Peut-être la manière la plus basique de s'engager dans Web3 est de acheter ou échanger des jetons de crypto.
Pour ce faire, un utilisateur doit se rendre sur une bourse de crypto, qui se présente sous l'une des deux formes : un échange centralisé (CEX) ou un échange décentralisé (DEX).
Bien que les CEX et les DEX permettent tous deux aux utilisateurs d'échanger des cryptomonnaies, ils diffèrent largement dans leur fonctionnement. Toute personne souhaitant échanger des cryptos doit connaître ces différences.
Dans cet article, nous passons en revue les principales différences entre les CEX et les DEX afin que vous puissiez prendre une décision éclairée sur l'endroit où effectuer votre prochain échange de cryptos.
Qu'est-ce qu'un échange centralisé (CEX) ?
Les échanges centralisés (CEX) sont des échanges de cryptocurrency qui surveillent et facilitent le trading d'actifs crypto entre utilisateurs avec l'aide d'un intermédiaire centralisé. Comme les échanges boursiers électroniques traditionnels, les CEX utilisent un carnet de commandes système pour afficher et apparier les ordres d'achat et de vente des utilisateurs.

Les CEX agissent également souvent comme ramps d'accès et de sortie pour la crypto car beaucoup permettent aux utilisateurs d'approvisionner leurs comptes en monnaie fiduciaire ou de liquider leurs actifs crypto en monnaie fiduciaire.
Comment fonctionnent les CEX ?
Pour commencer à trader sur des échanges centralisés, vous devrez peut-être d'abord obtenir une vérification KYC, ce qui nécessite de télécharger des informations telles qu'une photo de votre pièce d'identité gouvernementale, une preuve de domicile et une signature.
Vous pouvez ensuite déposer votre argent fiat ou votre cryptomonnaie pour commencer à acheter ou à échanger des actifs cryptographiques listés sur la bourse.
Lorsque vous passez un ordre d'achat sur un CEX pour acheter un jeton crypto, le moteur de correspondance des ordres du CEX recherche un ordre de vente placé au même prix que votre prix d'achat. Une fois qu'il y a correspondance, le CEX exécute votre transaction et crédite votre compte avec le jeton souhaité.
Des exemples de CEX notables incluent Binance, Kraken, Coinbase, et Gemini.
Qu'est-ce qu'un échange décentralisé (DEX) ?
Les échanges décentralisés sont des plateformes d'échange de crypto-monnaies où les utilisateurs peuvent échanger un jeton crypto contre un autre de manière décentralisée et non-dépositaire façon sans intermédiaires centralisés. Les DEX sont également sans autorisation, ce qui signifie que n'importe qui peut utiliser un DEX sans révéler ses informations privées.

Tout ce dont vous avez besoin pour vous connecter à un DEX est un portefeuille crypto non-dépositaire.
Comment fonctionnent les DEX ?
Au lieu de s'appuyer sur une entreprise centrale pour fonctionner, les échanges décentralisés utilisent des auto-exécutants, autonomes contrats intelligents pour traiter échange de jetons demandes.
Initialement, les DEX utilisaient des carnets d'ordres on-chain, mais cela nécessitait que chaque nœud d'une blockchain enregistre une commande de vente avant que celle-ci puisse être complétée. Comme on peut le deviner, cela rendait le processus insupportablement lent.
La solution : market maker automatisé (AMM) échanges décentralisés. Ils utilisent des pools préfinancés d'actifs cryptographiques appelés pools de liquidités qui détiennent généralement des paires de jetons dans un ratio de 50/50.
Aujourd'hui, les DEX les plus populaires comme Uniswap, Pancakeswap, Curve, et beaucoup d'autres sont tous des protocoles AMM.
En l'absence d'un carnet de commandes pour évaluer l'offre et la demande afin de mettre à jour les prix des actifs, les AMM utilisent une formule mathématique.
La formule la plus couramment utilisée est x*y = k, où x et y sont les soldes des jetons et k est une constante. Cela signifie que le solde constant des actifs détermine le prix des jetons dans le pool de liquidités.
Pour en savoir plus sur le fonctionnement des DEX, lisez notre article Qu'est-ce qu'un échange décentralisé (DEX) ?
Avantages et inconvénients des échanges centralisés
Avantages des CEX
Haute liquidité
En raison de leur ressemblance de l'interface utilisateur avec les plateformes Web2 et de leur intégration avec la finance traditionnelle, une vaste majorité d'utilisateurs de crypto préfèrent trader sur les CEXs plutôt que les DEXs. Cela apporte un volume de trade plus important et une liquidité plus élevée aux CEXs.
Transactions simples fiat-à-crypto
Les CEXs agissent comme des rampes d'accès et sorties, ce qui signifie que les utilisateurs peuvent facilement convertir des fiat en crypto et vice versa.
Transactions rapides
Les CEX peuvent traiter les transactions plus rapidement que leurs homologues décentralisés car ils utilisent des systèmes de correspondance hors chaîne conçus pour gérer un grand volume de transactions.
Plus convivial
L'interface utilisateur d'un CEX est similaire à celle des plateformes de trading boursier traditionnelles, donc elles peuvent être plus faciles à naviguer. De plus, l'échange gère la transaction au nom de l'utilisateur, ce qui rend généralement le processus moins compliqué, surtout pour les débutants.
Plus de fonctionnalités de trading
Avec les échanges centralisés, les utilisateurs peuvent également obtenir plus d'options pour le trading et l'investissement, comme le trading au comptant, les options, les futurs, les effets de levier, etc.
Inconvénients des CEX
Pas de confidentialité
Les utilisateurs doivent terminer un processus de vérification d'identité obligatoire tel que KYC pour utiliser un CEX. Cela oblige les utilisateurs à partager des informations privées, ce que certains peuvent considérer comme une barrière à l'entrée.
Manque de contrôle
Dans le cas des CEX, vous ne possédez pas vos clés privées– la plateforme le fait. Les CEX peuvent suspendre les activités de trading et vous empêcher d'accéder à vos fonds.
Perte due aux piratages
Les CEX maintiennent portefeuilles contrôlés par une organisation centralisée pour stocker les fonds des utilisateurs. En cas de piratage de portefeuille, vous pouvez perdre vos fonds malgré avoir activé toutes les mesures de sécurité.
Avantages et inconvénients des échanges décentralisés
Avantages des DEX
Garde personnelle
Avec les DEX, vos fonds restent toujours dans votre portefeuille non-custodial. Les DEX ne peuvent pas geler vos fonds ni suspendre les transactions.
Risque de sécurité réduit
Une attaque sur un DEX n'expose pas les fonds des utilisateurs. Cela signifie que le risque global en cas d'attaque est plus faible lors de l'utilisation d'un DEX.
Aucune restriction de compte
Étant donné que les DEX ne nécessitent pas que les utilisateurs complètent un processus KYC, tout le monde peut commencer échanger des crypto-monnaies en quelques secondes.
Accès à des jetons rares
Comme les DEXs sont sans permission, les nouveaux projets peuvent facilement inscrire leurs jetons et créer des pools de liquidité. Cela offre aux utilisateurs la possibilité d'investir tôt dans des projets avant qu'ils ne soient listés sur une CEX.
Inconvénients des DEXs
Options de trading limitées
Les DEXs sont principalement limités à effectuer des opérations de base échanges de jetons car ils n'ont pas le mécanisme nécessaire pour analyser les actifs et mettre en œuvre différents indicateurs, ce qui peut être important dans certains échanges de crypto-monnaies.
Vitesse de transaction plus lente
Étant donné qu'un DEX effectue des transactions sur la chaîne, les mineurs doivent valider ces transactions avant de les ajouter au bloc. Cela les rend plus lentes que les CEX comme Binance, dont le moteur de correspondance est capable de supporter plus de 1 400 000 commandes par seconde.
Volumes de trading et liquidité plus faibles
Bien que les DEX gagnent en popularité, on ne peut nier que les CEX les dominent encore en termes de volume de trading.
Selon les données de Dune et The Block, les CEX ont constamment géré la majorité du volume de trading au comptant. Le plus grand pourcentage du volume de trading au comptant effectué via DEXs a atteint un peu plus de 21 % en mai 2023, la plupart du volume oscillant entre 5 % et 15 % par rapport aux CEX.
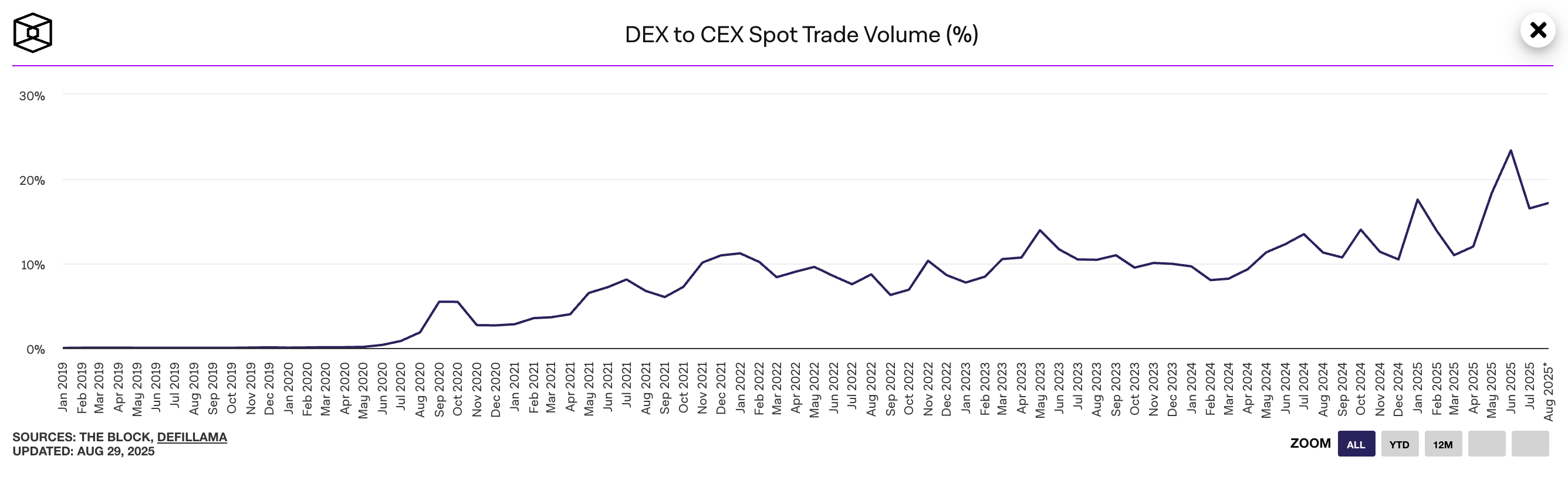
Par exemple, en 2021, les CEX ont vu plus de $14 trillions de volume d'échanges tandis que les DEXs n'ont atteint que $84,98 milliards au cours de la même période.
Moins convivial
L'interface utilisateur des DEXs peut être difficile à comprendre et à naviguer pour les débutants car elle ne ressemble pas à celle des plateformes de trading d'actions traditionnelles.
Les DEXs exigent également des utilisateurs de connecter des portefeuilles non-custodial pour exécuter des transactions et transférer des fonds, ce qui peut sembler être un processus complexe.
Commencez votre voyage crypto avec MoonPay
Maintenant que vous connaissez la différence entre les CEX et les DEX, il est temps de les tester par vous-même.
Pour commencer, il suffit de acheter de la cryptomonnaie via MoonPay en utilisant votre carte de crédit ou tout autre moyen de paiement préféré.
MoonPay facilite également la vente de crypto quand vous décidez qu'il est temps d'encaisser. Entrez simplement le montant du jeton que vous souhaitez vendre et saisissez les détails où vous souhaitez recevoir vos fonds.



.png?w=3840&q=90)

.png?w=3840&q=90)
