From its humble beginnings as just an idea in a whitepaper, Bitcoin has grown into a global phenomenon that has inspired a new generation of digital currencies.
Some even argue that cryptocurrency cannot be comprehended without first understanding Bitcoin. So what is it that makes Bitcoin (BTC), the largest cryptocurrency by market capitalization, so special?
This article explains the history of Bitcoin, how it differs from other cryptocurrencies, and where you can buy BTC.
What is Bitcoin?
Bitcoin is a type of digital currency that allows people to transact online without the need for an intermediary such as a bank. Bitcoin is decentralized, meaning no government or organization controls it. Instead, transactions are verified and recorded on a public distributed ledger called a blockchain.
Bitcoin is an open-source project, which means anyone can contribute to its development. At the same time, its decentralized nature ensures no one person is able to sabotage it.
To understand why Bitcoin is special, we need to first have an elementary understanding of the role money plays in society.
Money as a medium of exchange
In its most basic form, money is an agreed-upon medium of exchange. It is a way to simplify and standardize trade so that people can buy and sell without having to barter.
People used to use commodities like gold and silver as money. The problem with commodities, however, is that they are difficult to transport and divide. This made trade complex and impractical.

Paper money (commonly referred to as “fiat money”) was then created as a way to make trade easier. A government or a central authority would issue paper money that people could then use to buy and sell goods and services.
This is the way money has worked for thousands of years, but the further we progress into the digital age, many problems with traditional money are beginning to come to light.
Problems with traditional money
There are several major problems with traditional money (paper and digital):
- Inflation
- Centralization
- Trust
Bitcoin presents itself as a solution to all of them.
1. Inflation
Inflation is a problem that fiat currencies like the US dollar face. It is the currency's gradual loss of purchasing power over time.
The causes of inflation are many and varied, like the government printing more money. The end result, however, is always the same: each unit of the currency buys less than it did in the past.
Inflation is a particular problem for savers. When the prices of goods and services rise, the purchasing power of their savings falls. This can result in a loss of real value over time.
Bitcoin tries to address inflation by capping its total supply. There will never be more than 21 million Bitcoins in existence, and each Bitcoin can be divided into 100 million units (called Satoshis, or Sats, for short). This makes the currency highly available to anyone who wants to use it, while also trying to mitigate the issue of inflation eroding its value.
2. Centralization
Centralization can present an issue for any kind of digital currency. It occurs when there is too much power in too few hands.
This can take many forms, like when an entity has too much control over a network or too much control over the currency itself. Centralization can be a problem because it may make a system more vulnerable to manipulation and corruption.
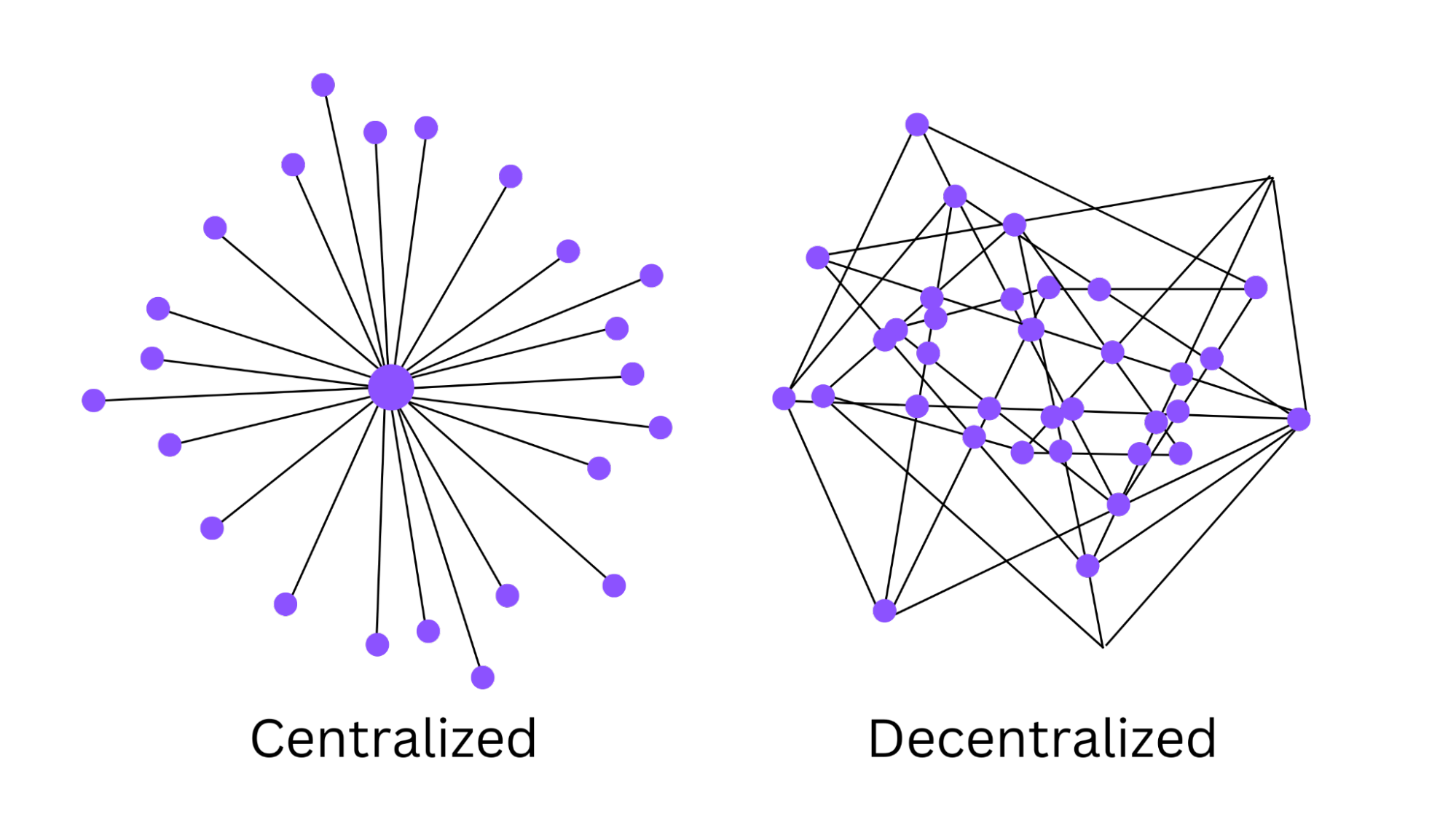

Bitcoin solves the centralization problem by using a decentralized network of “nodes” (devices that keep the blockchain running) to validate transactions and create new Bitcoins and blocks. This means that no single entity has too much power over the network.
3. Trust
Although the traditional financial system is good enough for some, there are still several shortcomings.
Many transactions in the traditional financial system require one party to put a certain level of trust in another party. For example, a seller must trust that a buyer has enough resources to pay for the transaction.
Bitcoin solves the issue of trust by offering a trustless payment model that is made possible by the use of cryptographic signatures (a mathematical technique to authenticate transactions). When a user wants to send BTC to another user, they sign the transaction with their private key, a 256-character binary code. This signature is then verified by the network to ensure that the Bitcoin transaction is valid.
Double spending
Double spending is an additional problem that is unique to digital currencies. It occurs when a user spends the same digital asset twice, or more specifically when they send the same digital asset to two different recipients. While this may sound like a trivial issue, it can have major consequences for businesses and consumers who use digital or virtual currencies.
Bitcoin solves the double spending problem by using a data structure called a blockchain. In a blockchain, a “block” is simply a collection of data that contains information about multiple transactions. Each block is linked to the previous block and secured using cryptography, forming a chain of blocks (hence the name “blockchain”).
If someone tries to spend the same bitcoin twice, they will have to create two separate blocks, and thus two different versions of the blockchain. This makes it easy for others to spot the fraud and reject one of the blocks.
How was Bitcoin created?
In 2008, a research paper titled "Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System" was published under the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto. In the paper, Bitcoin was presented as a solution to many of the problems faced by traditional money, with special emphasis given to the double spending problem.
The paper sparked a lot of interest among developers who saw potential in Nakamoto's idea, and in 2009, the vision outlined in the nine-page document manifested into the world's first fully decentralized cryptocurrency: Bitcoin. The first cryptocurrency officially launched when its first block was mined.
How does Bitcoin work?
The Bitcoin network is decentralized, which means there is no centralized authority controlling it. New transactions are verified by network nodes and recorded in a public, decentralized ledger called a blockchain.
But what are nodes and how do they verify transactions?
For this, we'll need to introduce two more concepts:
Proof of Work (PoW) consensus mechanism and Bitcoin mining
A consensus mechanism is a mathematical model that attempts to ensure a cryptocurrency blockchain functions properly.

Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS) are two of the most popular consensus mechanisms in use today by blockchains. PoW is what's used by the Bitcoin network.
In PoW, cryptocurrency transactions are verified by nodes, also called “miners.” These miners compete to verify transactions by solving complex mathematical puzzles. The first miner to solve the puzzle gets to add the next block to the blockchain and receives a block reward in the form of BTC.
The Bitcoin protocol has a built-in mechanism to adjust the difficulty of the puzzle so that a new block is added to the blockchain every 10 minutes on average. The Bitcoin mining process also allows for mining pools, distributed groups of Bitcoin miners who pool their computational resources to increase their chances of finding the next block.
Why does Bitcoin use the Proof of Work (PoW) consensus model?
The Proof of Work (PoW) consensus model was chosen for Bitcoin because of a belief that it is the most secure consensus model. Below are a few reasons underlying that belief.
1. Resistance to 51% attacks
A 51% attack is a potential vulnerability in a blockchain network in which an attacker who controls more than half of the network's computing power can manipulate the system and double-spend tokens, block legitimate transactions, and rewrite transaction history.
This type of attack can compromise the security and integrity of a blockchain.
In a PoW system, it is very difficult for an attacker to control more than 50% of the network. This is because in order to add a new block to the blockchain, an attacker would need to control more than 50% of the mining power in the network.
2. Resistance to Sybil attacks
The PoW consensus model is also very resistant to something called a “Sybil attack”.
A Sybil attack is when an attacker creates multiple fake identities in order to gain control of the system.
In a PoW system, it is very difficult for an attacker to create multiple fake identities because each identity requires large amounts of computing power.
3. Resistance to Denial of Service (DoS) attacks
The PoW consensus model is also very resistant to Denial of Service (DoS) attacks.
A DoS attack is when an attacker tries to prevent legitimate users from accessing the system. In a PoW system, it is very difficult for an attacker to prevent legitimate users from accessing the system because he or she would need to control more than 50% of the computing power in the network.
What is Bitcoin used for?
There are a few notable use cases for Bitcoin:
1. Borderless money transfer
Bitcoin has made it possible to send value to anyone in the world quickly and cheaply without the need for a bank or other financial institution. All you need is an internet connection and a public wallet address.
For instance, BTC worth over $2 billion was transferred anonymously on September 9, 2021 for fewer than $1 in transaction fees. Private value transfer of such magnitude would not be possible with traditional finance tools.
2. "HODLing"
Bitcoin has often been referred to by some as "digital gold". This is because some believe it has many of the same properties as gold: it's scarce, durable, divisible, and portable.
Supporters also claim that Bitcoin has a number of advantages over gold. For instance, it is much easier to store and transport Bitcoin than it is to store and transport gold.
Bitcoin can be easily stored (via "HODLing") in a digital wallet, whether you prefer custodial or non-custodial crypto wallets.
3. Investment diversification
The emergence of Bitcoin, for many investors, is a brand new asset class.
While some of these investors may be oblivious to the technological capabilities of Bitcoin (and blockchain technology in general), they still consider BTC to be an investment vehicle worth investing in.
4. Borrowing
Although not recognized as an asset by most government entities around the world, there are several decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols that allow users to borrow fiat at relatively low-interest rates by collateralizing their BTC holdings.
5. Company strategy
Several companies have announced Bitcoin strategies. For example, in late 2020, Square announced that it had purchased $50 million worth of BTC.
MicroStrategy, another publicly listed US company, holds over 125,000 BTC for a purchase price of about $4 billion.

Michael Saylor, the co-founder, former CEO, and current Executive Chairman of MicroStrategy, is a public proponent of Bitcoin and often speaks on the merits of the popular cryptocurrency.
6. Government Uses
When Ukraine's payments infrastructure took a massive blow due to the Russian invasion, the government began accepting Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies as a form of aid from other countries.
Halfway across the world, El Salvador made headlines for becoming the first country to accept Bitcoin as legal tender. In 2021, the government has even announced that all citizens will be able to pay their taxes in BTC.
Bitcoin's limitations
While supporters believe Bitcoin has many advantages over traditional fiat currencies, it also has some limitations:
1. Unregulated
Since Bitcoin is decentralized and not under the control of any government, central bank, or financial institution, it is currently not subject to any regulations in most jurisdictions. This lack of regulation could be seen as a good or bad thing, depending on one's perspective.
Some people see it as a good thing because it means that the currency is not subject to manipulation by central authorities. Others see it as a bad thing because it means there is no one to protect you if something goes wrong, e.g., your BTC is stolen by a hacker.
2. Volatility
The price of Bitcoin has been known to fluctuate greatly, which can make it difficult for people to use it as a store of value or payment for day-to-day purchases. And due to Bitcoin dominance, when Bitcoin's price swings one way or the other, it can affect the entire cryptocurrency market.
If you are "hodling" Bitcoin as an investment for the long term, then you may be able to weather the volatility. If you intend to use it for purchases, however, then volatility can be a big limitation.
3. Limited acceptance
Although Bitcoin is gaining in popularity, it is still not accepted as a form of payment by most businesses. This means that you may not be able to use it to pay for all of the goods and services that you want.
Some businesses are hesitant to accept Bitcoin because of its volatility, while others simply do not know how to accept it.
4. Not built for advanced financial applications
Bitcoin was designed as a digital currency with one simple goal: to exchange value in a peer-to-peer network. It did not account for other financial activities like borrowing, lending, and contractual agreements.
This means that it is not well-suited for more advanced financial applications. For these, you may want to look into other digital assets like Ethereum.
While the Bitcoin network is constantly evolving to meet the needs of the ever-shifting financial landscape (such as the Bitcoin Taproot upgrade), it is still not as robust or feature-rich as some of the other cryptocurrencies available today. Competing coins like Ethereum have stronger use cases when it comes to DeFi applications ad decentralized cryptocurrency exchanges.
5. Large carbon footprint
The Proof of Work consensus mechanism that Bitcoin uses has a large carbon footprint.
This is because the miners who secure the network need to use a lot of energy to power their computers.
As the price of Bitcoin goes up, more miners are incentivized to join the network, thus increasing the competition and energy usage of the network. This in turn causes Bitcoin's total energy consumption to rise.
Bitcoin's high energy usage has led to competing cryptocurrencies to develop greener blockchain technology solutions, such as Algorand (ALGO), Solana (SOL), and Avalanche (AVAX).
6. Poor scalability
The Bitcoin network can only process four to five transactions per second. To put this in perspective, Visa can process 1,700 transactions per second.
This is a big problem because as Bitcoin becomes more popular, the demand for transactions on the network will increase, creating long processing delays, increasing the cost of transaction fees, and potentially preventing some people from using Bitcoin.
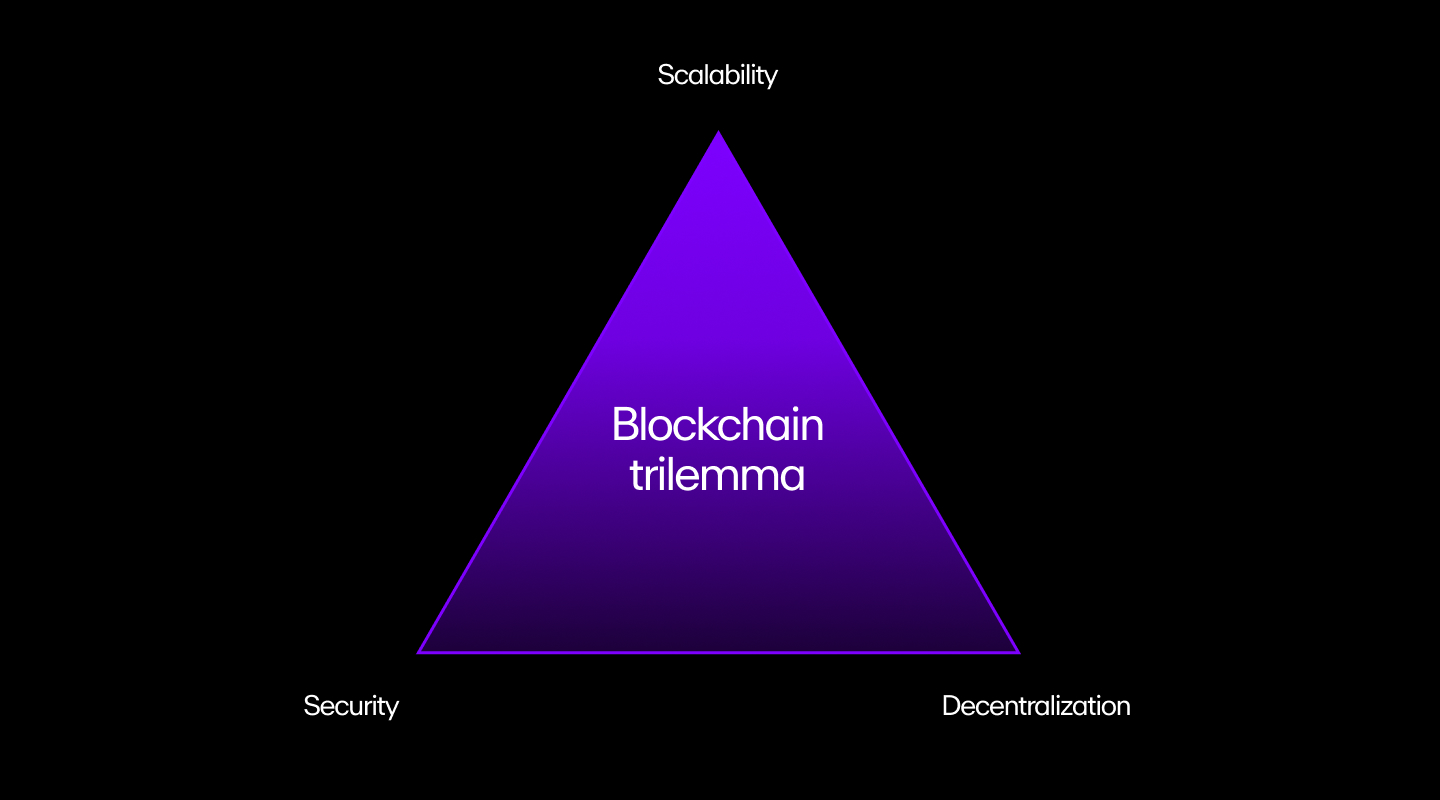
This compromise in scalability, security, and decentralization is what Vitalik Buterin, the creator of Ethereum blockchain, dubbed the "Blockchain Trilemma".
Bitcoin's shortcomings in these areas has led to the rise of other cryptocurrency competitors, though Bitcoin still dominates when it comes to price and market cap.
How is Bitcoin different from other cryptocurrencies?
While Bitcoin is not the only cryptocurrency, it is different from all others for a variety of reasons.
First and foremost, Bitcoin is the original cryptocurrency, launched in 2009. Every other cryptocurrency is known as an alternative coin, or “altcoin” since each one was developed after Bitcoin.
Secondly, Bitcoin has by far the largest and most active community of developers working on it. Well over 1,000 developers have contributed code to the Bitcoin Core project since its inception. This means there is a lot of talent and resources being used to making Bitcoin better.
Finally, Bitcoin is the most decentralized cryptocurrency. There is no centralized authority or company that controls Bitcoin. Instead, it is maintained by a global network of computers that anyone can join. Most of the other cryptocurrencies have fewer miners or validators, which makes them less decentralized than the Bitcoin network.
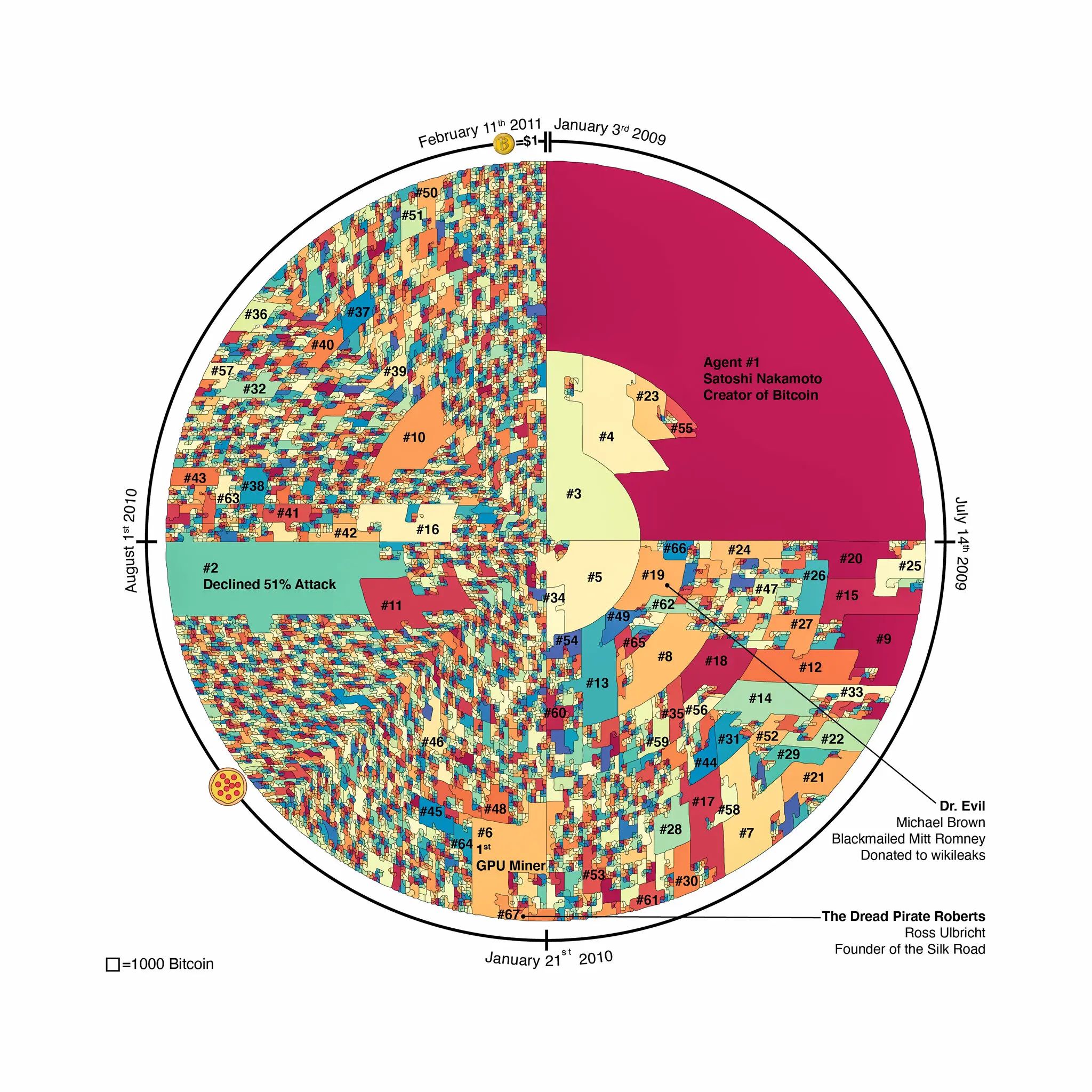
Bitcoin Pizza Day
Although Bitcoin launched in 2009, there were not yet any real-world use cases for it, and no company was ready to accept it. In fact, most people weren't even aware of its existence.
This all changed on May 22, 2010, when Florida-based programmer Laszlo Hanyecz made the first real-world purchase using Bitcoin. He paid someone to buy two pizzas from a Papa John's outlet for 10,000 BTC, which at today's prices would be worth hundreds of millions.
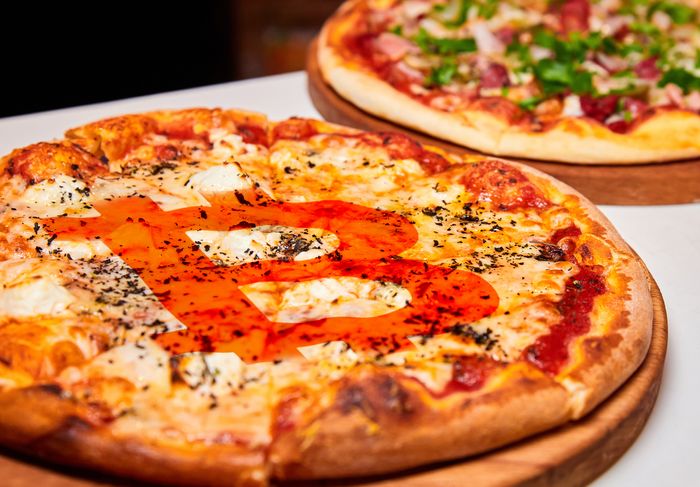

This event is now celebrated as Bitcoin Pizza Day every year on May 22, and serves as a reminder of how Bitcoin can be used to buy real-world goods and services.
Interesting facts about Bitcoin
- While BTC is the abbreviation used by cryptocurrency exchanges and most people, the ISO-prescribed abbreviation for Bitcoin is "XBT."
- Bitcoin is deflationary in nature. It has a maximum supply of 21 million BTC.
- The last Bitcoin is expected to be mined in the year 2,140.
- Experts predict that after the last Bitcoin is mined, the blockchain fee will be the incentive for miners to earn their Bitcoin reward and keep the blockchain running.
How to buy Bitcoin (BTC)
You can buy Bitcoin (BTC) via MoonPay or through any of our partner wallet applications with a credit card, bank transfer, Apple Pay, Google Pay, and many other payment methods.
Just enter the amount of BTC you wish to purchase and follow the steps to complete your order. MoonPay makes it easy to buy Bitcoin and send to any custodial or non-custodial Bitcoin wallet.
You can also top up your wallet in euros, pounds, or dollars and use your MoonPay Balance to purchase crypto like Bitcoin (BTC). Then, simply transact for cheaper and faster BTC transactions with higher approval rates. Plus, enjoy zero-fee withdrawals directly to your bank account when you decide to cash out.
How to sell Bitcoin (BTC)
MoonPay makes it easy to sell Bitcoin for fiat currency when you decide it's time to cash out your crypto.
Simply enter the amount of BTC you'd like to sell and enter the details where you want to receive your funds.




.png?w=3840&q=90)
.png?w=3840&q=90)
