While there are many types of wallets you can use to store your crypto, they can broadly be categorized as custodial wallets and non-custodial wallets.
Custodial wallets hold private keys on your behalf and require trust in a third party custodian to hold your cryptocurrencies. While this lowers your personal responsibility, it also means you do not have complete control over your private keys and therefore your crypto assets.
Non-custodial wallets, on the other hand, offer you complete control over your private keys and therefore your crypto assets.
This article explores how non-custodial (self-custody) wallets work and the different ways in which you can use them.
What is a non-custodial wallets?
Non-custodial wallets are cryptocurrency wallets that enable you to hold and transfer digital assets without the need for a centralized intermediary. Also called self-custody wallets, they are used to store and send crypto assets and can interact with decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols and decentralized applications (dApps).
These wallets use a private key and public key pair to access assets and allow users to execute transactions.
A private key is like your internet banking ID and password that proves that you own a wallet and the digital assets associated with it. A public key, on the other hand, is generated using the private key and is like an account number that you share with others to receive cryptocurrencies from other wallet holders.
Another concept closely related to the private key is the seed phrase or mnemonic phrase: a series of 12, 18, or 24 words that your wallet generates when it’s first set up.
Unlike a private key that allows you to access only one wallet address, the mnemonic phrase gives you access to the crypto assets stored in all the accounts within a crypto wallet.
Having the seed phrase allows you to recover access to your digital assets even if you lose your hardware or software wallet.
So, it goes without saying that you should keep your seed phrase safe, as anyone who knows your seed phrase can access your wallet and steal your funds.
What is self-custody?
Self-custody refers to having total control of your private keys and, consequently, the crypto assets accessible by them. When you have self-custody over your assets, no centralized third-party or financial institution has control over or can confiscate your crypto assets.
Another advantage of self-custody is not having to wait for withdrawal approvals, resulting in faster transaction times.
What are the different types of self-custody wallets?
Self-custody wallets are classified into different types depending on the device on which they store your private keys.
Mobile wallets
Mobile wallets, as the name suggests, are self-custody crypto wallet applications that enable you to send and receive crypto assets using a smartphone. You can find some popular mobile wallets like MetaMask, Trust Wallet, and Exodus in your app store.
These wallets store private keys on your mobile device - if there is a desktop version of a mobile wallet, then it will be stored on your laptop or desktop computer. In case you lose the mobile device with your private key, you can use your mnemonic phrase to recover your assets.
Hardware wallets
A web-based or mobile wallet, also called a “hot” wallet, is always connected to the internet. This unfortunately gives hackers the opportunity to steal your funds.
This is where hardware wallets, or “cold” wallets, come in. Hardware wallets like Ledger are hardware devices that keep your private keys offline at all times. Since they connect directly to the internet, they’re used with another device like a PC to make a transaction and display your balance.
Here’s what the typical transaction process on a hardware wallet looks like:
- A user unlocks and connects (using USB or Bluetooth) their hardware wallet to an internet-connected device
- The user then connects their wallet to a decentralized application and conducts a transaction that is sent to the hardware wallet
- The user verifies the information shown in the transaction request
- The PC receives the confirmation and broadcasts the information to the blockchain
Desktop wallets
Desktop wallets are programs that allow you to manage and store your private keys on a computer hard drive.
They work the same way as mobile wallets: the device stores your private keys, which you can use to sign transactions.
The process of recovering assets is also similar. You simply need to enter the seed phrase correctly on a new device and the desktop wallet will retrieve your assets for you.
Note: Some mobile wallet applications may also be available for desktop. Examples of this include MetaMask, Trust Wallet, Exodus and Phantom.
Paper wallets
A paper wallet consists of a piece of paper on which you print your public and private keys. The public keys are often displayed as QR codes along with their respective alphanumeric string, and you can receive transactions by sharing the QR code or the string.
Some paper wallets also provide users the option to generate wallet addresses in an offline ecosystem, ensuring that the key pairs are never exposed to any online activity.
People may opt to use paper wallets as an alternative to hardware wallets. The main drawback is that paper can be easily damaged.
Smart contract wallets
Non-custodial wallets, whether they’re mobile, web-based, or “cold” wallets (wallets that store private keys offline), have a serious limitation: whoever has access to your private keys also has access to your assets.
A smart contract wallet overcomes this by assigning “guardians” (trusted third parties) that can sign a special transaction to change the registered signature key in the contract to a new one if you lose your key. That way, when you lose your keys or suspect someone else has access to them, you can change the keys to prevent anyone from stealing your funds.
You can also set transfer limits to prevent hackers from emptying your wallet if it is compromised.
In other words, you can use a smart contract wallet like a regular non-custodial wallet and sign transactions with a single key. But unlike regular wallets, you don’t need a seed phrase to recover your wallet. You can simply ask your guardians to recover your wallet for you.
What can you do with a non-custodial wallet?
A non-custodial crypto wallet allows you to interact with decentralized applications (dApps) while you retain complete control over your funds. Here are a few ways you can use a non-custodial wallet.
Store funds
With a non-custodial wallet, you don't have to trust an external website to handle your funds. You can simply back up your seed phrase and private keys and recover your data and assets on your own. If you're using a multi-chain crypto wallet, you can even manage tokens across multiple blockchains from one wallet.
Buy and sell crypto
Some non-custodial wallets allow you to purchase or sell crypto directly using a debit/credit card or bank transfer. On and off-ramp services like MoonPay make this possible with integration directly in your wallet.
Swap tokens
Non-custodial wallets allow you to swap tokens easily. Most wallets also act as aggregators and provide prices from multiple crypto exchanges so you can exchange crypto at the most efficient exchange price and gas fee.
View our Bitcoin Price and Ethereum Price pages for live price and market data for these leading cryptocurrencies.
Send and receive crypto
With non-custodial wallets, you can easily send or receive crypto from anywhere in the world and transfer your crypto assets across different wallets by importing and exporting your wallet keys.
Pay with crypto
Many non-custodial wallets offer multiple ways to pay with crypto. Apart from enabling you to send crypto directly to another user’s wallet, some wallets also allow you to buy gift cards with crypto, use a crypto debit or credit card, and even shop with merchants that accept crypto payments.
Are self-custody wallets secure?
All cryptocurrency wallets, including non-custodial wallets, present some amount of risk.
Here are a few best practices you can follow to keep your non-custodial wallet and its contents safer from hackers and scammers:
- Use a strong password and lock your wallet when not in use. Most self-custody wallets have an auto-lock timer that will automatically lock the wallet after 24 hours. For additional security, you can modify the timer to a custom duration.
- Don’t share your private key or seed phrase with anyone. Doing so will give others complete access and control over your wallet and funds.
- Periodically review the dApps that can view your wallet's contents. Also, disconnect the ones you don’t use anymore.
- Use your wallet through a secure internet connection. Refrain from connecting to public WiFi networks as they’re more susceptible to cyber eavesdropping. Also called a “man-in-the-middle” attack, this is when an unauthorized entity inserts itself between you and the application you want to connect to so it can view or modify your data.
- Be cautious when clicking links. They may lead to fake websites that gather details like your private keys, which can result in you losing your funds.
- Add two factor authentication (2FA) to your wallet account's security settings. This will make it more difficult for a hacker to immediately access your account.
Can a non-custodial wallet provider access my funds?
No, non-custodial wallet providers can’t access your crypto assets. Only you (or someone who has your mnemonic phrase) have access.
Also, as long as you have backup and recovery mechanisms in place, you should be able to access your funds even if the wallet service provider stops supporting the wallet or goes out of business.
How do I self-custody my crypto?
There are different types of self-custody wallets to choose from.
For the purpose of this article, we will show you how to self-custody your crypto using one of the most popular self-custody hot wallets.
Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to set up a MetaMask wallet:
1) Go to the official MetaMask website to download the wallet’s browser extension.
2) Choose Chrome and select Install. (You can also download the app for your Android or iOS device and follow the same process from Step 4).

3) On the Chrome extension page, select Add to Chrome to add the MetaMask extension to your browser.
4) Once the extension (or app) is installed, open it, and select Get Started.

5) Read and agree to the terms and go to the next step.
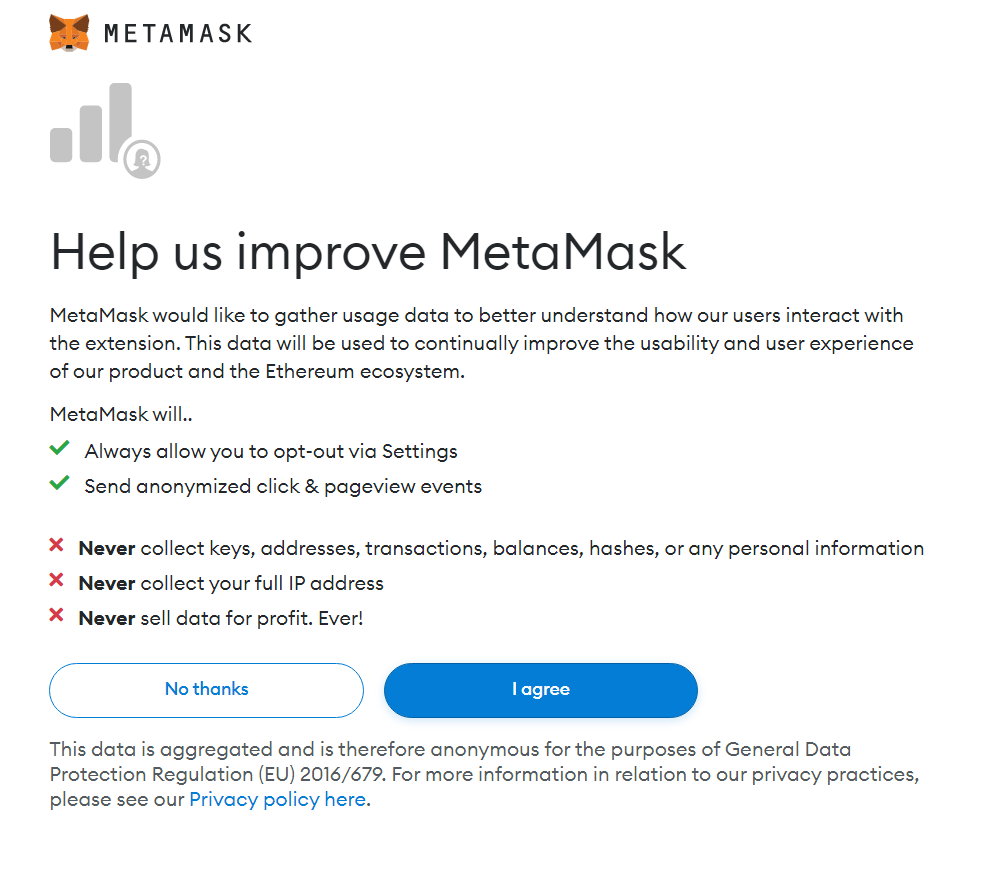
6) Select Create a Wallet.
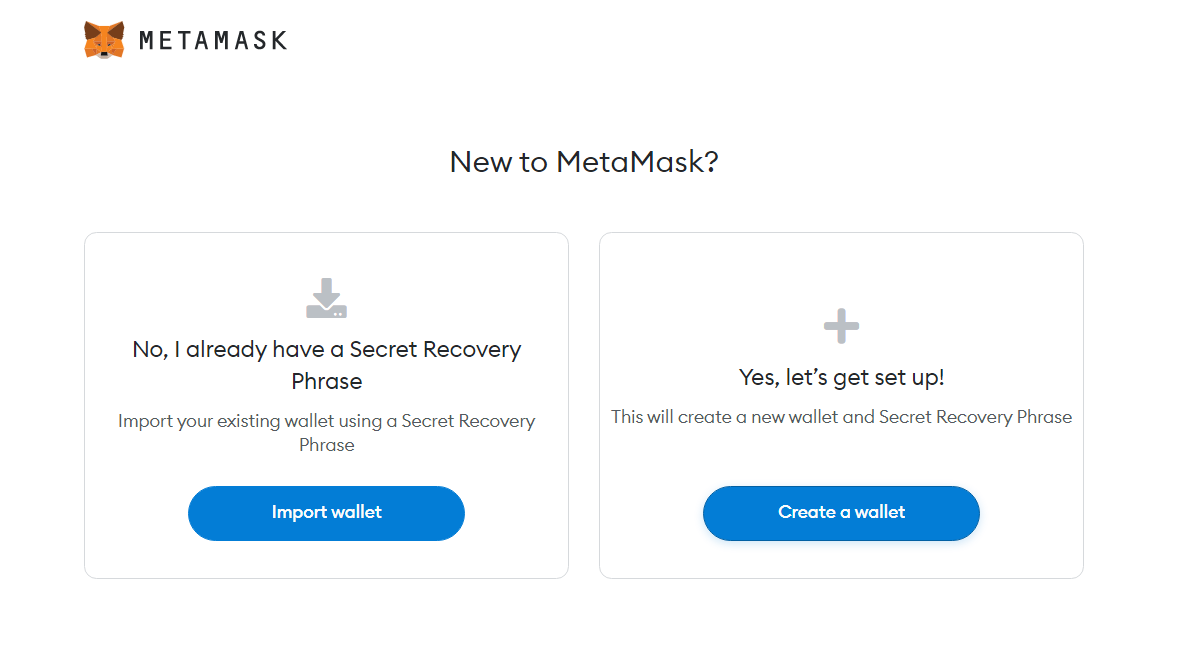
7) Create your password.
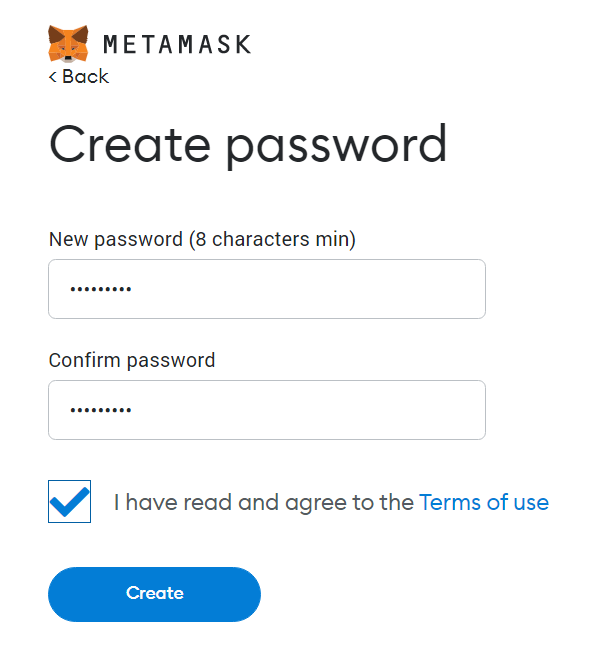
8) Securely store your secret recovery phrase (seed phrase).
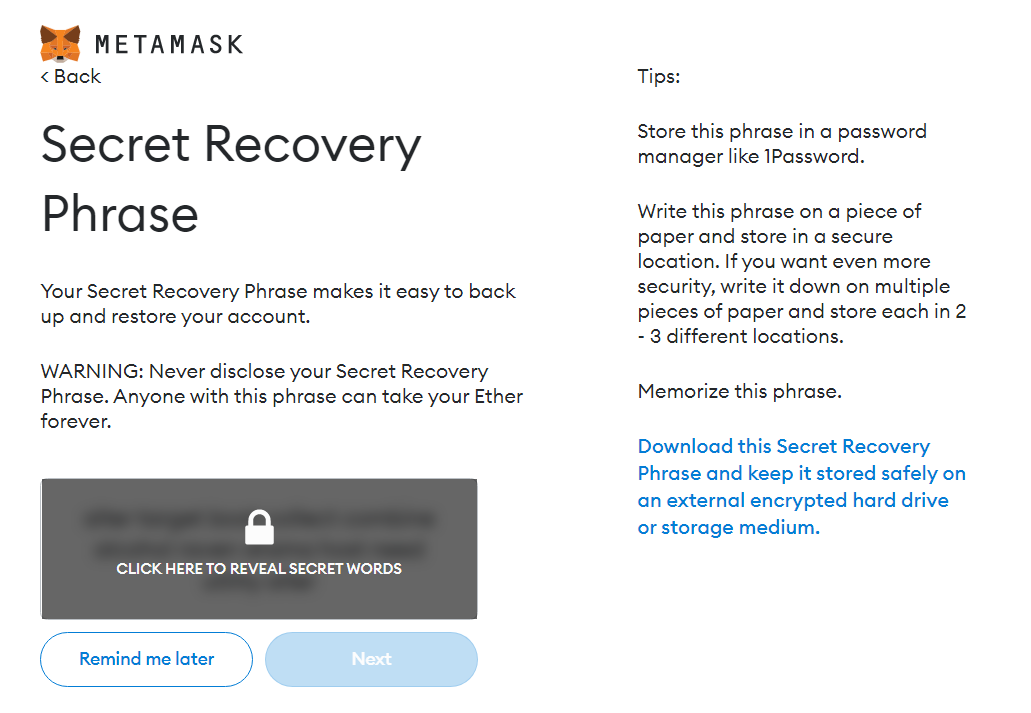
9) Select each word of the recovery phrase in the same order as it was shown in the previous window and select Confirm.
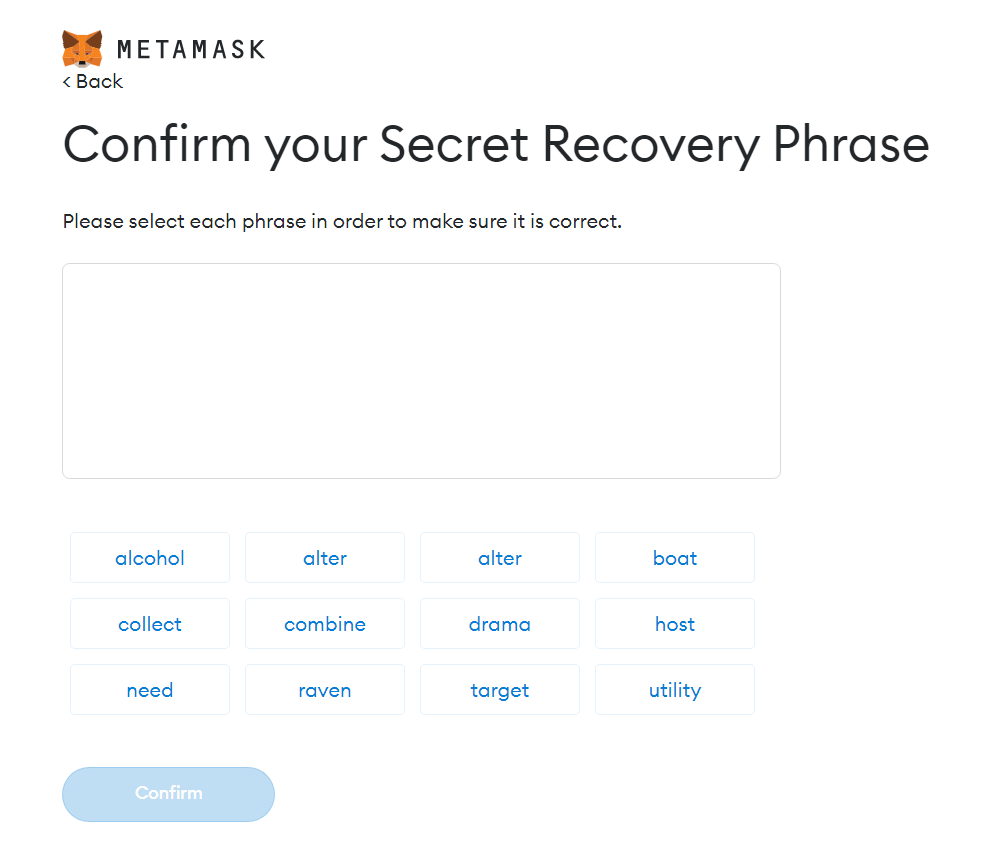
10) Select All Done on the next screen to finish setting up your wallet.
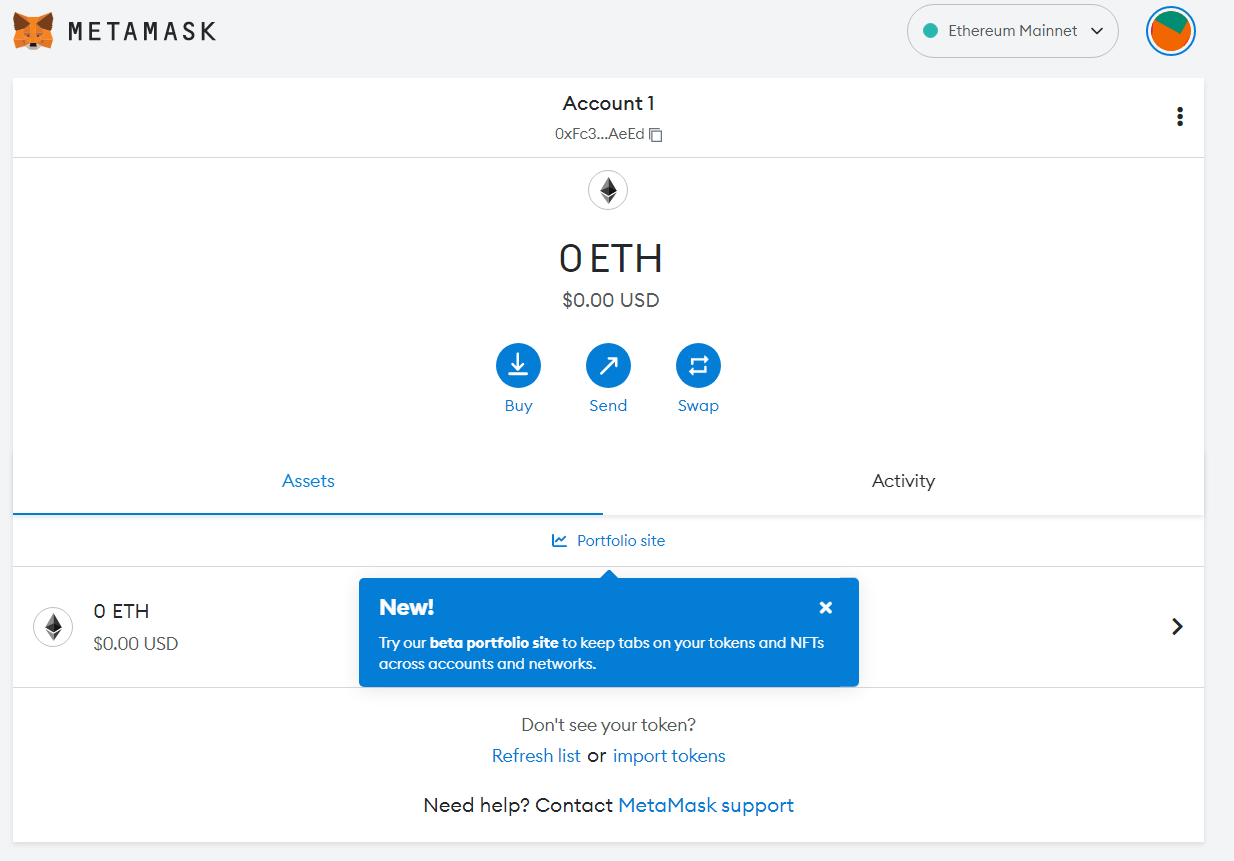
11) Log into your existing crypto wallet and initiate an asset transfer to your new non-custodial wallet address. The steps you take here may vary depending on your custodial service.
Here are some step-by-step guides for how to send crypto from:
Closing thoughts on non-custodial wallets
Self-custody wallets ensure that no centralized intermediary or third party can control, confiscate, or take any actions with your crypto assets.
But in exchange for this freedom, you are given complete responsibility for keeping your assets safe. It’s therefore crucial that you follow best practices to ensure the maximum security of your funds.
Start your crypto journey with MoonPay
Now you know the basics of non-custodial wallets, it’s time to explore them for yourself. Non-custodial wallet providers like MetaMask have partnered with MoonPay to make it easy to self-custody your crypto.
To get started, simply buy cryptocurrency via MoonPay using your credit card or any other preferred payment method. MoonPay's widget offers a fast and easy way to buy Bitcoin, Ethereum, and more than 50 other cryptocurrencies.
MoonPay also makes it easy to sell crypto when you decide it's time to cash out. Simply enter the amount of the token you'd like to sell and enter the details where you want to receive your funds.
You can also begin your crypto journey by funding your wallet with euros, pounds, or dollars and use your MoonPay Balance to purchase crypto like Bitcoin (BTC) and Ethereum (ETH). With MoonPay Balance, you'll enjoy faster transactions, lower fees, and higher approval rates. Plus, when it's time to cash out, take advantage of zero-fee withdrawals straight to your bank account.


.png?w=3840&q=90)

.png?w=3840&q=90)

