In today’s era of rapid innovation, the developers behind cryptocurrency and blockchain projects often find themselves strongly opinionated about its direction. Often, these debates are resolved by a voting mechanism where the option receiving the most votes wins.
But there are times when a large number of people are so passionate about their own beliefs that a consensus can't be reached, and the project splits into two - this split is what is known as a "hard fork."
That is exactly what happened with Bitcoin (BTC) and Bitcoin Cash (BCH).
In this article, we explore Bitcoin and Bitcoin Cash, how they differ.
The Bitcoin Scaling Debate
Bitcoin is first cryptocurrency, created by Satoshi Nakamoto 2008 as a way to enable peer-to-peer transactions without the need for centralized intermediaries. After the bull market of 2017, the Bitcoin blockchain was unable to handle the increased demand and provide adequate transaction throughput. This caused long delays for Bitcoin transactions, as well as high fees that peaked at almost $40 for a single transaction!
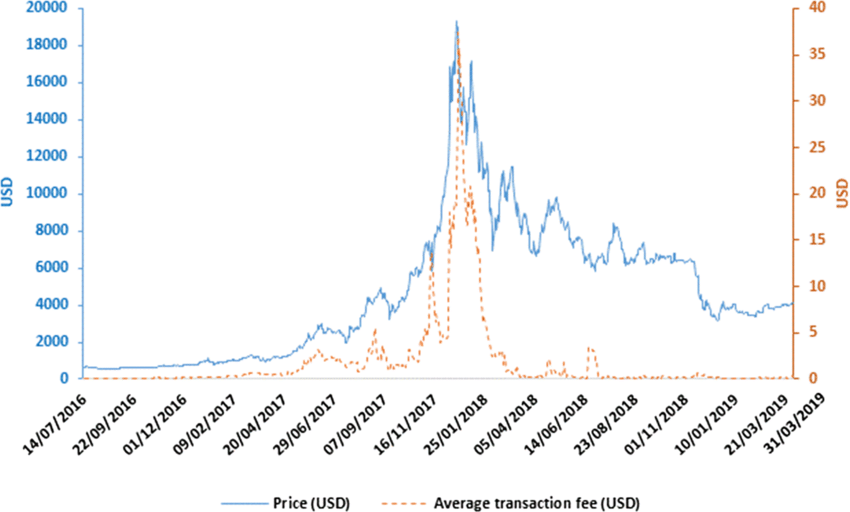
The long transaction confirmation times and transaction fees led to arguments that the design of Bitcoin was not favorable for micro-transactions and everyday usage. Advocates of this view argued Bitcoin was unfit for daily transactions as creator Satoshi Nakamoto intended in Bitcoin's white paper, and that it needed an upgrade.
The proposed solution was to increase the block size from 1MB to 8MB, which would result in a higher number of transactions being confirmed per second. Sounds quite straightforward, doesn't it?
Well, it wasn't that easy.
The change was met with some resistance from those who argued that larger block sizes would centralize the Bitcoin network, going against its very ethos. This is because increasing any network's block size increases the hardware requirements to run a node, making it more difficult for the average person to run their own node, and thus concentrating mining power among fewer participants.
The increase in block size would also mean lower Bitcoin transaction fees. Although this may be desirable for most Bitcoin users, it would affect the livelihood of Bitcoin miners, who earn block rewards in the form of transaction fees.
The Bitcoin Cash Hard Fork
As you've just learned, this scaling debate resulted in the splitting of Bitcoin into two separate chains - Bitcoin (BTC) and Bitcoin Cash (BCH).
The Bitcoin Cash network was created on August 1st, 2017 as a hard fork of the Bitcoin blockchain, with an increased block size limit of 8MB (later increased to 32MB).
The result was a new blockchain that could confirm transactions at a greater rate per second, with lower transaction fees than the original Bitcoin blockchain. The goal was to create a cryptocurrency like Bitcoin that could be used for daily transactions in the same way as someone would pay with cash.
What is a hard fork?
A hard fork is a divergence in the consensus rules of two networks with the same codebase. In this case, both Bitcoin and Bitcoin Cash both share the same codebase, but have different consensus rules.
To put it another way, Bitcoin Cash can be thought of as Bitcoin's clone but with different settings.
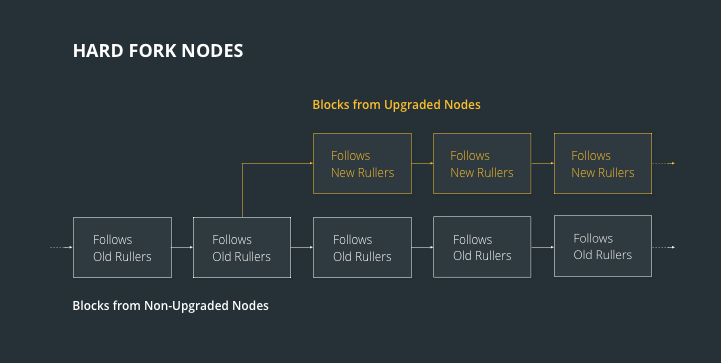
The Bitcoin Cash network also implemented a few other minor changes, such as easier difficulty adjustments and retargeting.
Difficulty adjustments and retargeting dictate how often or easily blocks are mined. An easier difficulty adjustment allows miners to adjust more quickly to changes in network hash rate, while retargeting allows miners to adjust the difficulty of mining a block more quickly in response to sudden changes in hash rate.
And as if one fork wasn't enough, Bitcoin Cash actually underwent a second one in November 2018, over the same block scaling debate, leading to the creation of Bitcoin SV (BSV), which is somewhat of a hybrid, combining elements of BTC and BCH.
Bitcoin vs. Bitcoin Cash: Key differences
The main difference between Bitcoin and Bitcoin Cash can be summed up in one word - scalability. But there's more to it than that.
Feature | Bitcoin (BTC) | Bitcoin Cash (BCH) |
Difficulty adjustment | Every 2016 blocks. Uses difficulty-adjustment algorithm | Every 6 blocks. Uses emergency difficulty adjustment algorithm |
Block size | 1 MB | 32 MB |
Smart contract functionality | Yes. Made possible by the Taproot upgrade | Yes. Natively implemented |
Token issuance | Issues tokens via the Omni Layer platform | Issues tokens via the natively implemented Simple Ledger Protocol (SLP) |
Transaction throughput | 3-7 transactions per second (TPS) | 61-200 transactions per second (TPS) |
Difficulty adjustment algorithms
In the early days of Bitcoin, it was so easy to mine the cryptocurrency that anybody with a desktop could start mining and collect Bitcoin tokens! Since Bitcoin is a Proof-of-Work (POW) cryptocurrency, Bitcoin miners with the most processing power (hash power) tend to have the upper hand in the fierce competition to produce the next block.
An obvious question that arises is, "What if someone brings a device with a lot of processing power and mines all the BTC at once?" Satoshi Nakamoto actually predicted this, and introduced what is known as the "difficulty adjustment."
The difficulty adjustment ensures that the supply of a cryptocurrency is controlled and dictated by the tokenomics (built into the source code) and cannot be sabotaged by any entity. When the hash power increases, the difficulty level of mining blocks increases. Conversely, when the hash power is lowered, so too is the difficulty level.
Both Bitcoin and Bitcoin Cash are designed to have a block time of about 10 minutes, with the difficulty adjusted periodically based on the time it took to mine the previous blocks.
Bitcoin uses the difficulty-adjustment algorithm (DAA), where the difficulty is adjusted every 2016 blocks. It is increased if the previous 2016 blocks were mined at a pace faster than 10 minutes per block, and decreased if they were mined slower than 10 minutes per block.
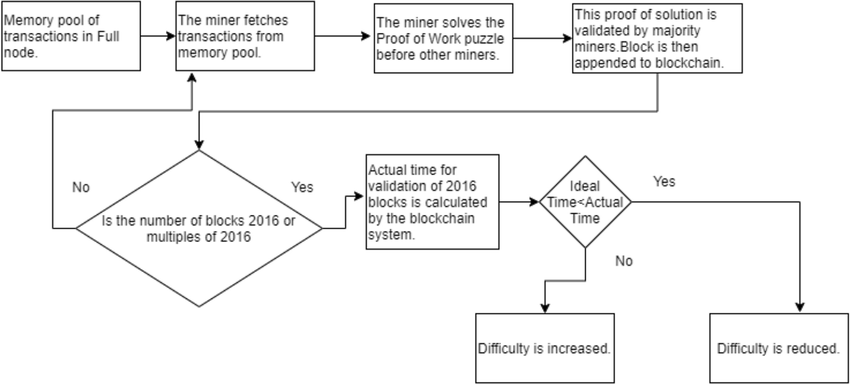
Bitcoin Cash uses the Emergency Difficulty Adjustment (EDA) algorithm. This algorithm dictates that the difficulty will be reduced by 20% if the time difference between the previous 6 blocks is more than 12 hours.
Block size differences
In Bitcoin, the block size is limited to 1 MB. Bitcoin Cash increased the block size limit to 32 MB, allowing more transactions to be processed per block and, consequently, a higher network throughput.
But larger block sizes also mean that the data stored in the blockchain will be greater. This can cause issues with storage, especially for the nodes that validate transactions and blocks.
It is important to note that increasing the block limit is a complex issue that involves trade-offs between various factors such as security, decentralization, and scalability.
Smart contract capability
Smart contracts are an innovation created by Ethereum developers several years after Bitcoin first came into existence. Hence, Bitcoin's architecture does not natively support smart contracts. This led to a problem: A lack of smart contract capability meant that Bitcoin cannot be used in DeFi (decentralized finance) protocols. To solve this problem, the Taproot upgrade was introduced.
This upgrade allowed for Bitcoin, the most popular cryptocurrency, to start supporting smart contracts by masking smart contract transactions as regular Bitcoin transactions. Taproot eventually helped pave the way for Bitcoin Ordinals, which are non-fungible tokens (NFTs) on the Bitcoin blockchain.
Additionally, another proposed solution to properly scale the Bitcoin blockchain is called the Bitcoin Lightning Network. The Lightning Network is a Layer-2 solution built on top of the Bitcoin network that enables faster and cheaper transactions by using smart contract functionality.
Bitcoin Cash, on the other hand, supports smart contracts natively. This allows developers to implement more complex DeFi protocols using CashScript, Bitcoin Cash's smart contract programming language.
Token issuance
Both the Bitcoin and Bitcoin Cash networks support token issuance (including custom utility tokens, stablecoins, NFTs, and more) but differ in how they do so.
To issue tokens on the Bitcoin blockchain, you need to use another platform called the "Omni Layer." The Omni Layer is designed to be a decentralized and trustless platform, allowing anyone to create and issue their own custom tokens. The protocol uses a series of special transaction types called "smart properties" to represent tokens on the Bitcoin blockchain.
Custom digital assets on Bitcoin Cash are implemented natively using the Simple Ledger Protocol (SLP), a token issuance and management standard built on top of the Bitcoin Cash (BCH) network.
One of the key features of SLP is that it is designed to be simple to use and understand, making it accessible to a wider range of users.
Bitcoin and Bitcoin Cash similarities
Although they are distinct networks and tokens, both Bitcoin and Bitcoin Cash share much in common:
Feature | Bitcoin (BTC) | Bitcoin Cash (BCH) |
Total supply | 21 million BTC | 21 million BCH |
Block time | ~10 minutes | ~10 minutes |
Hashing algorithm | SHA256 | SHA256 |
Advantages of Bitcoin Cash
Bitcoin Cash (BCH) was created to provide some unique advantages over the original Bitcoin (BTC) blockchain.
1) Lower transaction fees
Bitcoin Cash (BCH) offers significantly lower fees compared to Bitcoin, making it much more accessible for small transactions. Increased cost-efficiency allows users to make everyday purchases without worrying about higher fees eating into the transaction value.
2) Faster confirmation times
Bitcoin Cash transactions are confirmed faster than those on the Bitcoin network. Higher speed makes Bitcoin Cash particularly suitable for point-of-sale (POS) transactions, where quick confirmation time is essential for both merchants and customers.
3) Increased scalability
Bitcoin Cash was designed with increased scalability in mind, allowing for more transactions to be processed per block. Higher scalability means that the network can handle a higher transaction volume without significant delays or increased transaction fees.
4) Decentralized mining
The mining process for Bitcoin Cash remains decentralized, making it more resistant to the centralization issues that have plagued other cryptocurrencies. Decentralized mining means a more equitable distribution of mining power, which also helps preserve the integrity and security of the Bitcoin Cash network.
5) More accessible
Bitcoin Cash features a simpler script language compared to Bitcoin, which makes it more accessible to a broader audience, including developers and businesses looking to integrate cryptocurrency into their operations. It can also help lower the barriers to entry for those new to cryptocurrency, potentially encouraging wider adoption.
6) Better compatibility with existing infrastructure
With a larger block size than Bitcoin, Bitcoin Cash is better suited to integrate with existing payment infrastructure. The increased block size allows for more transactions to be processed simultaneously, enhancing compatibility with traditional payment systems.
7) Stronger focus on peer-to-peer transactions
Bitcoin Cash was specifically designed to prioritize peer-to-peer (P2P) transactions, staying true to the original vision of cryptocurrency as a decentralized, digital cash system. Compared to traditional digital payments, BCH remains a more practical tool for direct transactions between individuals, without the need for intermediaries.
8) More opportunities for merchants
The combination of faster confirmation times and lower transaction fees makes Bitcoin Cash a viable option for merchants. These features enable businesses to accept BCH as payment more easily, reducing overhead costs associated with payment processing.
Disadvantages of Bitcoin Cash
Although Bitcoin Cash offers certain advantages, it also carries unique risks like any other blockchain technology.
1. Lower adoption rate
It's no secret that Bitcoin Cash (BCH) has a lower adoption rate compared to Bitcoin. This means it may be more challenging to find merchants, online platforms, or physical stores that accept it as a form of payment, potentially limiting its utility as a currency.
2. Less infrastructure
The ecosystem surrounding Bitcoin Cash is less developed compared to Bitcoin, making it more difficult for users to access, store, and use BCH. This includes fewer crypto wallet options, fewer cryptocurrency exchanges that support BCH trading, and a smaller range of financial services like lending or staking that are support Bitcoin Cash.
3. Lower liquidity
Bitcoin Cash has less liquidity compared to Bitcoin, meaning there are fewer exchanges where BCH can be bought or sold quickly without impacting the BCH market price. Lower liquidity can result in greater price volatility and difficulty in executing large transactions without significant slippage.
4. More susceptible to manipulation
Due to its smaller market capitalization (or market cap), Bitcoin Cash is more vulnerable to price manipulation by large holders, sometimes referred to as "crypto whales." These individuals or groups can significantly impact the price of BCH by buying or selling large amounts at once, which can lead to sudden price swings and instability in the crypto market.
5. Weaker security
The Bitcoin Cash network has a smaller number of blockchain nodes and miners compared to Bitcoin, which can lead to reduced security. A smaller network means that there are fewer participants verifying transactions, making the blockchain more susceptible to hacks, such as a 51% attack.
6. More centralization
Though it is still a decentralized network, the Bitcoin Cash blockchain still faces centralization risks, as a small number of mining pools control a large percentage of the network's hash rate. Concentrated mining power can undermine the decentralized nature of the cryptocurrency and increase the risk of coordinated actions by these pools.
7. Risk of hard forks
Bitcoin Cash has a history of undergoing hard forks, which can create fear, uncertainty, and doubt (FUD) among users and investors. As we've seen with the creation of Bitcoin Cash itself, hard forks can lead to the creation of new coins and the fragmentation of a community.
8. Risk of losing investment
Like any cryptocurrency, investing in Bitcoin Cash carries the risk of significant price decreases. The volatility of the cryptocurrency market means that Bitcoin Cash's value (as well as the Bitcoin price) can fluctuate widely, and there is always the potential for losing a substantial portion of the investment if the market turns against it.
Recent Developments: Bitcoin and Bitcoin Cash
As the cryptocurrency landscape continues to evolve, both Bitcoin and Bitcoin Cash have experienced noteworthy changes that impact their technology, adoption, and user experience. Here’s a look at the most significant developments for each in recent years:
Bitcoin (BTC) Developments
- Spot Bitcoin ETF Approvals: In early 2024, several Spot Bitcoin ETFs received approval and launched in major markets like the US, increasing institutional investment and mainstream adoption.
- Network Upgrades: The implementation of enhancements such as the Taproot upgrade (completed in late 2021) and ongoing proposals for further scalability and privacy improvements, including work on bringing Schnorr signatures and further second-layer solutions like the Lightning Network into broader use.
- 2024 Bitcoin Halving: In April 2024, Bitcoin underwent its fourth halving event, reducing the block reward from 6.25 to 3.125 BTC per block. This event, which happens roughly every four years, is designed to decrease the rate at which new bitcoins are created.
- Ordinals and NFTs: The popularization of Bitcoin Ordinals (NFTs on Bitcoin) brought new attention and developers to the Bitcoin ecosystem.
Bitcoin Cash (BCH) Developments
- Network Upgrades: In May 2023, BCH implemented a network upgrade that improved transaction efficiency and brought new features for smart contract development via CashTokens, enabling more complex DeFi and tokenized applications natively on BCH.
- 2024 Halving Event: Just like BTC, the Bitcoin Cash network also experienced its scheduled block reward halving in April 2024, reducing the reward from 6.25 to 3.125 BCH per block. This event impacted miner economics and brought renewed market attention.
- Merchant and Payment Integration: BCH has expanded its merchant acceptance, aiming to be a leading peer-to-peer electronic cash system. Several POS providers and global payment gateways have integrated BCH, making it easier for merchants to accept.
- Increased Throughput and Lower Fees: BCH’s large blocks continue to allow for consistently low fees (often under $0.01) and rapid confirmations, strengthening its narrative as “everyday crypto cash.”
The Verdict: Bitcoin or Bitcoin Cash?
At a fundamental level, both Bitcoin and Bitcoin Cash are digital currencies that can be used to pay for goods and services, just like fiat money. However, they differ in many ways including their goals, philosophy of development, block sizes, transaction fees, scalability, and more.
As far as goals are concerned, Bitcoin is focused on becoming a global digital asset and currency, while Bitcoin Cash is focused on becoming a peer-to-peer payment system.
There is no simple answer to which is better when it comes to Bitcoin vs Bitcoin Cash. Of course, Bitcoin Cash has introduced several improvements that Bitcoin lacks, but it has made some significant trade-offs in the process that many Bitcoin maximalists frown upon.
Like any cryptocurrency investment, it all comes down to personal preference.
Did you know? You can pay with Bitcoin and Bitcoin Cash
Frequently Asked Questions about BTC and BCH (FAQ)
1. Is BCH faster than BTC?
Yes, Bitcoin Cash (BCH) processes transactions more quickly than Bitcoin (BTC) due to its larger block size (32 MB vs. 1 MB for Bitcoin), allowing it to handle more transactions per block. This means faster confirmations and less network congestion, especially during periods of high activity.
2. Is Bitcoin Cash a good investment compared to Bitcoin?
Any cryptocurrency decision will depend on your investment goals. Bitcoin (BTC) is more widely adopted and has a higher market cap. Bitcoin Cash (BCH) offers faster transactions and lower fees, appealing to those who value payment utility. Always research and consider your risk tolerance before investing.
3. Why did Bitcoin split into Bitcoin Cash?
Bitcoin split into Bitcoin Cash in August 2017 due to a disagreement within the Bitcoin community about how to scale the network. Some wanted to keep small block sizes for decentralization (leading to BTC), while others pushed for larger blocks to allow more transactions and lower fees (leading to BCH). The result was a hard fork, creating Bitcoin Cash as a separate cryptocurrency.
4. Can you convert Bitcoin to Bitcoin Cash?
Yes, you can convert Bitcoin (BTC) to Bitcoin Cash (BCH) using most major cryptocurrency exchanges or non-custodial swapping services like MoonPay. The process typically involves selling BTC for fiat (or a stablecoin) and then buying BCH, or using a direct swap feature if supported by your platform or wallet.
5. Is BCH safer than BTC?
While no cryptocurrency token can be deemed 100% safe, BTC has a much higher network hashrate and larger number of miners than BCH, making it less vulnerable to attacks like a 51% attack. While BCH is still generally secure, its smaller network size and lower mining participation mean it can be more susceptible to certain security risks compared to BTC.
*Cryptocurrency is a volatile and evolving asset class. Always do your own research (DYOR) before buying Bitcoin, Bitcoin Cash, or any other crypto asset, and only use reputable, secure platforms for purchases and storage. Investing in cryptocurrencies is not suitable for everyone and can result in significant losses.
How to buy Bitcoin and Bitcoin Cash
Now that you have a bird's eye view of BTC vs BCH, you may be looking to acquire and explore them both yourself.
You can buy Bitcoin (BTC) and Bitcoin Cash (BTC) via MoonPay or through any of our partner wallet applications with a credit card, bank transfer, Apple Pay, Google Pay, and many other payment methods. Just enter the amount of BTC or BCH you wish to purchase and follow the steps to complete your order.
Users can also top up in euros, pounds, or dollars and use MoonPay Balance for buying cryptocurrencies like BTC and BCH. Once funded, use your balance for faster, cheaper transactions and higher approval rates. When you're ready to withdraw, enjoy zero-fee transfers straight to your bank account.
How to sell Bitcoin and Bitcoin Cash
MoonPay makes it easy to sell Bitcoin and Bitcoin Cash when you decide it's time to cash out your crypto.
Simply enter the amount of BTC or BCH you'd like to sell in the MoonPay widget and enter the details where you want to receive your funds.



.png?w=3840&q=90)


.png?w=3840&q=90)