The terms "fungible" and "non-fungible" have been around for a while, but let's face it, they're not exactly household terms. Sure, they have always been fairly common among economists, but they never really broke into the mainstream until a few years ago.
In fact, the first time many people heard these words might have been in the context of cryptocurrencies and NFTs. The surge in popularity of these digital assets has caused an increase in interest and awareness of these concepts, which were previously limited to finance and economics circles.
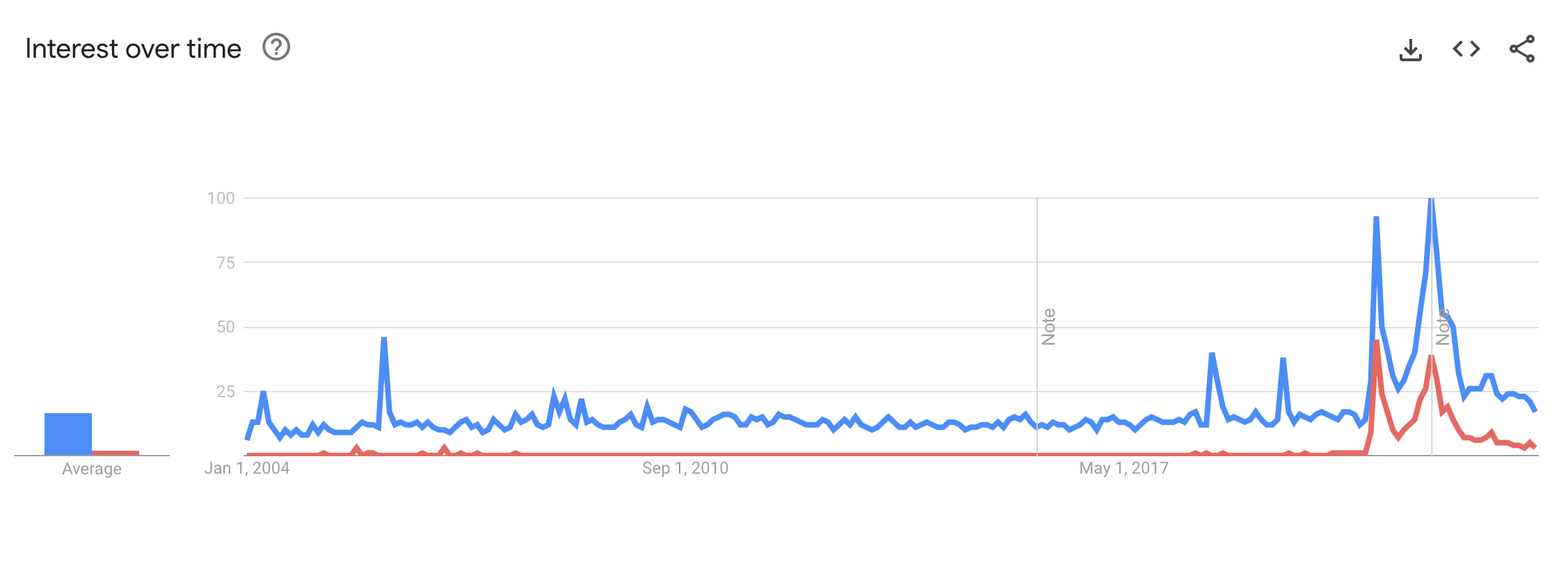
Interestingly, data from Google Trends shows that there's a direct correlation between the rise of cryptocurrency and the increase in searches for these terms. This is hardly surprising, given that the world of digital currencies, tokens, and NFTs is built upon these concepts.
In this article, we will explore fungible and non-fungible assets. We'll examine what these terms mean, discuss the key differences between these two concepts, and how they impact the value and usage of digital assets.
What is a fungible token?
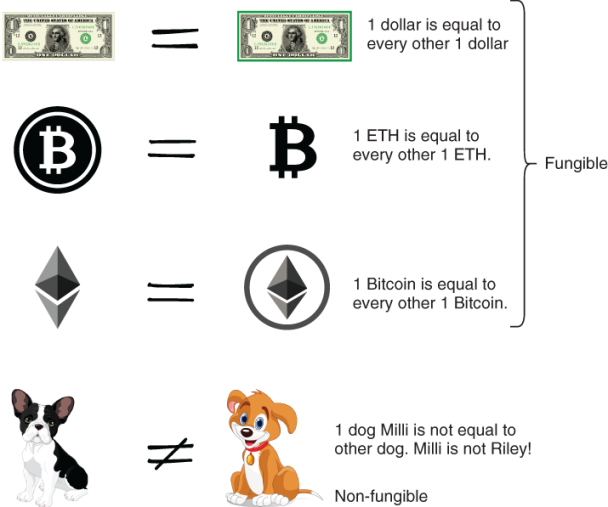
A fungible token is a type of digital asset that is designed to be identical in value and interchangeable with other tokens of the same type. Fungibility is a fundamental concept in traditional finance and economics, and it is closely associated with government-issued money, also known as fiat currency.
For example, each Dollar bill or Euro in circulation is identical in value to every other Dollar or Euro in circulation. This means that each unit of fiat currency is interchangeable with any other unit of the same denomination and value.
You can think of it this way — the bill in your wallet is no different (in value or utility) from a bill you find in your jeans.
However, the emergence of blockchain technology has revolutionized the way we think about fungibility, opening up new possibilities for decentralized finance (DeFi) and digital asset management.
Fungible tokens are ideal for use in financial transactions because they provide a high degree of standardization and uniformity. They are widely used in the cryptocurrency ecosystem, with popular examples including Bitcoin and Ethereum.
Additionally, fungible tokens have a more straightforward valuation process, making them ideal for use in trading and investment. This is because the value of each token is identical to the value of any other token of the same type and value.
Fungibility also has its limitations. For example, fungible tokens cannot represent unique or non-interchangeable assets such as real estate or art. This is where non-fungible tokens (NFTs) come into play.
What are fungible tokens used for?
From everyday micropayments to sophisticated financial derivatives, fungible tokens are used everywhere. In the cryptocurrency world, they are used as a medium of exchange, store of value, and unit of account.
Fungible tokens are a crucial component of many DeFi protocols, providing the liquidity and efficiency necessary for these platforms to function effectively. The most common use case is within DeFi, where fungible tokens are used for liquidity pools, yield farming, automated market makers (AMMs), and more.
They are also used in a variety of smart contract applications, including decentralized exchanges (DEXs), prediction markets, and identity management solutions.
Unlike fiat currencies, which are centralized and regulated by governments, fungible tokens exist in a permissionless system, allowing anyone to access and transfer value without the need for a trusted third-party intermediary.
Examples of fungible tokens
- Cryptocurrencies: Bitcoin (BTC), Ethereum (ETH), Litecoin (LTC), Cardano (ADA)
- Stablecoins: Tether (USDT), USD Coin (USDC), Dai (DAI), TrueUSD (TUSD)
- Utility tokens: Basic Attention Token (BAT), Chainlink (LINK), Uniswap (UNI), Aave (AAVE), Compound (COMP)
- Gaming tokens: Axie Infinity (AXS), The Sandbox (SAND), Decentraland (MANA), Gods Unchained (GODS)
- Governance tokens: Maker (MKR), Compound (COMP), Uniswap (UNI), Aave (AAVE)
- DEX tokens: SushiSwap (SUSHI), PancakeSwap (CAKE), 0x (ZRX), Kyber Network (KNC)
Note that this is not an exhaustive list. Moreover, a cryptocurrency can be classified into more than just one type, so some of the tokens listed can fall under multiple categories.
What is a non-fungible token (NFT)?
A non-fungible token (NFT) is a digital asset that represents a unique item on a blockchain. Each NFT is distinct with its own set of attributes, making it one-of-a-kind. They can only have one owner and exist in a single crypto wallet at a time.
Non-fungible tokens can represent anything from art to music to in-game items to virtual real estate and are often used to verify ownership and authenticity of digital content.
In mainstream economics, non-fungible assets are those that cannot necessarily be easily replaced by something else.
For example, a piece of artwork or a unique collectible may be considered a non-fungible asset because it has its own unique value that cannot be easily quantified or replaced. Non-fungible assets are often bought and sold through auctions or private sales, where their value is determined by supply and demand, rarity, and other factors.

Ethereum's introduction of smart contract technology, the programmability of tokens, and blockchains' ability to allow easy provenance tracking meant that non-fungible assets could now take a digital form — NFTs.
NFTs have created new opportunities for creators, artists, collectors, and brands to buy, sell, and trade unique digital content that was previously difficult to monetize or authenticate.
NFT technology takes ownership a step further with fractionalization. Unlike non-fungible assets of the real world like paintings, cars, and other collectibles, digital assets such as NFTs can be easily split into infinitely small fractions.
What are non-fungible tokens (NFTs) used for?
Non-fungible tokens (NFTs) can be used in a wide range of digital assets, including art, collectibles, video game items, real estate, sports memorabilia, and much more. NFTs can also be used to securely track ownership of digital content.
Digital art
For artists, NFTs open up a new world of possibilities. By tokenizing their work as NFTs, any artist can reach a global audience and even earn from their art in perpetuity via easy-to-configure smart contract royalties.
You can support digital artists by buying NFTs they create on NFT marketplaces. Purchase one for yourself or even gift them to your friends!
Brand loyalty
Recently, large brands have also begun embracing NFTs to create and nurture loyal and active communities, rather than passive audiences. For example, Alo Yoga, a popular fashion and lifestyle brand, used NFTs to launch its luxury winter collection. The holders of these NFTs can access personalized shopping experiences and other Alo Yoga benefits.
Token-gating events are now becoming popular with the ability to mint NFTs and set specific conditions on them. This helps brands monetize their content, reward loyal fans, and unlock exclusive product releases.
At MoonPay, we are providing token holders with personalized experiences inside the MoonPay ecosystem with the launch of MoonPay Passport (in collaboration with ThankYouX).
"I'm super fired up to use this technology and drive better outcomes and better experiences for the people that use MoonPay," said Ivan Soto-Wright, the CEO of MoonPay, at NFT Paris 2023.
Future use cases
These use cases have only scratched the surface of what's possible with non-fungible tokens. With more and more use cases being introduced every day, the possibilities of how NFTs can be used are endless.
Examples of non-fungible tokens
- Art: CryptoPunks, Doodles, Pudgy Penguins
- Gaming: Axie Infinity, Star Atlas, Gods Unchained
- Sports: NBA Top Shot, Sorare, ZED RUN
- Music: RAC's $TAPE, Kings of Leon's NFT Album
- Collectibles: CryptoKitties, VeeFriends, Clone X
- Virtual real estate: Decentraland, Upland, The Sandbox
- Domain names: ENS domains, Unstoppable Domains
- Fashion: RTFKT Studios, adidas Virtual Gear
- Film & TV: BigB Punks, Paris Hilton NFTs
What is the difference between fungible and non-fungible tokens?
Fungible tokens are identical, interchangeable and have the same value, like any fiat currency. On the other hand, non-fungible tokens are unique and one-of-a-kind. Like collectibles, they may have vastly different values based on their rarity, provenance, and other factors.
Feature | Fungible tokens | Non-fungible tokens |
Value | Each token is of equal value and interchangeable with another token of the same type | Each token has a unique value based on its characteristics, scarcity, and demand |
Divisibility | Divisible into smaller units, e.g., 0.0001 BTC | Can be divided into smaller units, and ownership can be fractionalized |
Creation | Created primarily through mining | Created through smart contracts |
Storage | On-chain | Usually, only the metadata is stored on-chain, while the digital file is off-chain on a distributed storage network or centralized database |
Governance | May have governance mechanisms that allow token holders to vote on network upgrades or changes | Governance is typically decided by the token creator and cannot be changed |
Rarity | Not rare or unique | Rare and unique asset |
Utility | Generic utility as a medium of exchange or store of value | Specific utility as digital assets, representing unique or rare items |
What are semi-fungible tokens?
Semi-fungible tokens (SFTs) are a relatively new type of token that have characteristics of both fungible and non-fungible tokens (NFTs). SFTs are unique and represent specific assets, but they can be exchanged for other tokens of the same type or value.
This makes them partially interchangeable, unlike non-fungible tokens, but still unique and distinguishable from tokens of the same type, unlike fungible tokens. Simply put, semi-fungible tokens combine both worlds: scarcity and fungibility.
ERC-1155 tokens
The most popular standard for semi-fungible tokens is the ERC-1155 standard, which was introduced by Enjin in 2018.

The ERC-1155 standard allows for the creation of multiple types of tokens within a single contract, each with its own unique attributes and supply.
Prior to ERC-1155, developers had to create separate contracts for each token type, resulting in higher gas fees and more complex contract interactions.
ERC-1155 proposed a solution by introducing a single contract that can manage multiple token types, both fungible and non-fungible, using a modular design.
Now, developers can create complex token ecosystems without having to deploy multiple contracts, reducing the cost and complexity of decentralized application (dApp) management.
Essentially, ERC-1155 makes it possible to create tokens that represent unique assets, such as in-game items or collectibles, while still allowing them to be traded and exchanged.
Example of a semi-fungible token (SFT)
To illustrate semi-fungible tokens (SFTs), let's take an example of an in-game item that is a sword used for attacking.
Say the sword that has a certain level of durability, where the durability can decrease as the sword is used. In this case, the SFT can be partially interchangeable with other swords that have the same durability level.
Partial interchangeability means that some aspects of the tokens are identical while others may differ. In the case of SFTs representing swords, they can have different properties such as durability, sharpness, or strength. While two swords may have different properties, they may still have the same level of durability and are thus interchangeable.
On the other hand, an NFT can represent a one-of-a-kind item, such as a rare collectible or a unique character skin, that cannot be replaced or exchanged with any other token.
Fungible and non-fungible tokens summarized
The time people spend in the digital world is steadily increasing. In all of 2022, the average user spent almost 7 hours online. In some countries, like South Africa, the figure is nearly 10 hours per day!
As our lives become more digital, so too will our assets. Fungible and non-fungible tokens powered by distributed ledger technology are a promising solution for safe and effective asset tokenization, distribution, tracking, and management.
Understanding the difference between fungible and non-fungible tokens is essential for those looking to navigate the digital asset space. With this knowledge in hand, you are one step closer to participating in the token economy.
How to buy fungible tokens
To get started with your first fungible tokens, simply buy crypto via MoonPay using your credit card, bank transfer, or any other preferred payment method. MoonPay's widget offers a fast and easy way to buy Bitcoin, Ethereum, and more than 50 other cryptocurrencies.
MoonPay also makes it easy to sell crypto when you decide it's time to cash out. Simply enter the amount of the token you'd like to sell and enter the details where you want to receive your funds.
How to buy non-fungible tokens
MoonPay's NFT Checkout solution makes it easier than ever to buy NFTs directly using a credit card, with fewer roadblocks and dropout points.
We've removed excessive steps in the purchasing process, including needing to acquire the necessary crypto first and transfer between multiple cryptocurrency exchanges and wallets.
Just choose the NFT you wish to purchase and enter your card details to complete your transaction.


.png?w=3840&q=90)

.png?w=3840&q=90)
