers miscellaneous banking services like buying insurance or trading derivatives and futures contracts. The experience is similar to buying or selling stocks, but without the involvement of brokers.
Prediction markets
DeFi has made inroads into betting and prediction. Prediction markets are empowering users to rely on quantified forecasting as an essential tool to better predict future results. Prediction markets can help to answer complex social questions and deliver robust information by weeding out faulty forecasters.
Advantages of DeFi over traditional finance
Decentralized finance has an edge over centralized finance for a number of reasons:
Minimal transaction fees
In the absence of a financial institution, DeFi participants don't need to pay high fees for complex financial transactions. DeFi applications (dApps) do, however, charge a small fee for the maintenance and upkeep of their platforms.
Trustless setup
With smart contract-enabled DeFi applications, users no longer need to trust traditional financial institutions with their money. Users retain control of all their cryptocurrency assets in a secure digital wallet and use their private keys for financial transactions.
Low entry barriers
Users don't need to go through an extensive onboarding process. A stable internet connection may be enough to start using decentralized financial applications from a mobile phone or computer.
Fast transaction settlement
Since the centralized financial system involves multiple intermediaries, the transaction processing and approval time can be quite high. In a peer-to-peer network, however, transaction settlement happens instantaneously and users can transfer their crypto assets in seconds.
Better identity protection
DeFi applications may not not ask for a user's name, email, or any other personal information, thereby protecting the user's identity. Pseudonymous usage on a public ledger prevents any possibility of theft of user data.
What are the risks of DeFi?
Even with its clear advantages, there are still some drawbacks of decentralized finance compared to centralized finance:
DeFi hacks
Hackers can exploit a bug or other vulnerabilities in the smart contract code to steal investor funds. To date, DeFi hacks have accounted for over $7.2 billion in stolen funds. In 2022 alone, more than $3.1 billion was hacked from DeFi protocols, representing 82.1% of all cryptocurrency thefts.
Minimal consumer protections
In the current financial system, banks maintain a private ledger that is open to scrutiny from regulatory bodies. With DeFi, however, transactions are mostly beyond the scope of regulatory bodies like the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) or the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC). Cryptocurrency investors, therefore, have little to no protection from rug pulls or fraud.
Private key management
DeFi users often use a non-custodial wallet to store their cryptocurrencies, making them sovereign owners of their assets. Losing these keys, however, means losing access to the wallet's funds. Users must therefore take extra precautions to safely store their keys.

Read our articles How to spot and avoid crypto scams and Crypto security basics: Staying safe in Web3 to learn about scams and how to stay safe while investing.
Market Volatility
Decentralized finance relies on the cryptocurrency market, which can be highly volatile. Price fluctuations can impact the value of assets locked in DeFi applications, leading to potential liquidations and unexpected losses.
The Future of DeFi
DeFi is one of the fastest-growing blockchain sectors, recording 47% growth in one year. During the 2021 bull run, the total value locked (TVL) in DeFi protocols surpassed $233 billion from just $13.6 billion in 2020. Since then, however, the TVL of decentralized finance has fallen from its high of $166.67 billion at the start of 2022 to $41.79 billion in 2023
As DeFi protocols continue to innovate and become more decentralized, they hope to successfully decouple themselves from legacy market conditions. Once that happens, the DeFi market might bring more value to the global economy.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about DeFi
DeFi offers the potential for very high ROI, but high-profit percentages are often accompanied by greater risks. Users therefore need to do their own research before using or investing in any DeFi application.
It is often best to choose protocols that offer bug bounty programs, invite white hat hackers, are not fully anonymous, and conduct third-party audits. These methods help decentralized protocols lower the risk of major theft.
How do you make money in DeFi?
Users can try to make money in DeFi by trading their assets on a decentralized crypto exchange and participating in lending, borrowing, yield farming, staking, or prediction markets.
Although these decentralized applications offer the opportunity to make money, there is no guarantee that they will return more than if a user simply decided to "hodl" cryptocurrency. Furthermore, there always exists the chance that a user will suffer losses, due to factors such as impermanent loss, potential hacks and scams, as well as general market conditions,
Can Bitcoin be used in DeFi?
Initially, Bitcoin was not a part of the DeFi ecosystem. However, Wrapped Bitcoin (wBTC), as well as other technologies like discreet log contracts, are starting to enable Bitcoin DeFi transactions.
Which cryptocurrencies can you use in DeFi?
There is a growing number of cryptocurrencies that can be used in decentralized finance. Here are a few examples:
- Wrapped Bitcoin (WBTC)
- Ethereum (ETH)
- Tron (TRX)
- Binance Coin (BNB)
- Polygon (MATIC)
- Avalanche (AVAX)
- Solana (SOL)
What are the most popular DeFi platforms?
Although this list is by no means exhaustive, here are some of the most popular DeFi applications by total volume locked (TVL)
Begin your DeFi journey with MoonPay
DeFi can help you earn passive income and grow your crypto portfolio.
To get started, simply buy cryptocurrency via MoonPay using your credit card or any other preferred payment method. MoonPay's widget allows you to easily buy Bitcoin, Ethereum, and more than 50 other cryptocurrencies.
MoonPay also makes it easy to sell crypto when you decide it's time to cash out, including several tokens mentioned in this article like BTC, ETH, AVAX, SOL, USDT, USDC, TRX, and BNB. Simply enter the amount of the token you'd like to sell and enter the details where you want to receive your funds.
Plus, buy USDC (SOL) to enjoy Solana DeFi trading on MoonPay, and trade for any supported Solana SPL token like SOL, BONK, TRUMP, RAY, JUP, and much more.

.png?w=3840&q=90)




