Each day, there are billions of dollars traded on cryptocurrency exchanges.
With so many people depending on both centralized and decentralized exchanges to buy, sell, and trade digital assets, understanding how they operate is crucial for anyone venturing into the world of cryptocurrency.
In this article, we examine the inner workings of cryptocurrency exchanges, how they work, their different types, and the factors to consider when choosing one.
What is a cryptocurrency exchange?
A cryptocurrency exchange is a platform that facilitates the transfer of digital assets like cryptocurrencies. Crypto exchanges provide users with tools to place buy or sell orders, enabling them to trade digital currencies swiftly and efficiently.
Similar to how traditional stock exchanges facilitate the trading of stocks and bonds, cryptocurrency exchanges function as intermediaries, providing a trading platform and enabling crypto transactions between buyers and sellers.
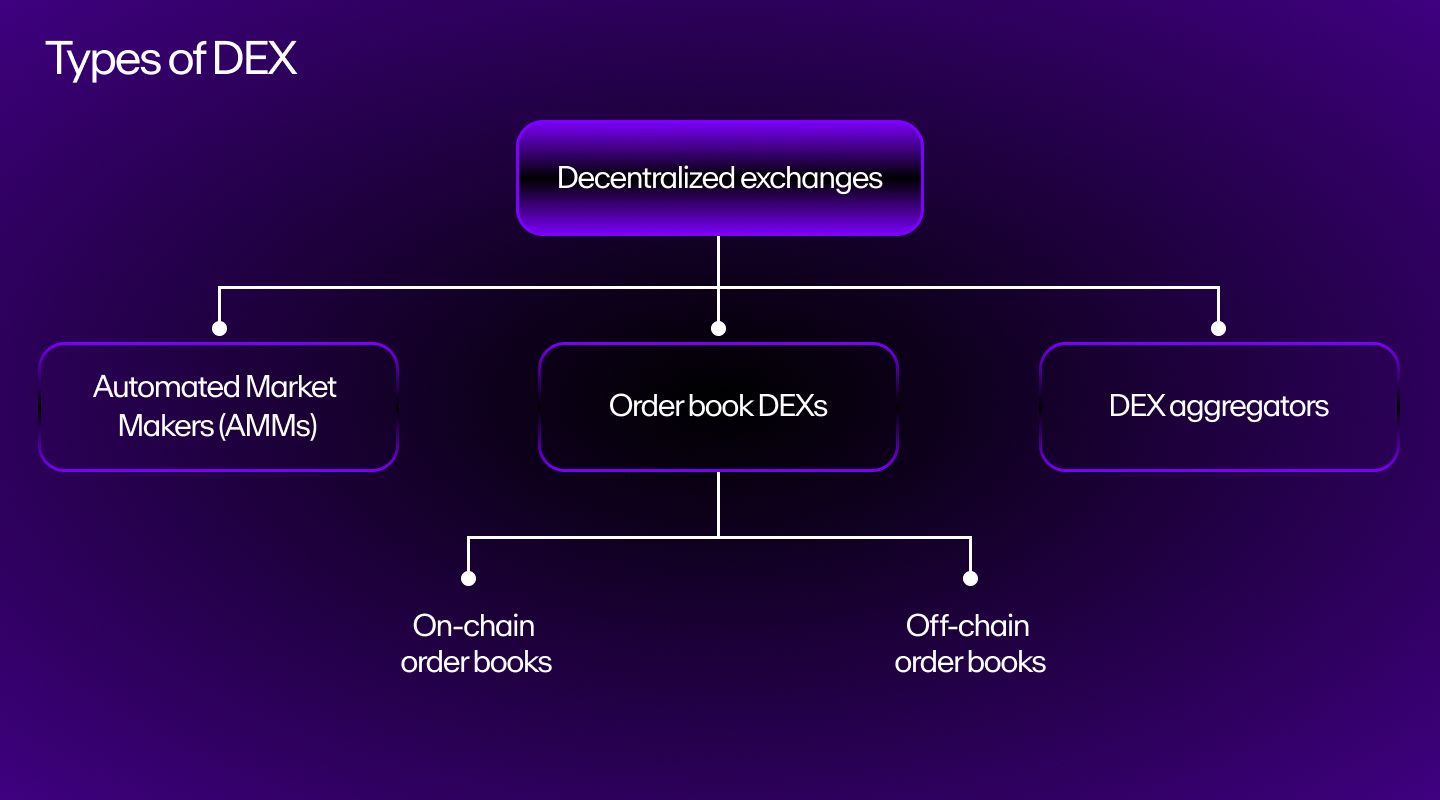
Cryptocurrency exchanges can come in various forms, most commonly as centralized exchanges (CEX) and decentralized exchanges (DEX).
Centralized exchanges are operated by a centralized authority or company, offering user-friendly interfaces though less autonomy over users' assets. On the other hand, decentralized exchanges operate without a centralized platform or authority, relying instead on smart contracts via blockchain technology to facilitate peer-to-peer trading directly between users.
How cryptocurrency exchanges work
The mechanics behind cryptocurrency exchanges involve a series of steps that attempt to ensure the proper execution of transactions and security of users' assets. Here's a simplified breakdown of how crypto exchanges work:
Exchange registration and KYC
Users typically need to register an account on most centralized exchanges before making any trades. They must provide necessary personal information and verify their identity via KYC procedures to comply with regulatory requirements. These steps may or may not be necessary for decentralized exchanges, however.
Deposit funds
Once registered, users can deposit funds into their exchange account (or wallet). Depending on the particular exchange, deposited funds can either be denominated in cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin (BTC) or fiat currencies like USD.
Placing orders
Users can place various types of orders, such as market orders (executed at the current market price) or limit orders (executed only at a specified price). They can buy or sell cryptocurrencies based on factors like personal preferences and market conditions.
Matching engine and order book
When a user places an order, the exchange uses a sophisticated algorithm called a matching engine to match an order with corresponding buy or sell orders from other users.
The order book, a central component of most crypto exchanges, displays all active buy and sell orders, allowing traders to assess market depth and liquidity. This matching process ensures that transactions occur at agreed-upon prices and quantities.
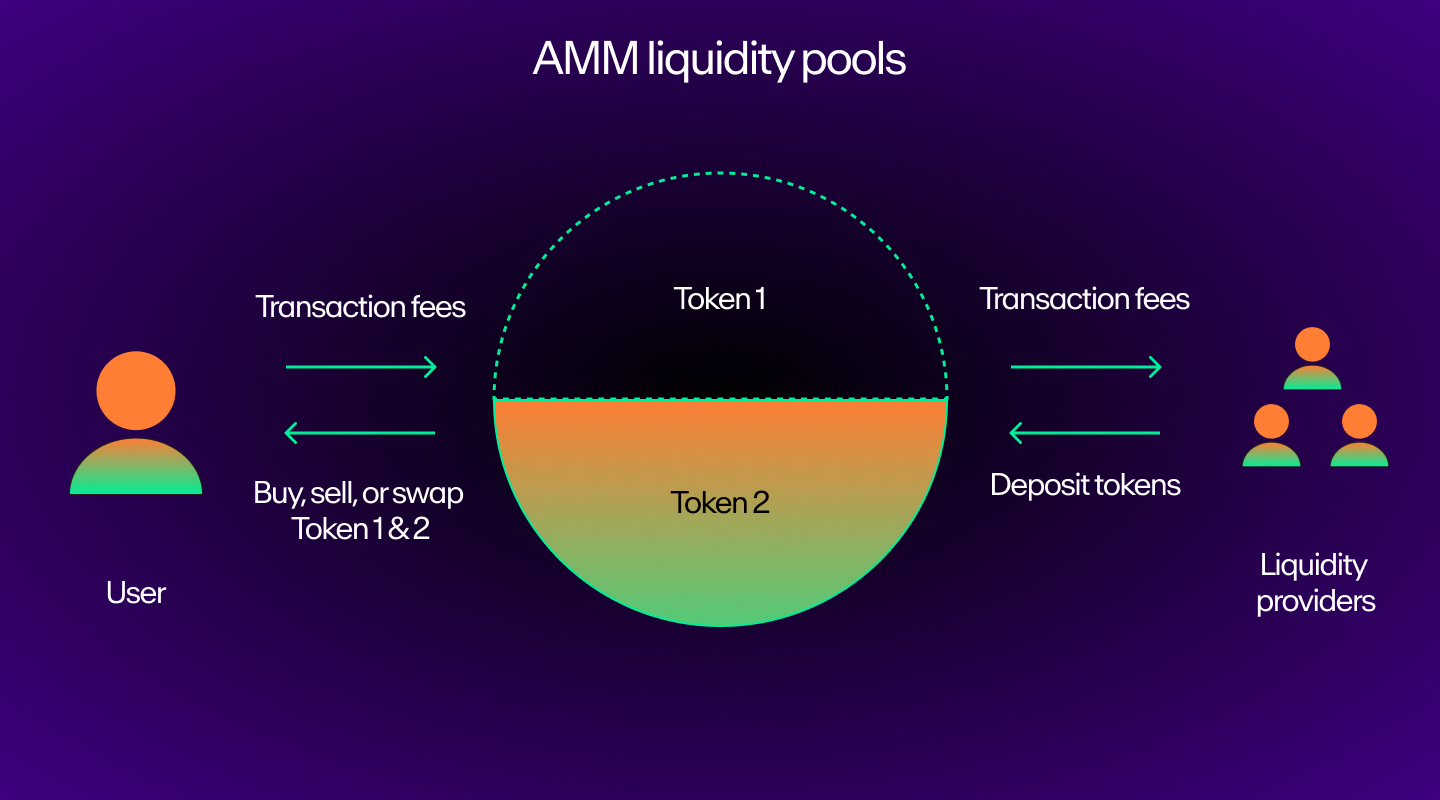
Some decentralized exchanges like Uniswap instead use an automated market maker (AMM) protocol that allows users to make trades via smart contracts and liquidity pools.
Execution and settlement
Once an order is matched, the crypto exchange executes the transaction, transferring the purchased cryptocurrencies to the buyer's account and deducting the corresponding funds from the seller's account. Settlement usually occurs in real-time or within a specified timeframe.
Types of orders: market, limit, & stop-loss
Some cryptocurrency exchanges may support various order types, such as:
- Market orders: execute immediately at the prevailing market price
- Limit orders: enable users to specify a price at which they wish to buy or sell
- Stop-loss orders: automatically trigger a sale when the price reaches a predetermined level.
Trading pairs and liquidity
- Trading pairs represent the assets being traded against each other on the exchange.
- Liquidity is a measure of how easily an asset can be bought or sold without significantly impacting its price. Liquidity is essential for any crypto exchange to have efficient trading and price discovery.
Withdrawal of funds
After completing transactions, users have the option to withdraw their cryptocurrencies or fiat funds from the exchange platform to their own digital wallet or bank account.
Fee structures: maker vs. taker fees
Digital currency exchanges typically charge transaction fees for executing trades, which may fall under two categories:
- Maker fees apply to traders who provide liquidity to the market by placing limit orders.
- Taker fees are transaction fees incurred by those who execute trades against existing orders.
It's important to note that different cryptocurrency exchanges may have varying features, fees, and security measures in place. Therefore, users should conduct thorough research and choose exchanges that best align with their trading needs, financial position, risk appetite, and other preferences.
What are the different types of cryptocurrency exchanges?
Before deciding to trade cryptocurrencies on an exchange, users must first choose which type of exchange fits their needs:
Centralized Exchanges (CEX)
Centralized exchanges operate under the control of a central authority, usually facilitating trading through an order book. While offering perks such as high liquidity, a user-friendly interface, and a wide range of trading pairs, the downside of centralized cryptocurrency exchanges is that they are often vulnerable to security breaches and hacks.
Since CEXs hold users' assets on their behalf, an attack on the exchange and its centralized servers could result in the loss of funds for users.
Some of the most widely-used centralized exchanges by volume include:
Decentralized Exchanges (DEX)
Decentralized exchanges operate as applications that enable peer-to-peer trading without the need for centralized intermediaries. They prioritize user privacy and ownership, but may suffer from lower liquidity, limited trading pairs, and less user-friendly features (especially for beginners).
With DEXs, users are in control of their own private keys, which means that the exchange host cannot access their wallet and its contents. This does not mean, however, that DEXs are immune to security breaches; attacks on DEXs may affect users that provide liquidity to the exchange, as their provided tokens could be at risk.
Some of the most widely-used decentralized exchanges by volume include:
Other crypto exchange types
Although centralized exchanges and decentralized exchanges are the most common types of crypto exchanges, there are some other options that users should be aware of:
- Hybrid exchanges: A hybrid exchange combines elements of both centralized and decentralized models, offering a balance between liquidity, privacy, and security.
- Peer-to-peer exchanges: Peer-to-peer crypto exchanges facilitate direct transactions between users, allowing them to negotiate prices and terms independently.
Factors to consider when choosing a cryptocurrency exchange
Whether you choose to use a centralized or decentralized exchange, there are certain criteria you should keep in mind before using a specific platform:
- Reputation and track record: Choose a crypto exchange with a solid reputation and a proven track record of security and user privacy.
- Security measures: Prioritize exchanges with robust security features, such as two-factor authentication and cold storage compatibility, and consider exchanges that maintain insurance policies against hacks and theft.
- Supported assets and trading pairs: Select a digital currency exchange that supports the assets and trading pairs you intend to trade.
- Fees and trading costs: Evaluate the fee structures of the exchange, considering factors such as maker and taker fees, withdrawal fees, and deposit/cash out methods.
- User interface and experience: Beginners may choose to opt for a centralized exchange with user-friendly interfaces and intuitive trading platforms to streamline their trading experience.
Advantages of cryptocurrency exchanges
As the cornerstone for crypto trading, exchanges offer several features and benefits to users that wish to buy and sell cryptocurrencies:
Supported assets
Cryptocurrency exchanges offer access to a diverse array of digital assets, enabling users to explore new trading opportunities. Exact supported assets will vary by platform, with specific exchanges catering to certain blockchains and cryptocurrencies.
Liquidity access
Digital currency exchanges provide liquidity and facilitate price discovery by connecting buyers and sellers from around the world.
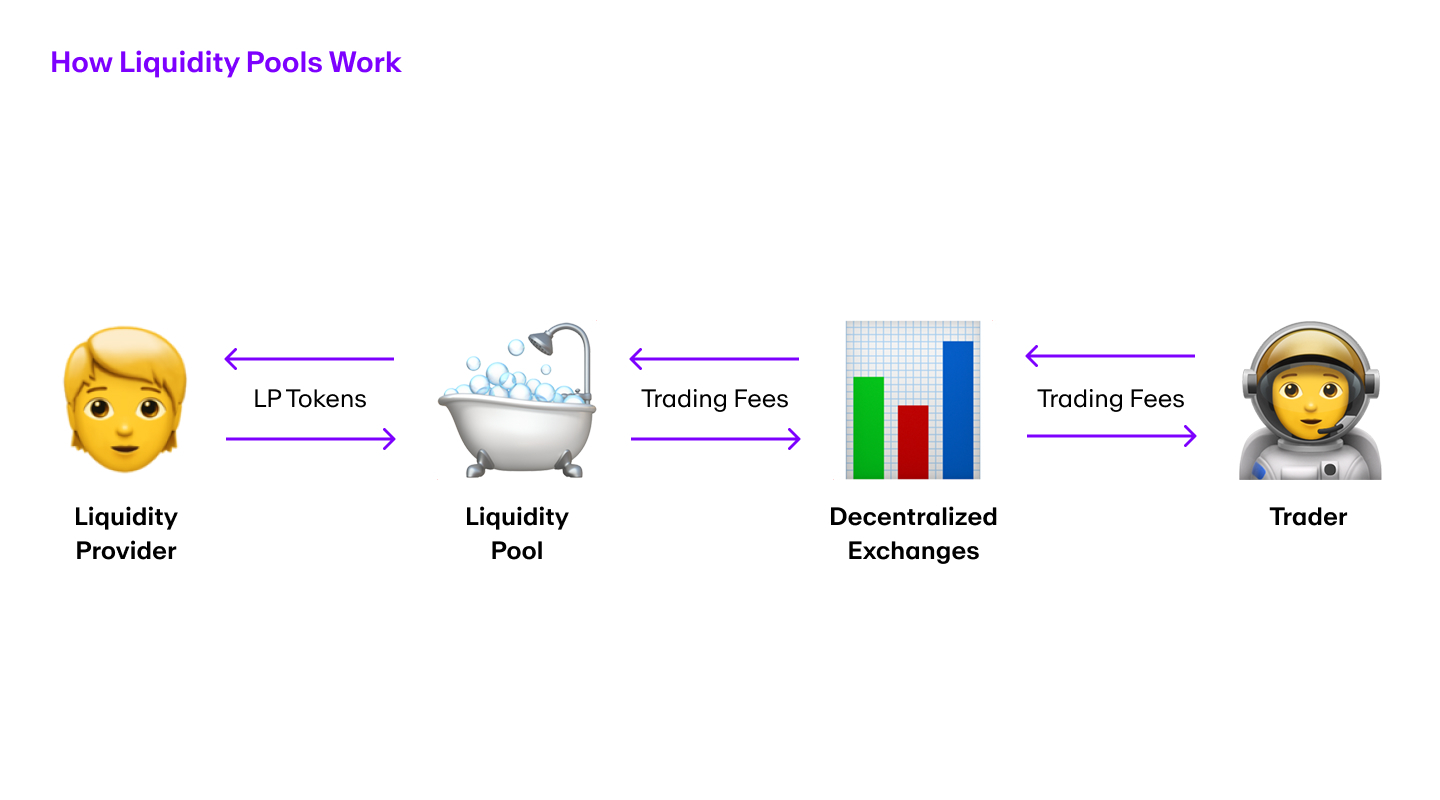
Speaking of liquidity, some decentralized exchanges even allow users to earn rewards by providing liquidity used for others to trade.
Trading flexibility
With both decentralized and centralized exchanges operating 24/7, users have the flexibility to trade anytime and anywhere, accommodating diverse trading preferences and time zones.
Additional exchange advantages
Exchanges may offer additional features such as margin trading, staking, and lending, enhancing the trading experience for users of all levels.
Risks of cryptocurrency exchanges
Security vulnerabilities and hacks
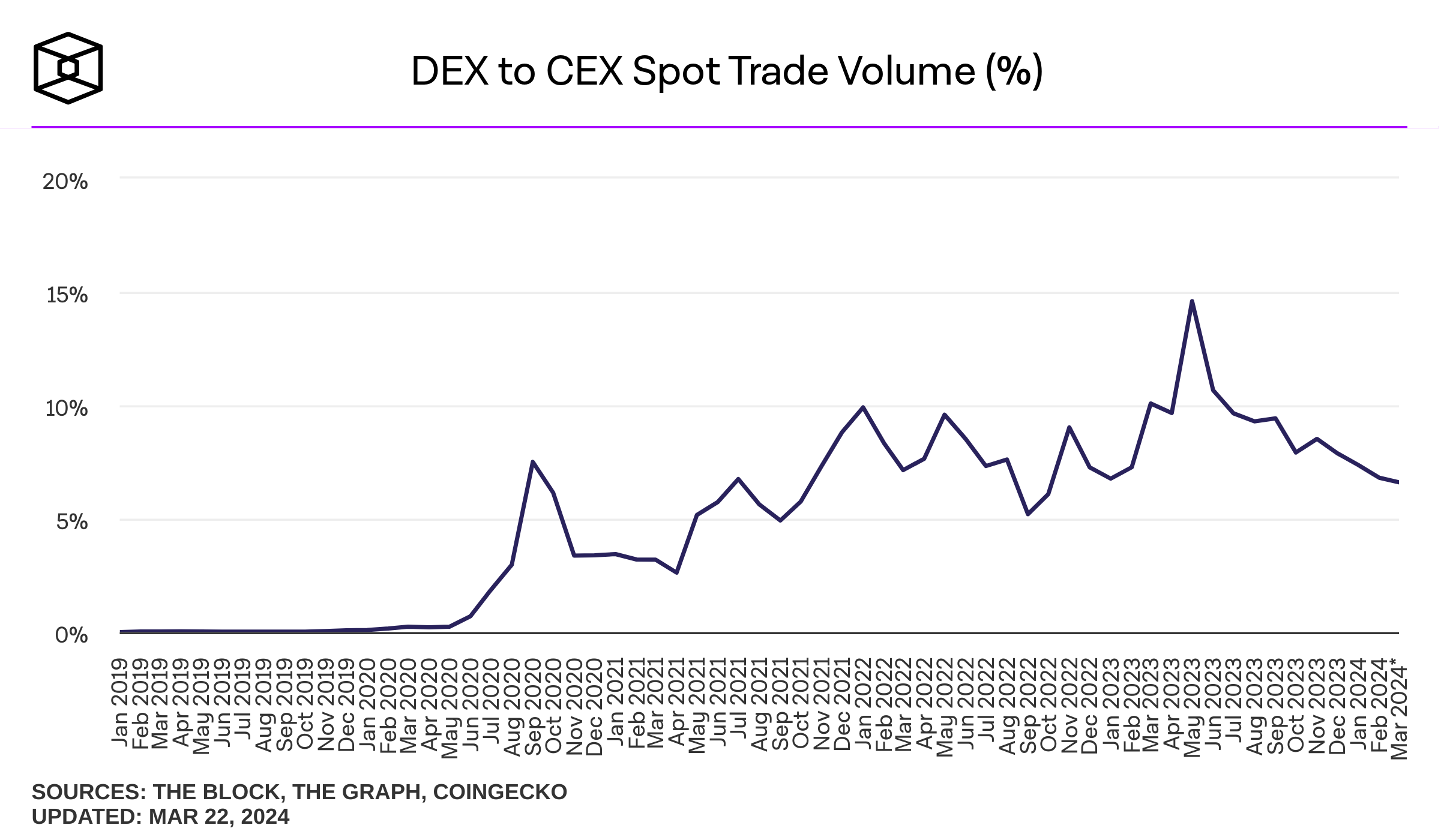
Exchanges can be vulnerable to security breaches and hacks, potentially leading to the loss of user funds and erosion of trust. In late 2023, attacks on both centralized and decentralized finance accounted for over $540 million in stolen funds from just five different platforms.
Market manipulation and insider trading
Cryptocurrency markets are susceptible to manipulation and insider trading, posing risks to traders that use certain exchanges and invest in cryptocurrencies.
Counterparty risks
With centralized exchanges, users rely on the platform to hold their assets, exposing them to counterparty risks in the event of exchange insolvency or malfeasance.
Additional exchange risks
Other risks include technical glitches, unscheduled downtime or maintenance, market volatility, and each exchange's ability to navigate a complex and evolving regulatory landscape.
Concluding thoughts on crypto exchanges
Cryptocurrency exchanges play a pivotal role in the Web3 ecosystem, facilitating the buying, selling, and trading of cryptocurrencies.
By understanding their functionalities, types, advantages, and risks, users can navigate the landscape more effectively and make informed decisions when choosing an exchange. Whether opting for a centralized, decentralized, or hybrid platform, users should prioritize factors like security, liquidity, and user experience to maximize the benefits of cryptocurrency trading.
FAQs about cryptocurrency exchanges
Which cryptocurrencies can you trade on exchanges?
Cryptocurrency exchanges offer a wide range of digital assets for trading, including popular cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin (BTC), Ethereum (ETH), and many others. Additionally, some exchanges may list lesser-known altcoins, catering to users with diverse interests.
Though not an exchange, MoonPay supports over 100 cryptocurrency assets available to buy and sell with a card. Choose from popular tokens like BTC and ETH, stablecoins like Tether (USDT) and USD Coin (USDC), and altcoins such as Solana (SOL), Dogecoin (DOGE), and Cardano (ADA).
Do crypto exchanges charge fees from their users?
Yes, cryptocurrency exchanges typically charge fees for various services, including trading, deposits, and withdrawals. Exact fees may vary depending on factors such as the exchange's fee structure, trading volume, type of order placed, platform (i.e., web or mobile app) as well as the cryptocurrency being traded. Additionally, some cryptocurrencies may carry their own gas fees for transactions made on the blockchain.
How is a cryptocurrency exchange different from a cryptocurrency wallet?
While both cryptocurrency exchanges and wallets are essential components of the digital asset ecosystem, they serve distinct purposes. A cryptocurrency exchange is a platform where users can buy, sell, and trade cryptocurrencies with other users, while a cryptocurrency wallet is a digital tool for storing, sending, and receiving cryptocurrencies.
Can cryptocurrency be converted into fiat currencies via exchanges?
Yes, many cryptocurrency exchanges allow users to convert cryptocurrencies to fiat currencies such as US dollars (USD), euros (EUR), or yen (JPY). This process typically involves selling the cryptocurrency on the exchange's platform and withdrawing the resulting fiat currency to a bank account or other payment method. Some exchanges may require users to complete identity verification procedures before enabling fiat currency withdrawals.
MoonPay allows users to easily sell crypto for fiat currency and cash out directly to a bank account, bypassing the many steps required to buy and sell cryptocurrencies via an exchange.
An alternative to cryptocurrency exchanges
MoonPay offers a different approach than traditional cryptocurrency exchanges, providing a seamless platform to buy, sell, and swap digital assets all in one place.
With MoonPay, users can easily acquire cryptocurrencies without the complexities and extra steps associated with traditional exchanges, making it an ideal choice for both newcomers and experienced traders alike.



.png?w=3840&q=90)


