Bitcoin maximalists have a vision: to make Bitcoin the world's most dominant currency. But with the network's throughput of just five to seven transactions per second (TPS), this dream is currently far from reality.
The Bitcoin developer community is actively making efforts to upgrade the network to improve performance. The introduction of SegWit in August 2017 was a significant step in this direction, as well as Taproot in 2021 and Bitcoin Ordinals in 2023.
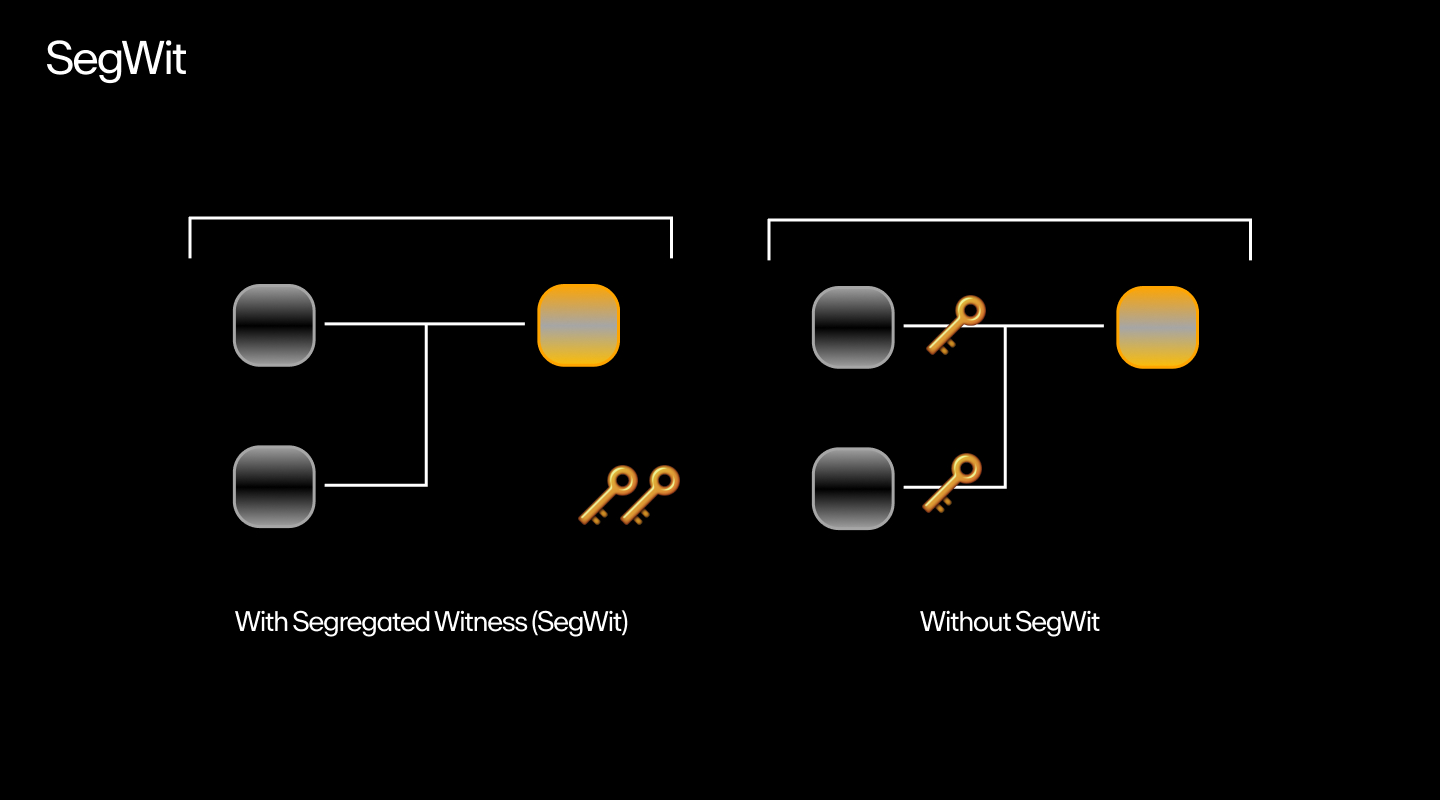
But even with these efforts, the question of how to make Bitcoin a truly global currency persists. After all, payment processors like Visa are lightyears ahead with a transaction speed over 340 times that of Bitcoin.
That’s where the Lightning Network comes in.
This article explains what the Lightning Network is, why it exists, and how it could be a key to unlocking Bitcoin's potential.
What is the Bitcoin Lightning Network?
The Bitcoin Lightning Network is a decentralized network that uses smart contract functionality in the blockchain to enable faster payments across a network of participating nodes. It is an off-chain scaling solution that enables near-instant, low-cost, private transactions.
Simply put, the Lightning Network is a Layer-2 solution that enables faster and cheaper Bitcoin transactions.
The Lightning Network was proposed in a 2016 white paper by Joseph Poon and Thaddeus Dryja. It is based on the concept of trustless off-chain payments, which are settled on the main blockchain.
In order to understand how the Lightning Network works, let's first take a look at what happens during a typical Bitcoin transaction.
How does a Bitcoin transaction work?
A Bitcoin transaction is made up of three parts: the input, the output, and the signature.
The input is the address from which the funds are being sent, the output is the address to which the funds are being sent, and the signature is used to verify that the transaction is valid.
The network must verify each Bitcoin transaction before it can be included in a block and added to the blockchain. This process is known as mining.
Mining is done by special computers called miners. Miners use their computing power to verify transactions and add them to blocks. In return, they are rewarded with newly minted bitcoins.
The protocol is designed in such a way that it takes an average of 10 minutes to mine a block. This is why a Bitcoin transaction can take very long to be confirmed.
How does the Lightning Network work?
The Lightning Network enables trustless off-chain payments by creating a network of bi-directional payment channels between nodes or users. These channels can exist indefinitely and can be opened and closed anytime.

In order for a channel to be opened, both parties must deposit an equal amount of Bitcoin into a multi-signature wallet, meaning that both parties must sign off on any transactions. This deposit is then used as collateral.
Once a channel is open, the two parties can conduct an unlimited number of transactions between each other without ever touching the Bitcoin blockchain. Transactions are only recorded on the blockchain when the channel is closed.
At this point, both parties settle, and any remaining balance is sent back to their respective wallets.
Sounds great so far, but what happens if one party tries to cheat?
For example, let's say that Alice and Bob have a channel open with a balance of 5 BTC. Alice then tries to close the channel and claim the entire 5 BTC for herself.
This is where things get interesting.
In order to prevent this type of fraud, the Lightning Network uses a technique called Hashed Timelock Contract (HTLC).
HTLC is a smart contract requiring the transaction's sender to wait for a specific period before they can claim the funds.
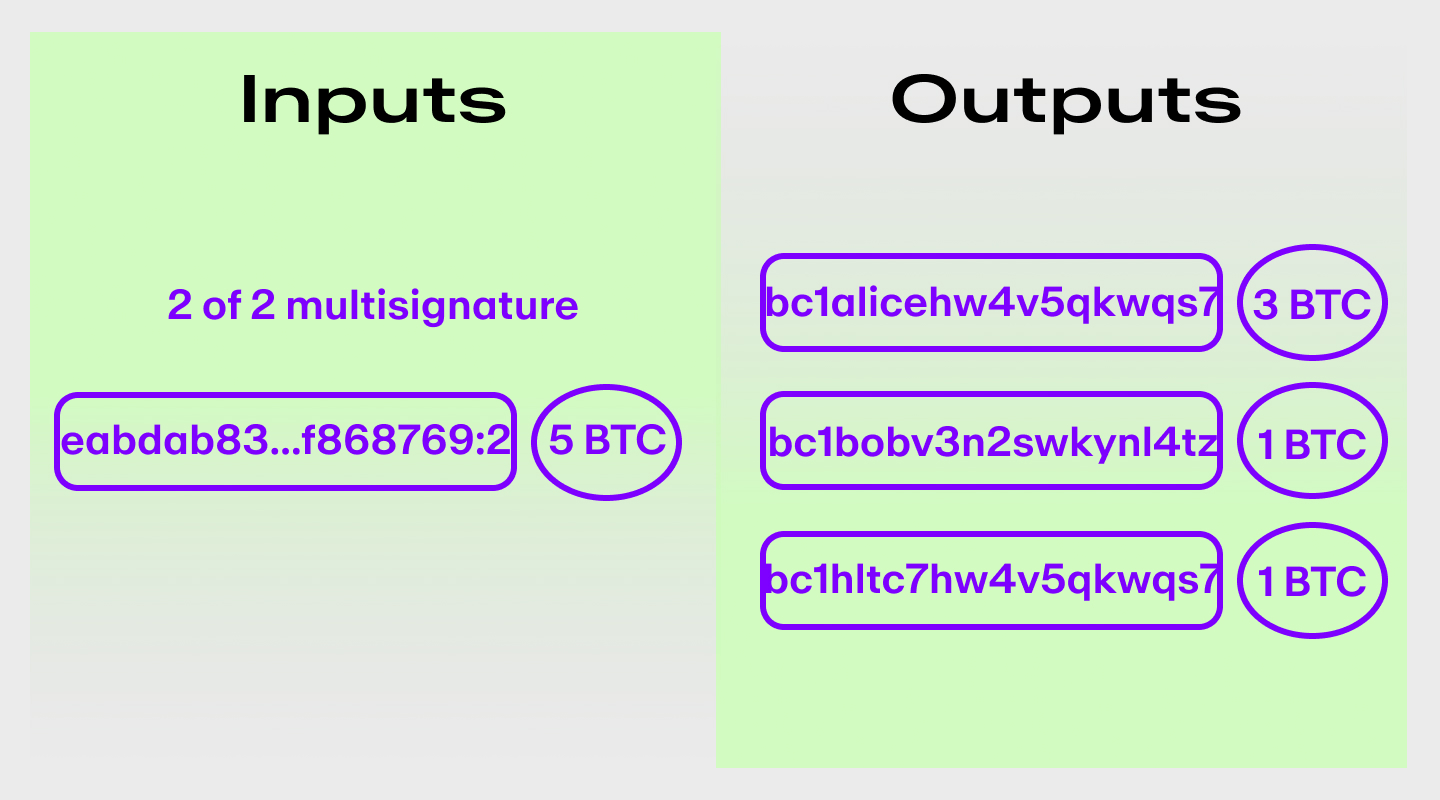
With HTLC, Alice cannot claim the 5 BTC until a certain condition is met. In this case, the condition would be that Bob signs off on the transaction.
If Alice tries to close the channel without Bob's signature, she will not be able to claim the BTC. And if Bob tries to cheat by not signing off on the transaction, he will not be able to claim his share of the funds either.
This system of trustless payments is what makes the Lightning Network so powerful. It enables fast, cheap, and private transactions without the need for a third party.
What is the Lightning Network trying to solve?
The Lightning Network is trying to solve two main issues: Bitcoin’s high fees and slow confirmation times.
The average fee for a Bitcoin transaction peaked at over $60 in 2021. This may not seem like much, but it's a massive problem for businesses that need to process small payments (such as a $2 cup of coffee). In 2023, the highest average transaction peaked at half this amount, which occurred in May of that year.
With the Lightning Network, businesses can accept Bitcoin payments without having to pay high fees. This is because Lightning Network transactions are cheap and fast.
The other issue that the Lightning Network is trying to solve is slow confirmation times.
As we mentioned, it can take up to an hour for a Bitcoin transaction to be confirmed. This is because each transaction needs to be verified by miners and added to a block.
With the Lightning Network, transactions are confirmed instantly. This is because they are not added to the blockchain until the channel is closed.
Did you know? You can pay with Bitcoin
Lightning Network use cases
The Lightning Network opens up several possibilities for Bitcoin.
1. Cross-chain atomic swaps
The LN allows users to make cross-chain atomic swaps. Atomic swaps are a way of trading one cryptocurrency for another (across blockchains) without the need for a third party.
For example, let's say you have Bitcoin and want to trade it for Litecoin. With an atomic swap, you can do this without going through a cryptocurrency exchange.
The condition is that both networks should use or support the same cryptographic hash function.
For instance, Bitcoin uses the SHA-256 hashing algorithm while Ethereum uses the Keccak-256 hashing algorithm. Therefore, atomic swaps are not possible in this case.
2. Scaling
If Bitcoin is ever to be used at scale, it should be able to accommodate thousands of daily transactions regardless of size. Only then could it be adopted by large communities or even countries.
That's why the Lightning Network is so useful. The LN can process a large number of transactions without congesting the Bitcoin blockchain.
The first country to adopt Bitcoin as legal tender, the Republic of El Salvador, also uses the Lightning Network in its payments infrastructure.
3. Microtransactions
The LN allows for microtransactions—something that was not possible with Bitcoin before. This could be used to tip content creators.
Another use case of the LN is to facilitate microtransactions. Since transactions are not settled on the main chain instantly, multiple smaller transactions can take place without having to pay a hefty fee every time.
This opens the door to applications like tipping, in-game payments, and pay-per-use services.
Twitter and Substack are among the early web2 giants to have jumped on this bandwagon and enabled peer-to-peer Bitcoin payments on their platform as a method of subscription or tipping.
4. Power dApps
The Lightning Network can also be used to power dApps that use Bitcoin.
This is because the LN allows for off-chain transactions. This means that developers don't have to worry about Bitcoin's scalability issues when building their applications.
Lightning.video is one such dApp that uses the Bitcoin Lightning Network to power its video streaming service.
Concerns surrounding the Lightning Network
The Lightning Network is still in its early stages, and there are some concerns around issues like security and regulations.
1. Closed channel fraud
One of the risks associated with the Lightning Network is closed channel fraud.
This happens if one party tries to cheat by publishing an old version of the channel's transaction history, thus allowing them to spend the same bitcoins multiple times.
While this is not possible on the main Bitcoin blockchain, it is a risk with the LN, especially if one of the parties in the payment channel is inactive for an extended period.
2. Regulatory issues
Regulators worldwide are still trying to figure out how to deal with cryptocurrencies.
This is especially true when it comes to Bitcoin because it's decentralized and not under the control of any government or financial institution.
The Lightning Network could add another layer of complexity for regulators. This is because LN transactions are not recorded on the main blockchain.
3. Expensive “watchtowers”
Watchtowers are an essential part of the Lightning Network, especially for businesses.
A watchtower is a third-party node in the Lightning Network (a.k.a. lightning node) that is responsible for monitoring the channel and detecting any fraudulent activity.
Enterprises are able to choose which watchtowers to use, and these watchtowers could charge a high fee.
4. Network centralization
A Lightning Hub is a Bitcoin node that operates as a Lightning Network payment hub. They are responsible for routing payments through the network and maintaining channels with other nodes.
The problem is that a few hubs have become very popular and control a large portion of the network.
The cost of opening and closing payment channels is also high. Therefore, most payment channels are custodial intermediaries similar to banks.
This could lead to centralization and a single point of failure.
5. Lower liquidity
Users need to deposit BTC into a multi-sig wallet in order to create a payment channel.
This could lead to a situation where there is less BTC in circulation because it's locked up in these multi-sig wallets. Since these Bitcoins are locked up, they are not easy to sell.
6. Network shrinkage
The Lightning Network could be negatively affected by a sharp drop in the price of Bitcoin.
This is because when the price of BTC falls, the value of the BTC in the channels also falls.
This could lead to a situation in which users close their channels in order to cash out their BTC while it's still worth something.
If this happens on a large scale, it could lead to a significant shrinkage of the Lightning Network.
7. Large transactions may not be possible
If users want to send BTC across multiple payment channels, every channel should have a BTC balance larger than or equal to the amount sent.
For example, if you're trying to send 5 BTC, every channel in the path should have at least 5 BTC.
This could be a problem because it may not always be possible to find a path with enough capacity.
How to get started with the Lightning Network
Getting started with the Lightning Network as a beginner is fairly simple. First, you need to buy some Bitcoin.
An easy way to do this is with MoonPay. You can use your credit or debit card to buy Bitcoin instantly.
Once you have your Bitcoin, you need to find a Lightning Network wallet that supports your device. There are many different custodial and non-custodial wallets to choose from.
Lightning-supported custodial wallets:
Lightning-supported non-custodial wallets:
Next, fund your LN wallet with BTC.
Once you have BTC in your wallet, you can open a payment channel. To do this, you need to find another Lightning Network user with whom you want to transact.
To connect your wallets, you and the other user need to know each other’s public key. After that, you can open a channel.
The amount of BTC you can send through the channel is limited by the amount you have deposited.
For example, if you open a channel with 1 BTC, you can only send 1 BTC through the channel.
Alternatively, you can download a wallet like Breez that runs a micro-node on your behalf and saves you the hassle of locking up your BTC, running an entire node, and creating payment channels from scratch.
Bitcoin Lightning Network Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Who uses the Lightning Network?
According to Arcane Research, over 80 million people across the world use the Lightning Network.
Thanks to the LN, even some of the largest brands have started using Bitcoin.
Some brands that have used the Bitcoin LN are:
- McDonald's
- KFC
- Subway
- Substack
- Starbucks
Several exchanges have begun to support the LN. Here are a few of them:
- OKX
- Kraken
- Zebpay
2. How fast is the Lightning Network?
The Lightning Network can handle a maximum throughput of 1,000,000 transactions per second.
3. Is the Lightning Network secure?
The LN is based on smart contracts and multi-signature technology, and the use of HTLC helps mitigate malicious activity.
Further, the support for Schnorr Signatures (a type of signature that allows for more complex smart contracts to be executed on-chain), which were introduced by the Bitcoin Taproot Upgrade, gave the LN a much-needed privacy and security boost.
That said, there are still some security concerns, which the community is actively working to address.
You should do your own research to determine if the Lightning Network is secure enough for how you want to use it.
Buy Bitcoin via MoonPay
Start your Bitcoin journey and buy Bitcoin (BTC) via MoonPay or through any of our partner wallet applications with a credit card, bank transfer, Apple Pay, Google Pay, and many other payment methods. Just enter the amount of BTC you wish to purchase and follow the steps to complete your order.
You can also top up in euros, pounds, or dollars and use your MoonPay Balance to purchase cryptocurrencies like BTC. Once funded, use your balance for faster, cheaper transactions and higher approval rates. When you're ready to withdraw, enjoy zero-fee transfers straight to your bank account.
Sell Bitcoin via MoonPay
MoonPay makes it easy to sell Bitcoin when you decide it's time to cash out your crypto.
Simply enter the amount of BTC you'd like to sell and enter the details where you want to receive your funds.
Swap Bitcoin for more tokens
Want to exchange Bitcoin for other cryptocurrencies like Ethereum and Wrapped Bitcoin? MoonPay allows you to swap crypto cross-chain with competitive rates, directly from your non-custodial wallet.

.png?w=3840&q=90)


.png?w=3840&q=90)
