Bitcoin halving is a much-awaited recurring event in the cryptocurrency space. The entire crypto community eagerly anticipates its once every four-year occurrence, the latest of which occurred in April 2024.
But what is it all about? And is the Bitcoin halving event really worth the hype it gets?
We explain what there is to know about Bitcoin halving, its history, and how it affects the price of Bitcoin.
What is Bitcoin halving?
Bitcoin halving is the process in which the block reward for verified transactions on the Bitcoin network is reduced by 50%. Building upon the basic principles of supply and demand, Bitcoin halving operates to combat inflation and increase the value of the cryptocurrency.
Bitcoin's pseudonymous founder, Satoshi Nakamoto, encoded certain predefined rules that would govern how the Bitcoin network would function. One of these rules is what Satoshi called "the Bitcoin halving event".
There are two principles of the Bitcoin blockchain that will help us understand Bitcoin halving.
Mining rewards affect Bitcoin’s inflation
Satoshi conceptualized the Bitcoin network to run on a Proof of Work (PoW) consensus mechanism. In a PoW consensus model, miners use their computing power to create new ‘blocks' in the network.
In return, they get ‘mining rewards' in the form of Bitcoins on a per-block basis. This mining reward component is crucial in regulating the rate of supply of Bitcoin flow into the network. Simply put, this is the pace at which new Bitcoins enter circulation.
Block time is kept nearly constant
The Bitcoin mining algorithm has an internal ‘clock' that aims to add a new block to the network roughly every ten minutes.
Bitcoin's maximum supply is capped at 21 million and the tokens are gradually released into circulation as and when miners add blocks. Since blocks are added roughly every 10 minutes, that's the same amount of time that new Bitcoins enter circulation.
So, what happens when you suddenly add a bunch of new miners to the network or increase processing speeds in an effort to add blocks in under 10 minutes?
In Bitcoin's case, that would not be possible because the Proof of Work algorithm's difficulty level is adjusted to meet the increased computational power of the miners.
This change in the difficulty level ensures that the block time is always maintained at around 10 minutes. In other words, new Bitcoins are released every ten minutes: no more and no less.
Why does the Bitcoin halving event occur every four years?
Bitcoin halving is programmed to occur after every 210,000 blocks are mined.
Since we know that the block time for Bitcoin is always around 10 minutes, we know that the halving occurs roughly every four years.
Time taken to mine 210,000 blocks = (210,000 * 10) minutes, or 3.9899 years
Bitcoin mining rewards are reduced by half every four years, ensuring that fewer Bitcoins are added to the circulation until the very last Bitcoin is mined. The last Bitcoin to be mined is predicted to happen in the year 2140.
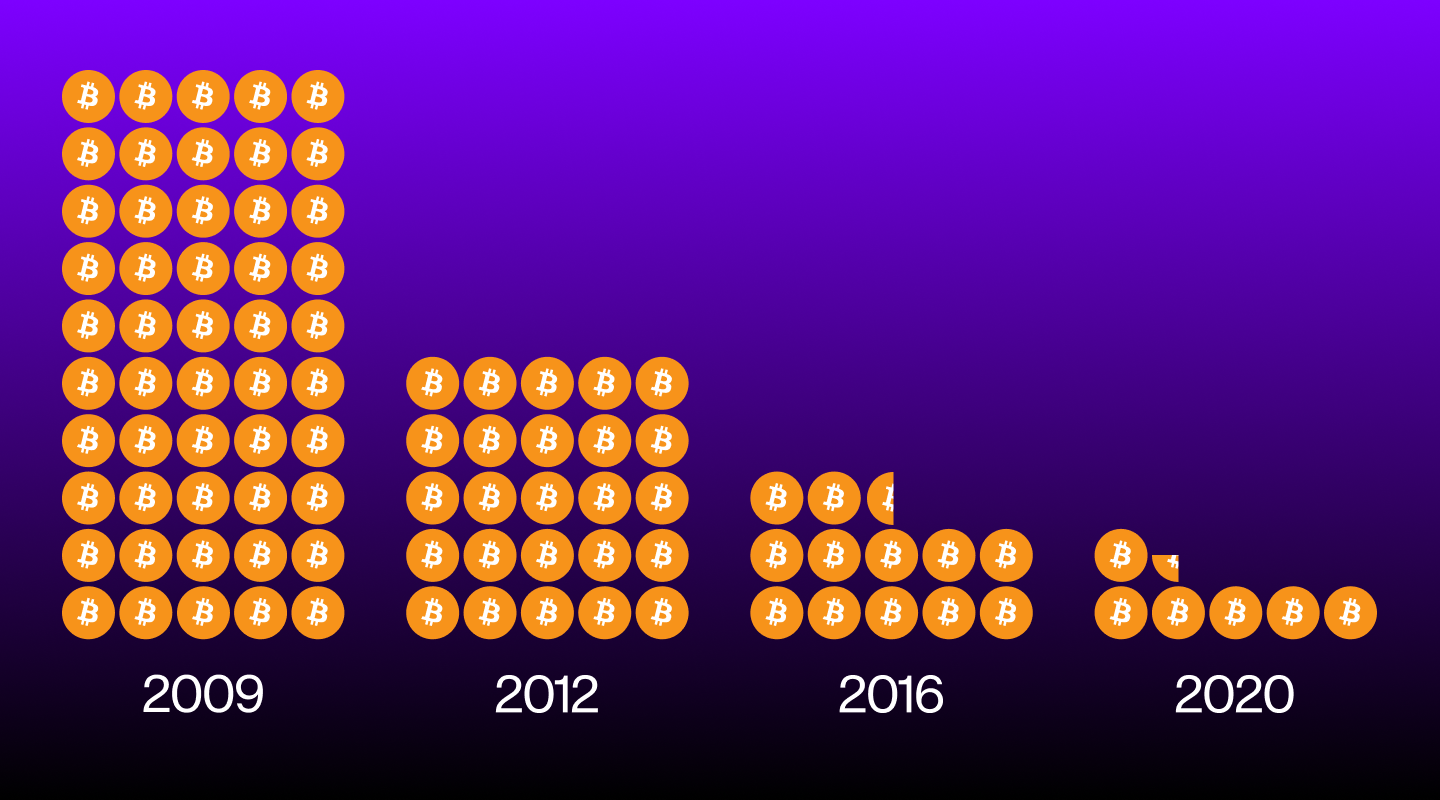
Currently, over 19.4 million Bitcoins have been mined, leaving just under two million to be mined in the future. These last two million coins will take the most time to mine due to Bitcoin's halving schedule.
Why is Bitcoin halving important?
By cutting down the block rewards by half, Bitcoin halving ensures that there is deflationary pressure on the cryptocurrency. This means that as time progresses and more coins are mined, Bitcoin becomes increasingly scarce.
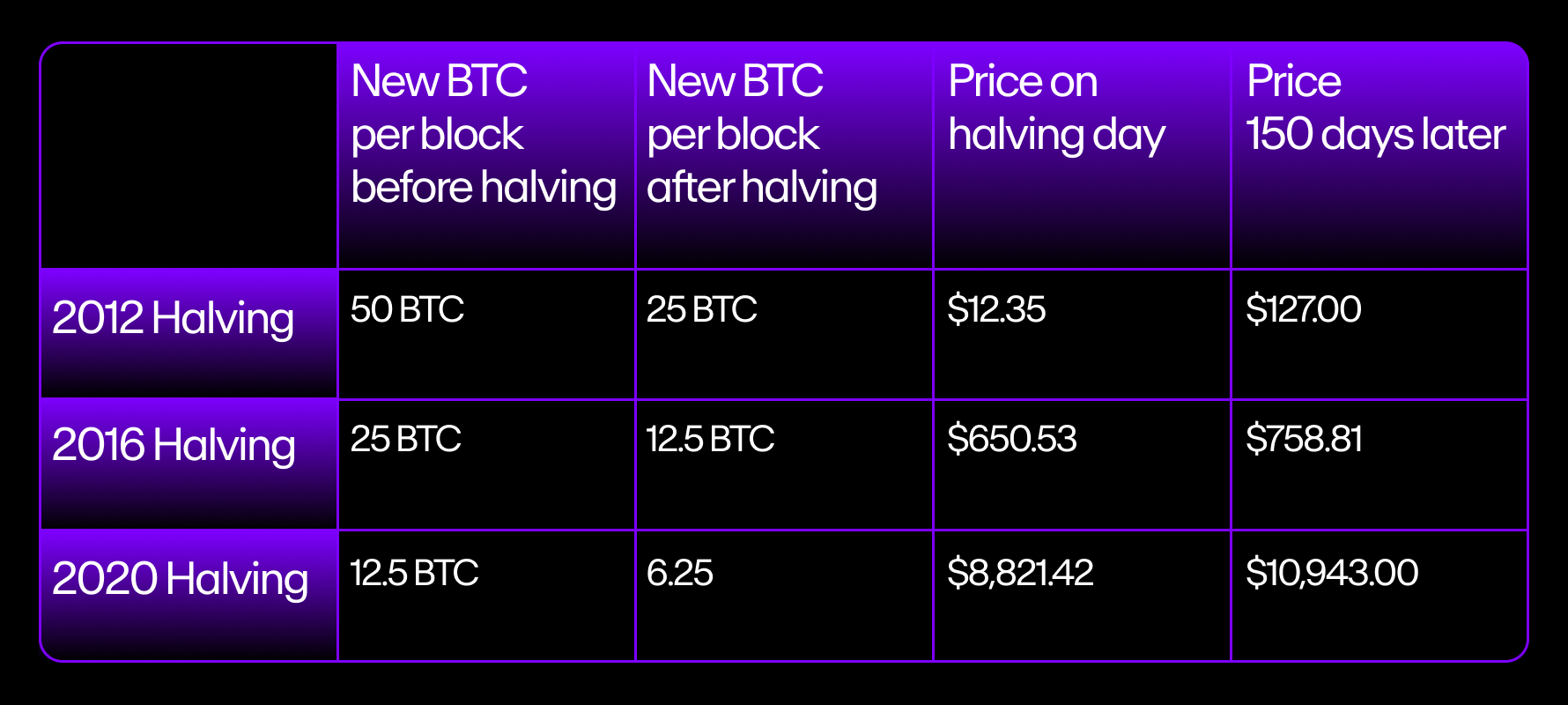
Certain halving events in the past (which occur roughly every four years) were followed by gradual increases in Bitcoin's price over extended periods of time. This is because as the Bitcoin supply decreased, the demand for Bitcoin increased in turn.
Block rewards can be viewed as a form of Bitcoin inflation, so halving reduces Bitcoin's inflation rate. For example, the last Bitcoin halving event in 2020 reduced the inflation rate of Bitcoin by 50% (from 3.6% to 1.8%), a figure below the Central Banks' 2% target reference.
Bitcoin halving dates history
Bitcoin's inception in 2009 was marked by its creator, Satoshi Nakamoto, mining the first block of the Bitcoin blockchain. The block reward at the time was set at 50 BTC per block, and today Satoshi reportedly holds one million BTC earned through mining.
At the time, Bitcoin did not have much monetary value, so there was no real incentive for miners to join the network. It's worth noting, however, that 50% of the available Bitcoins were mined by Satoshi in the period preceding the first Bitcoin halving event.
The first halving took place on 28 November 2012. This was marked by the mining block reward being halved from 50 BTC to 25 BTC. The value of Bitcoin climbed steadily after the first halving event. It corrected shortly afterward, however, in what is known as a “pullback compression phase”, when prices contract before continuing an upward trend.
The second halving occurred on July 9, 2016, when the block reward further halved to 12.25 BTC. This was a highly anticipated event because popular interest in Bitcoin was on the rise in 2016.
The third halving occurred on May 11, 2020, when rewards for mining each block were cut to 6.25 BTC. Different from previous halving events, this one coincided with the breakout of the COVID-19 pandemic, causing prices to collapse.
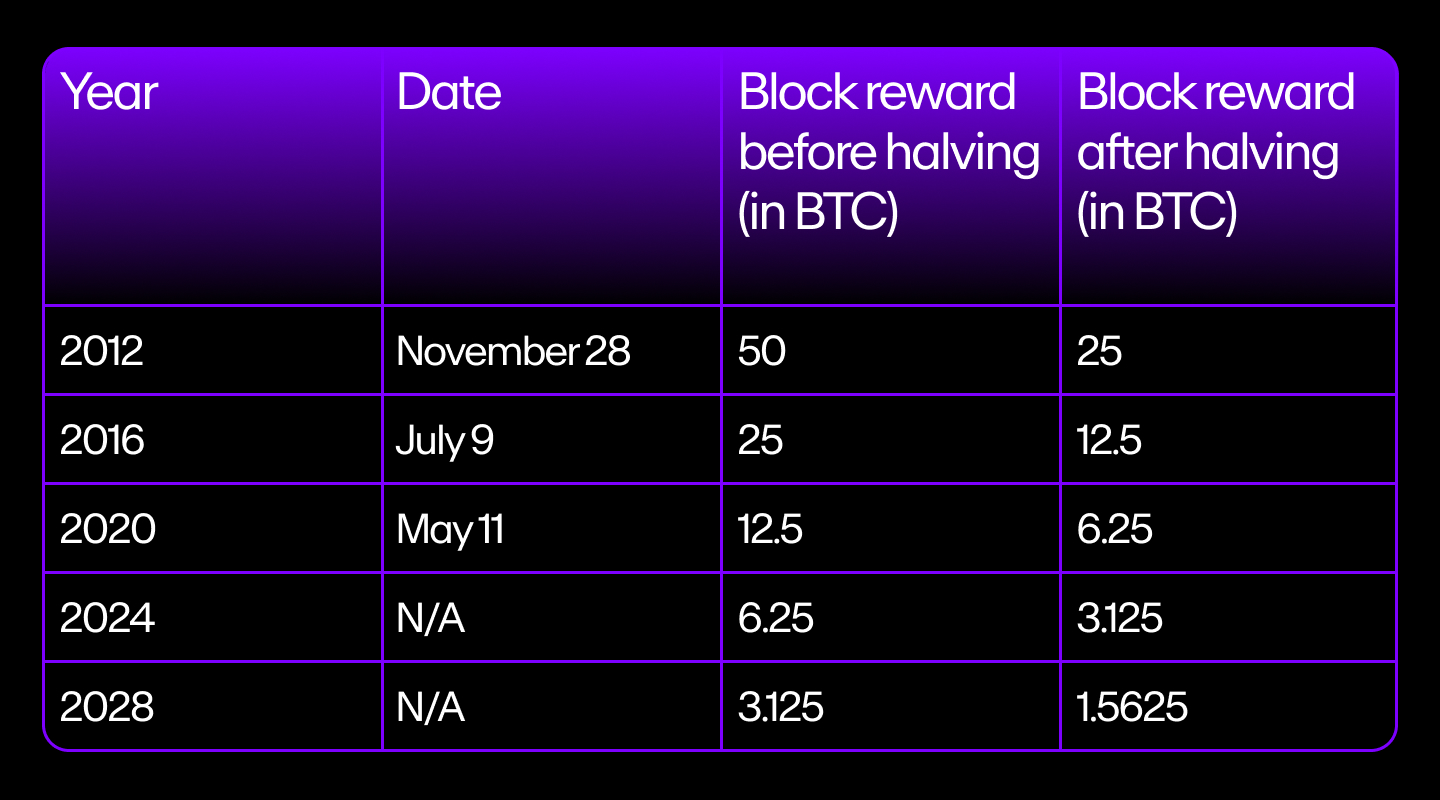
The latest halving for Bitcoin took place in April 2024 and will continue until 2140, the year in which all 21 million Bitcoins will have been mined.
What happens to Bitcoin miners after Bitcoin halving events?
Reward halving has an effect on miners as well. As mentioned earlier, with each halving event, the block reward per miner is cut in half. While this may not seem like much, it does have an impact on miners' profitability.
Bitcoin block rewards are the backbone of the BTC blockchain. So what incentivizes miners to be part of the network when the rewards start to decline?
Bitcoin halving is based on the assumption that the token's price would increase when demand increases. But what if demand does not rise? Will miners stop mining altogether and close shop?
This is certainly a possibility. As the price of high-end mining hardware and electricity continues to rise, the gap narrows between the benefits of Bitcoin mining and incurred costs. Bitcoin halvings would only accelerate this gap if the demand starts sliding.
We can already see this happening in the current bear market as Bitcoin slips below the shutdown price (the price of BTC below which mining is no longer profitable) and miners flock to other cryptocurrencies that promise greater returns.
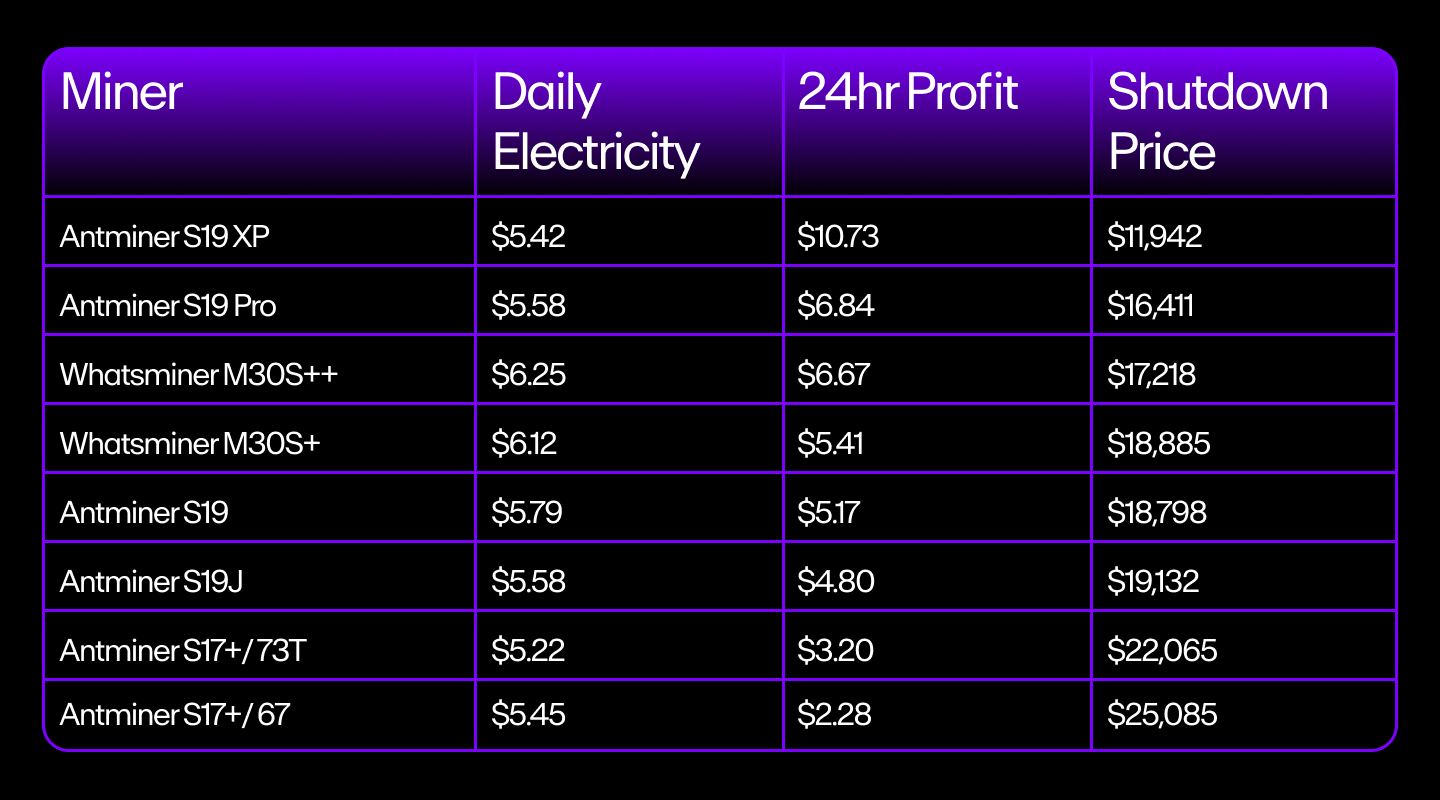
But as miners flee, the network's hash rate (the computational power of the network) begins to decrease and the algorithm's difficulty is lowered. This increases the reward for existing miners as the number of competitors drops. It has also successfully kept the price of Bitcoin high after halving events.
A more pressing question is: “What happens when the last Bitcoin is mined in 2140?”
Well, miners would still be required to keep the network operational by validating transactions. Experts theorize that the transaction fee that users pay each time they engage in executing a buy / sell call will become the new source of remuneration for miners.
When blockchain technology reaches global acceptance, the number of transactions may rise drastically and, by default, so will transaction fees. This would therefore act as the new reward for miners. Nevertheless, it remains to be seen how this issue plays out.
How does Bitcoin halving affect Bitcoin's inflation?
The previous three halvings have resulted in inflation rates being cut. Bitcoin's inflation rate was 50% in 2011, but after halving in 2012, it plummeted to 12%, and then to 4-5% in 2016.
After the halving event in 2020, BTC's annual inflation rate was almost 50% of the world average inflation rate at 1.8% and lower than the average inflation target of 2% of central banks worldwide.
This is one of the main reasons why Bitcoin's tokenomics is considered so favorably by Bitcoin maximalists: Bitcoin is programmed to combat inflation.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) about Bitcoin halving
When is the next Bitcoin halving event?
The estimated date for the next Bitcoin halving event is April 2028.
Why do Bitcoin halvings occur every four years?
The Bitcoin halving event takes place after every 210,000 blocks. With the network's block time being approximately 10 minutes, you can calculate that the time between halving events is a little less than 4 years.
What happens when there are no more Bitcoins left in a block?
It is predicted that the last Bitcoin will be mined in the year 2140. After this, Bitcoin miners will likely be compensated through transaction fees rather than mining rewards. When this happens, the security of the Bitcoin blockchain will still be ensured and miners will still be incentivized to add transactions to the blockchain.
What is the current Bitcoin supply?
Bitcoin is a deflationary asset with a finite supply (a maximum of 21 million Bitcoins).
Currently, the total supply of Bitcoin is about 19.5 million Bitcoins, with all of these coins in circulation.
For live Bitcoin price and market metrics, view our Bitcoin Price page
Where to buy Bitcoin
You can buy Bitcoin (BTC) via MoonPay or through any of our partner wallet applications with a credit card, bank transfer, Apple Pay, Google Pay, and many other payment methods.
Just enter the amount of BTC you wish to purchase and follow the steps to complete your order.
How to sell Bitcoin
MoonPay makes it easy to sell Bitcoin when you decide it's time to cash out your crypto.
Simply enter the amount of BTC you'd like to sell and enter the details where you want to receive your funds.
Swap Bitcoin for more tokens
Want to exchange Bitcoin for other cryptocurrencies like Ethereum and Wrapped Bitcoin? MoonPay allows you to swap crypto cross-chain with competitive rates, directly from your non-custodial wallet.

.png?w=3840&q=90)
.png?w=3840&q=90)



