Today, cryptocurrency is a household word, with thousands of digital currencies and significant adoption and trading volume across the globe. But it wasn't always smooth sailing for digital assets.
The road has been paved with many regulatory challenges and criticism from governments and banks, and has been susceptible to scams and fraud. For many years, crypto was difficult to acquire. And if you wanted to trade digital currency, it was difficult to find a cryptocurrency exchange and fund the transfer.
But how did cryptocurrency begin?
Bitcoin was the first cryptocurrency, created in 2009. With it came the initial use of blockchain technology and its distributed ledger to verify transactions on a public database.
Confused? Don't worry, you're not alone. Despite being one of the most innovative technologies to have developed in the last decade, cryptocurrency continues to baffle even the sharpest of minds.
This article explains the world of cryptocurrency for beginners, covering the basics of how cryptocurrency works and the different types of crypto assets available.
What is cryptocurrency?
Cryptocurrency is a type of digital currency, often defined by a lack of any central authority. Crypto transactions are secured using cryptography, and are very difficult to counterfeit as they use blockchain technology to verify transactions.
Cryptocurrencies use different types of consensus mechanisms to process transactions and verify them on the blockchain. A consensus mechanism allows a decentralized system (like a blockchain network) to come to agreement about the state of the network.
There are two main types of consensus mechanisms: Proof of Work and Proof of Stake. Let's break them down further.
Proof of Work cryptocurrency
Proof of Work (PoW) cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin utilize a mining process to validate transactions on the blockchain. In Proof of Work, miners compete to solve complex mathematical equations to produce the next block to be added to the blockchain.
Although Proof of Work is one of the consensus mechanisms in cryptocurrency, it can be quite expensive and . The computing power needed to solve a cryptographic hash function is quite high, and PoW thus has a greater than other consensus mechanisms.
So why would miners invest in the necessary mining hardware, if it is costly for their wallet and the environment? The incentive lies in the block reward, which is given to the miner that correctly solves each hash function. This reward comes in the form of the native cryptocurrency of the respective blockchain, like Bitcoin.
Examples of Proof of Work cryptocurrencies include:
Proof of Stake cryptocurrency
Proof of Stake (PoS) cryptocurrencies like Ethereum came about as an alternative to Proof of Work in response to some of its drawbacks. In Proof of Stake, users "stake" a portion of the native cryptocurrency to become validators and verify transactions on the blockchain.

Examples of Proof of Stake cryptocurrencies include:
- Ethereum (ETH)
- Binance Coin (BNB)
- Cardano (ADA)
- Polkadot (DOT)
- Avalanche (AVAX)
- Cosmos (ATOM)
- Near Protocol (NEAR)
- Algorand (ALGO)
- MultiversX (EGLD)
Recommended reading: Proof of Work vs Proof of Stake
Why were cryptocurrencies created?
When most people think of cryptocurrencies, the first thing that comes to mind is Bitcoin. Bitcoin was released in 2009 and, after gaining the attention of the public a few years later, has still remained the biggest cryptocurrency by market capitalization.
But it may surprise you to know that Bitcoin wasn't the first kind of crypto – that was something called DigiCash, which was created in 1990 by cryptographer David Chaum.

Despite the decades between the two, and all the incarnations of crypto in between and since, the driving force behind the concept has always been the same: to decentralize finance. In practice, this means taking out the “middle man” role that financial institutions play and the control they have over our money.
Back when DigiCash was created, it was also a unique way to transfer funds digitally. While we're now able to electronically transfer most currencies, the thing that made and continues to make cryptocurrency unique is the freedom that the lack of a middle man provides – no exchange rates, no interest, significantly lower fees, no reliance on a third party: a truly global currency.
But how do you take out a middle man that's existed in some way or other for centuries? Let's take a look.
How does cryptocurrency work?
Cryptocurrency works a bit like code breaking. These digital assets use cryptography to:
1. Verify transactions
2. Control the creation of units
3. Facilitate the transfer of crypto assets.
Simply, cryptography is what enables cryptocurrency to work without a middle man.
Earlier we mentioned how the first cryptocurrency was created by a cryptographer. Cryptography is where the “crypto” in “cryptocurrency” comes from, and refers to a method of keeping something (in this case, a digital currency) safe and secure by transforming it into a form that cannot be easily deciphered.
Cryptocurrencies are made through a process called mining – but not in the old fashioned way. Cryptocurrency mining swaps out a hammer for computers, and a rock for a lot of complex mathematical problems. The computers tap away at the problems, solving each and every one, and this process generates units of cryptocurrency, or coins.
Back in the day, your average at-home computer could mine crypto, but these days it takes an army of them, so most people simply purchase already-mined units from brokers, usually cryptocurrency exchanges and on-ramps.

Acquiring crypto is just like going to a financial institution and exchanging one currency for another. The difference, of course, is that you won't get anything tangible, because cryptocurrencies are all digital and run on something called a blockchain.
A blockchain is a type of distributed ledger (which is essentially a database of information shared across multiple places). Blockchain technology isn't controlled by any central authority. Instead, it's controlled by a network of computers all over the world. This is part of what makes cryptocurrency transactions so secure.
When you purchase cryptocurrency, it's stored in a cryptographic wallet and this is what you use to make purchases – we'll get into what you can buy with crypto a little later.
If you pay for something with crypto, it's transferred directly to the seller's wallet. This transaction is stored on the blockchain. Each one of the computers in the blockchain shares and validates that information, which is visible to everyone.
What are the different types of cryptocurrencies?
Since the explosion of Bitcoin, the crypto economy has become a much larger world.
Bitcoin was followed by Litecoin, then Namecoin, then Peercoin, then Dogecoin and now there are anywhere between 9,000 and 23,000 cryptocurrencies.
But the term “cryptocurrency” doesn't just apply to blockchain-based digital currencies. Actually, a lot of different crypto assets fall under this term. Here's a quick run through:
Altcoins
Altcoin is a term used to describe essentially any cryptocurrency that isn't Bitcoin. Since Bitcoin is the most popular cryptocurrency, with a price and market cap that dominate the competition, any other token is considered alternative by comparison.
Some altcoins are branched versions of existing blockchains (an exception is Ethereum, which is built on the original Ethereum blockchain). If a cryptocurrency splits (or forks) from the chain, it creates a new branch that is no longer compatible with the original.

Examples of altcoins include:
- Ethereum (ETH)
- Tether (USDT)
- Binance Coin (BNB)
- XRP (XRP)
- USDC (USDC)
- Solana (SOL)
- Cardano (ADA)
- Dogecoin (DOGE)
Stablecoins
Stablecoins are a more recent development in the world of crypto, and really exploded in 2021. Stablecoins aim to “peg" (tie themselves) to fiat currencies or commodities as a way to attempt to mitigate some of the volatility that comes with other types of cryptocurrencies.
There are four categories of stablecoins: fiat-backed, crypto-backed, commodity-backed, and algorithmic.
Examples of stablecoins include:
Note: Europe’s MiCA (Markets in Crypto-Assets) regulation sets strict standards for stablecoin authorization. While USDC has achieved full compliance, major stablecoins, including Tether (USDT), Dai (DAI), TrueUSD (TUSD), and Binance USD (BUSD), have not been approved under the framework.
DeFi tokens
DeFi tokens are a category of cryptocurrency that can be used in decentralized finance (DeFi). This asset type has enhanced functionality compared to other tokens, and can be used across a range of decentralized applications (dApps).
For example, DeFi tokens can be used to earn passive income in liquidity pools and yield farming, and on DeFi platforms such as decentralized exchanges (DEXs). They can also be used for various purposes within decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs), as utility tokens—more on those below.
Examples of DeFi tokens include:
Asset-backed tokens
Asset-backed tokens are, as the name suggests, backed by physical assets, and the token acts as a digital claim to that asset. Any real-life asset can become an asset-backed token, but the most common are things like gold, equity or even property.
The important thing to note is that, while asset-backed tokens represent ownership, that isn't to say you could go and swap your token for a piece of a gold bar, for example. Instead, the gold bar acts as a security, and the value of your token can increase and decrease based on the value of the backed asset.
Examples of asset-backed tokens include:
Utility tokens
Utility tokens are similar to DeFi tokens, and in some cases a cryptocurrency may be classified as both. Utility tokens are not necessarily finance-based in nature, but instead represent rights within a specific project or community. These rights tend to fall into two categories: voting or profit sharing (or both).
Voting rights tend to be proportionate to the number of utility tokens: the more tokens, the more votes. This gives holders the chance to have their say in governance and decision making in a project. As the name says, profit sharing allows token holders to split a portion of earnings within a community or organization.
Examples of utility tokens include:
Security tokens
Last but not least are security tokens. These are essentially the digital form of more traditional investments like stocks and shares. So, if a company is looking to raise capital by selling shares, they could choose to do so by using security tokens.
NFTs
NFTs, or ‘non-fungible tokens', are units of data stored on a digital ledger (such as a blockchain) that represent a piece of digital media such as art, video, audio or text.
Unlike tokens or coins, NFTs are totally unique, and therefore not interchangeable. They can, however, be sold, traded or sometimes even used as virtual currency in online games.
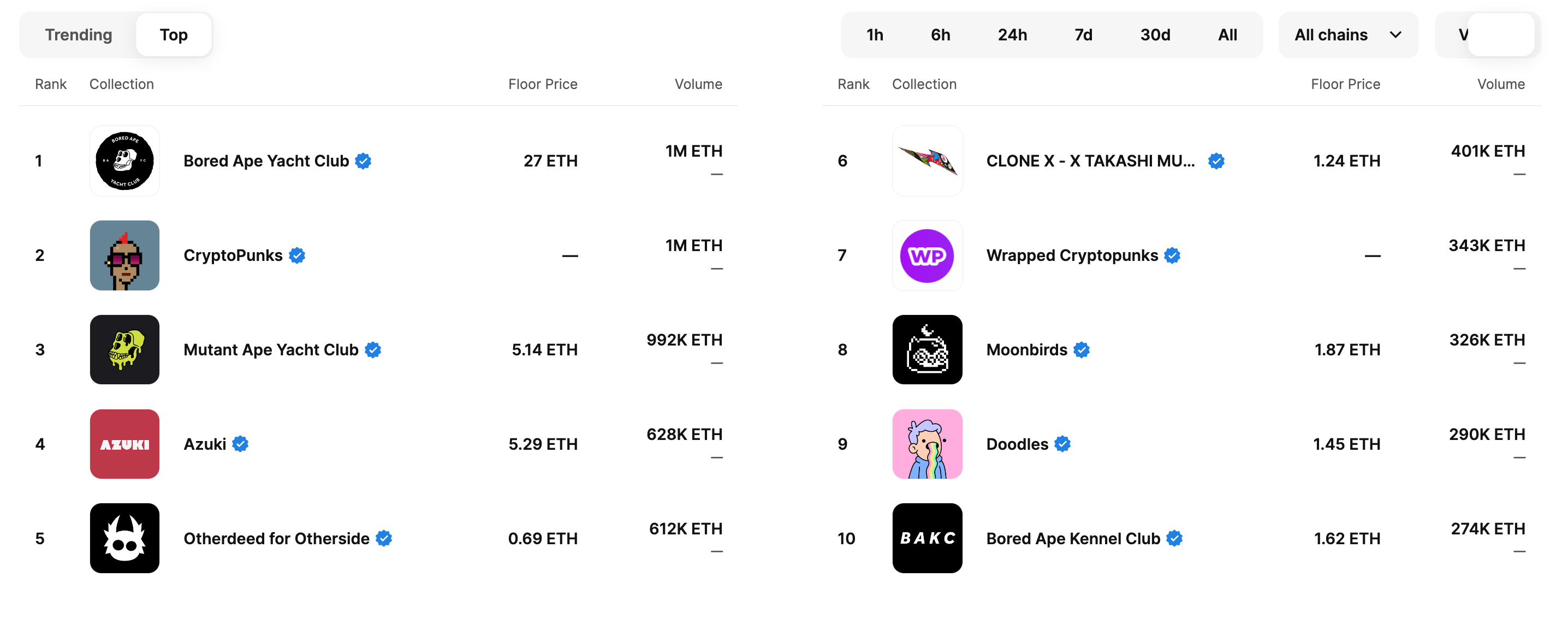
Examples of popular NFT collections include:
Crypto vs traditional currency: Pros and Cons
There are some people who believe that cryptocurrency is better than the traditional financial system for certain purposes, but others disagree. So, what are the advantages and disadvantages?
Cryptocurrency Pros
No central authority
Taking out the middleman puts your money in your own hands and removes the ability of someone else to place restrictions on your financial transactions.
Security and safety
Cryptography plus a distributed ledger provides a system with publicly available data that is difficult to alter.
Global coverage
Low fee exchange rates, minimal waiting times and 24/7 trading. Cryptocurrency is unencumbered by borders, oceans or time zones.
Cryptocurrency Cons
Risk and volatility
Cryptocurrencies can make for volatile investments, so they aren't necessarily the investment choice for stable returns.
Real-world applications
Crypto and web3 are still in their early stages, so real-world use cases aren't as plentiful as other financial assets.
Lack of education
Cryptocurrency can feel complicated for beginners, and while there's a lot of resources available, it's on the individual to go out and find them.
Longevity
It's also important to remember that crypto is still young and has only seen its growth in the last decade.
Scalability
While huge advances have been made in crypto and the tech that powers it, there are challenges when it comes to cryptocurrency transaction capacity.
What does the future look like for crypto?
The headlines may have you believe that crypto has had its day. But if one thing is for certain, it's that the crypto economy is able to not only withstand volatile conditions, but also to evolve through them.

So what does the future hold for cryptocurrency? While no one can say for sure, there are a few possibilities:
Increased regulation
Crypto will be regulated. The European Union has already passed the markets in crypto assets (MiCA) regulation and there are a number of other countries that have passed laws governing crypto assets. The Biden administration has also put together a team to drive the crypto regulation process.
Increased adoption
Despite the surge in popularity, we're still in the early adoption phase of crypto and it's still seen mostly as a vehicle for investment or storage of wealth. As time goes on, though, we could start to see increased adoption, both from individuals and business.
Legal tender
Another possibility is that certain countries may follow the lead of El Salvador, which introduced Bitcoin as legal tender in 2021.
Cryptocurrency FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
How to buy cryptocurrency?
Buying crypto is as easy as making any other online purchase, though where and how you buy cryptocurrency will depend on the digital asset itself.
If you're looking to buy cryptocurrency like Bitcoin or Ethereum using a card, the best option is an on-ramp provider like MoonPay.
MoonPay allows you to use your fiat currency to buy crypto with a credit card or bank transfer. When you want to cash out, you can convert crypto to fiat currency, too.
Where to store cryptocurrency?
Just as you carry fiat money in your physical wallet, you'll need a crypto wallet to store cryptocurrency. A digital wallet is safe and easy to set up, and essential for buying, selling, and swapping crypto.
Popular cryptocurrency wallet options include Bitcoin.com, MetaMask, Trust Wallet, Exodus, and Phantom.
What are the most popular cryptocurrencies?
We've mentioned some of the most popular cryptocurrencies throughout this article, but here are some of the more popular tokens across the different types:
Cryptocurrency: Bitcoin (BTC), Ethereum (ETH), Tether (USDT), Binance Coin (BNB), XRP (XRP), USD Coin (USDC), Solana (SOL)
NFT: Bored Ape Yacht Club, CryptoPunks, CloneX, Moonbirds, Doodles, Cool Cats
DeFi tokens: Uniswap (UNI), Aave (AAVE), Maker (MKR), Compound (COMP), Curve DAO Token (CRV)
Stablecoins: Tether (USDT), USD Coin (USDC), Dai (DAI), True USD (TUSD)
Utility tokens: Binance Coin (BNB), Uniswap (UNI), Basic Attention Token (BAT), Decentraland (MANA), The Sandbox (SAND)
* Coins are listed in order by market cap
How is cryptocurrency created?
Most cryptocurrencies are created through a process called mining. In cryptocurrency mining, miners use computing power to solve increasingly complex mathematical equations, in order to produce the next block and add it to the blockchain.

How many cryptocurrencies are there?
According to Statista, there are about 8,800 cryptocurrencies in existence at the end of 2023. Some estimates put this figure much higher, though there are many insignificant cryptocurrencies out there, with negligible volume and market cap.
There are new cryptocurrencies created everyday, so this number will change in the future.
Is cryptocurrency safe?
While the use of a distributed ledger like a blockchain makes it incredibly difficult to cheat the cryptocurrency system, that doesn't mean it's impossible for bad actors to cheat other individuals. Just as you take steps to keep your fiat currency safe, it's important to do the same with your crypto.
There are some that try to scam people out of their crypto. These scams can be incredibly convincing, so it's important to know how to spot them.
There are also some basic steps you can take to protect your assets, like securing your wallet and practicing good password hygiene.
What can you buy with crypto?
At the moment, the purchases you can make with cryptocurrencies are limited, but there is a growing number of merchants across various industries that accept Bitcoin and cryptocurrency payments. You can use crypto to buy products such as electronics, entertainment services, tickets, digital goods, hotels, airlines, clothing, and more.
If you don't see your selected product available for crypto purchases, you can always buy gift cards with cryptocurrency, and use that to purchase what you want.
Begin your crypto journey with MoonPay
Now you know the basics of cryptocurrency and blockchain technology, it's time to experience it for yourself.
To get started, simply buy cryptocurrency via MoonPay using your credit card or any other preferred payment method.
MoonPay's widget offers a fast and easy way to buy Bitcoin, Ethereum, and more than 100 other cryptocurrencies.
MoonPay also makes it easy to sell crypto when you decide it's time to cash out. Simply enter the amount of the token you'd like to sell and enter the details where you want to receive your funds.


.png?w=3840&q=90)



.png?w=3840&q=90)