The cryptocurrency market is vast and complex, filled with meme coins, stablecoins, utility tokens, and many more token types. While most people are familiar with Bitcoin, the original cryptocurrency, Solana is another token that has emerged as a significant player in the Web3 domain.
Solana, a high-performance blockchain designed for decentralized applications (dApps), uses a unique Proof of History (PoH) consensus mechanism. With extremely fast processing times and low transaction fees, Solana has gained attention for its scalability and has become a popular platform for decentralized finance (DeFi) and non-fungible tokens (NFTs).
Bitcoin, the first and most well-known cryptocurrency, was created by the pseudonymous Satoshi Nakamoto in 2009. It operates on a Proof of Work (PoW) consensus mechanism, offering greater decentralization compared to traditional fiat currency.
In this article, we'll explore the key differences between Bitcoin (BTC) and Solana (SOL), examining their histories, technologies, use cases, and other crucial aspects.
History of Bitcoin vs Solana
Bitcoin is regarded as the pioneer cryptocurrency, leading the way and dominating all other tokens in terms of price and market cap. Solana, on the other hand, is a newer entrant focusing on more scalability and speed, catering to applications requiring fast and cost-effective transactions.
Origins and evolution of Solana
Solana has experienced rapid growth since its inception in 2017. Here's a look at some important milestones in its history that have shaped its development and popularity.
(2017) Solana founded by Anatoly Yakovenko and a team of ex-Qualcomm employees.

(2020) Mainnet beta launch.
(2021) Solana DeFi ecosystem expansion.
(2021) NFT projects and marketplaces launch on Solana.
(2021) Solana's native token SOL reaches all-time high ($260)
(2021) Solana undergoes a major VC funding round.
(2021) The first Breakpoint conference is held, highlighting Solana's growth.

(2022) Solana integrates with major cryptocurrency exchanges.
(2023) Solana continues to grow its ecosystem, focusing on user adoption.
Origins and evolution of Bitcoin
Bitcoin has had a rich and eventful history since its creation as the first peer-to-peer decentralized currency in 2009. Here are some significant milestones in Bitcoin's journey:
(2009) Bitcoin's Genesis Block mined.
(2010) First Bitcoin transaction (Laszlo Hanyecz's pizza purchase).
(2011) Bitcoin price reaches $1.
(2012) Bitcoin's first halving event.
(2013) Bitcoin price reaches $100.
(2014) Major companies start accepting Bitcoin as a form of payment.
(2016) Bitcoin's second halving event.
(2020) Bitcoin's third halving event.
(2021) Canada approves first Spot Bitcoin ETF.
(2024) First Spot Bitcoin ETFs approved in United States.

(2024) Bitcoin's fourth halving event.
Core technology and architecture: PoW vs PoH
Blockchain technology uses consensus mechanisms to validate transactions, maintain the integrity of the ledger, and secure the network from malicious actors. Among mechanism options, Solana and Bitcoin use two distinct approaches, each with its own benefits and trade-offs:
Bitcoin: Proof-of-Work consensus
Bitcoin operates on a Proof-of-Work (PoW) consensus mechanism. In PoW, miners use computational power to solve complex mathematical puzzles to validate transactions and add them to the blockchain. When a miner successfully solves a puzzle, that block is added to the chain and they receive their block reward in the form of BTC.
Although PoW is secure, its high energy usage and slower transaction times have sparked debates about the environmental impact and scalability of Bitcoin. Despite these concerns, Bitcoin's PoW mechanism remains a robust security feature, making it difficult for any single entity to gain control over the network.
Solana: Proof-of-History consensus
Solana's high-performance blockchain introduces a unique consensus mechanism known as Proof-of-History (PoH). PoH is designed to increase transaction throughput by providing a method to timestamp transactions before they are included in the blockchain. This timestamping process creates a verifiable order of events, allowing transactions to be processed quickly and efficiently.
In addition to PoH, Solana also uses a Proof-of-Stake (PoS) consensus mechanism to secure the network. In PoS, validators are chosen to create new blocks based on the number of tokens they hold and are willing to "stake" or lock up as collateral. This combination of PoH and PoS gives Solana the capacity to handle significantly more transactions per second than Bitcoin, with low latency.
Bitcoin and Solana monetary policy
Monetary policy of Bitcoin
Bitcoin's monetary policy is characterized by a fixed supply limit that ensures there will never be more than 21 million bitcoins in circulation. The primary way new bitcoins enter the ecosystem is through increasingly difficult mining rewards, given to miners who successfully validate blocks through the Proof-of-Work (PoW) process.
To control the rate of inflation, Bitcoin undergoes a "halving" event approximately every four years, where the block reward given to miners is cut in half. This periodic reduction in mining rewards has a significant impact on Bitcoin's issuance rate and creates a predictable decrease in new supply over time.
These halvings, the latest of which just occurred in April 2024, are designed to mimic the effects of a deflationary currency. They ensure that the Bitcoin supply diminishes as demand potentially grows, contributing to Bitcoin's reputation as "digital gold."
Monetary policy of Solana
Solana, in contrast, employs a dynamic monetary policy designed to support a high-throughput blockchain network. Unlike Bitcoin, the Solana network does not have a fixed supply cap. Instead, it starts with an initial inflation rate that decreases over time. This approach allows for a more flexible and adaptable issuance strategy, supporting network growth and incentivizing participation.
New SOL tokens are created and distributed primarily through staking rewards. Validators who participate in Solana's Proof-of-Stake (PoS) consensus mechanism receive rewards proportional to their staked tokens. This structure encourages network security and decentralization, as validators are rewarded for actively contributing to the network's stability.
Use cases of Bitcoin vs Solana
Although these lists are not exhaustive, here are some primary use cases of both Bitcoin and Solana:
Bitcoin use cases
- Digital gold / HODLing: Some users simply prefer to "HODL" Bitcoin long term, while practicing dollar-cost averaging strategies to purchase small amounts at regular intervals.
- Peer-to-peer transactions: Bitcoin enables peer-to-peer transactions without the need for intermediaries like banks or payment processors.
- Purchase goods and services: Bitcoin can be used to buy goods and services, with some merchants and online platforms accepting Bitcoin as a form of payment.
- Cross-border remittances: Bitcoin facilitates cheap and fast international transfers without relying on traditional banking systems or money transfer services.
Solana use cases
- Decentralized finance (DeFi): Solana hosts a growing ecosystem of DeFi projects and decentralized applications, such as decentralized exchanges (DEXs), lending platforms, and yield farming protocols.
- Gaming and metaverse: Solana's scalability makes it suitable for immersive gaming and metaverse applications that host many users at once.
- Non-fungible tokens (NFTs): Solana is a popular choice for NFT projects, artists, and marketplaces due to its fast transaction processing and low fees.
- Cross-chain bridges: Solana supports cross-chain functionality, enabling users to interact with other blockchains and their tokens.
Bitcoin vs Solana programming languages
Different blockchain platforms often employ specific programming languages that reflect their underlying philosophies and development goals.
Bitcoin programming languages
Bitcoin uses Script as its primary scripting language, while its core codebase is written in C++, a powerful and well-established programming language.
Changes to Bitcoin's network are subject to a stringent review process, involving extensive testing, community consensus, and broad agreement among developers. This conservative development philosophy helps maintain the robustness and security of Bitcoin, which is critical for a network with billions of dollars in market cap.
Solana programming languages
Solana's core development is based on Rust, a modern programming language known for its emphasis on safety, high performance, and concurrency.
Rust's design allows developers to write code that efficiently handles complex operations for dApps and smart contracts without sacrificing security. Although Solana also has support for C/C++, its use of Rust reflects its focus on achieving high throughput and low latency, key factors in its ability to process thousands of transactions per second.
Security of Bitcoin vs Solana
Security is a critical aspect of any blockchain network, affecting its reliability, resilience, and ability to withstand attacks. Let's compare the approaches to network resilience for Bitcoin and Solana.
Bitcoin security
The Bitcoin network is secured via its Proof-of-Work (PoW) consensus mechanism, supported by a high network hash rate. This hash rate reflects the vast computational power dedicated to mining, making it extremely difficult for any single entity to gain control of the network.
The decentralized nature of Bitcoin, with a large number of miners distributed globally, adds to its resilience against attacks such as double-spending and 51% attacks. Its long history without major security breaches underscores the effectiveness of its PoW mechanism and the strength of its network.
Solana security
Solana's security approach combines Proof-of-Stake (PoS) with Proof-of-History (PoH), enabling high throughput and low latency. While this architecture allows Solana to process a large volume of transactions quickly, it relies on a smaller network of validators compared to Bitcoin. This difference in network size can impact resilience, with fewer validators potentially leading to centralization risks.
Despite Solana's speed, it has faced challenges with network outages, often due to its rapid throughput and complex consensus mechanisms. These incidents highlight the trade-offs between high performance and stability in a fast-growing blockchain.
Bitcoin and Solana market performance
Market performance of BTC
Since Bitcoin's creation over 15 years ago, it has garnered widespread adoption among retail and institutional investors, becoming a household name in the financial world. Despite its high volatility, Bitcoin has shown remarkable growth, often leading the broader cryptocurrency market's trends in terms of the Bitcoin price, market cap, trading volume, and adoption.
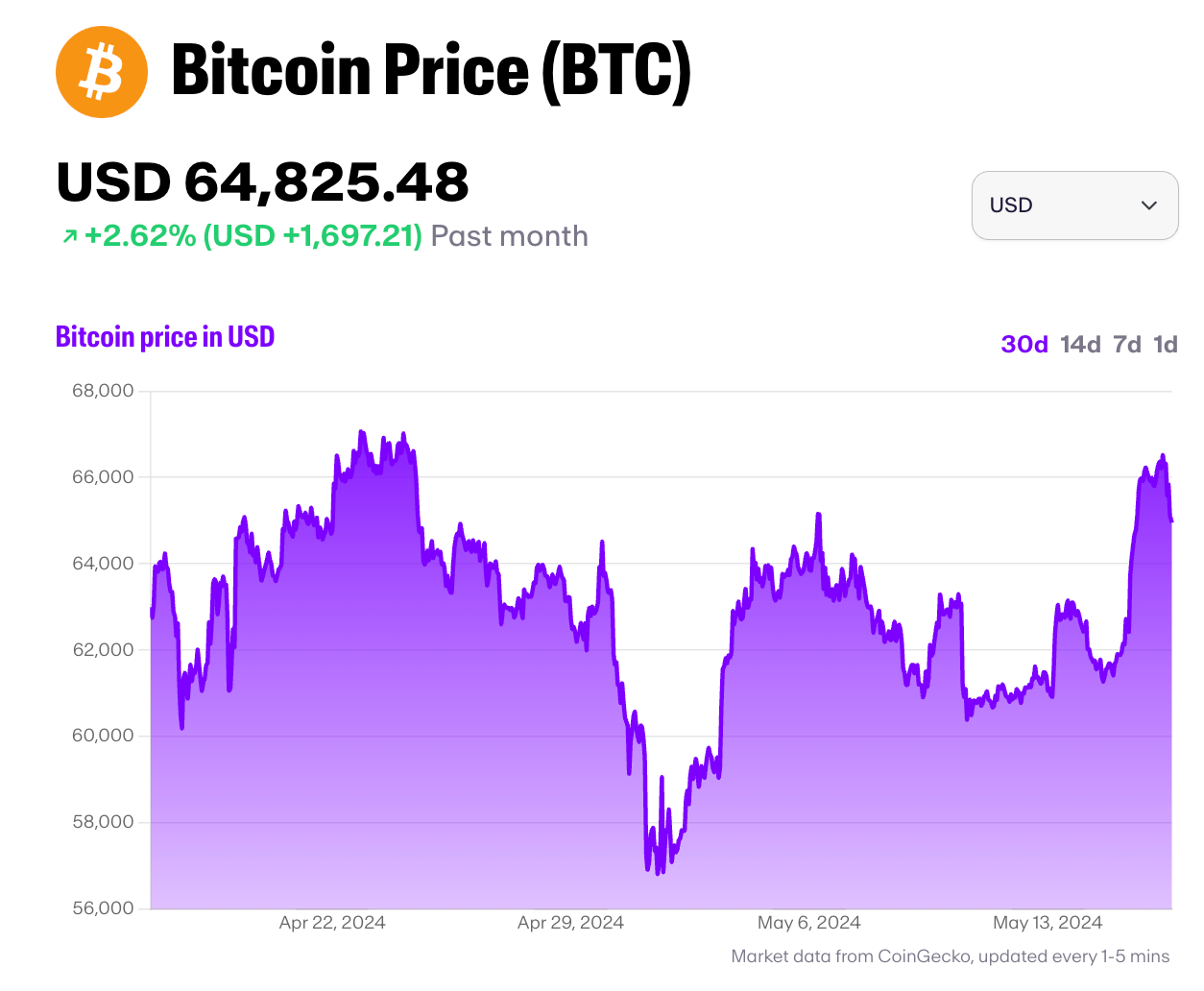
Recently, Bitcoin has seen greater institutional interest. Companies such as MicroStrategy, Tesla, and Square have publicly invested in Bitcoin, and some prominent firms have launched Bitcoin-based financial products, such as Spot ETFs and futures contracts.
Market performance of SOL
Since Solana's mainnet launch in 2020, the blockchain's high throughput and low transaction costs have made it attractive to developers and users, leading to a swift rise in popularity. Solana's focus on scalability has allowed it to compete with established blockchains like Ethereum, resulting in a surge of decentralized finance (DeFi) applications, non-fungible tokens (NFTs), and an entire ecosystem of innovative blockchain projects.
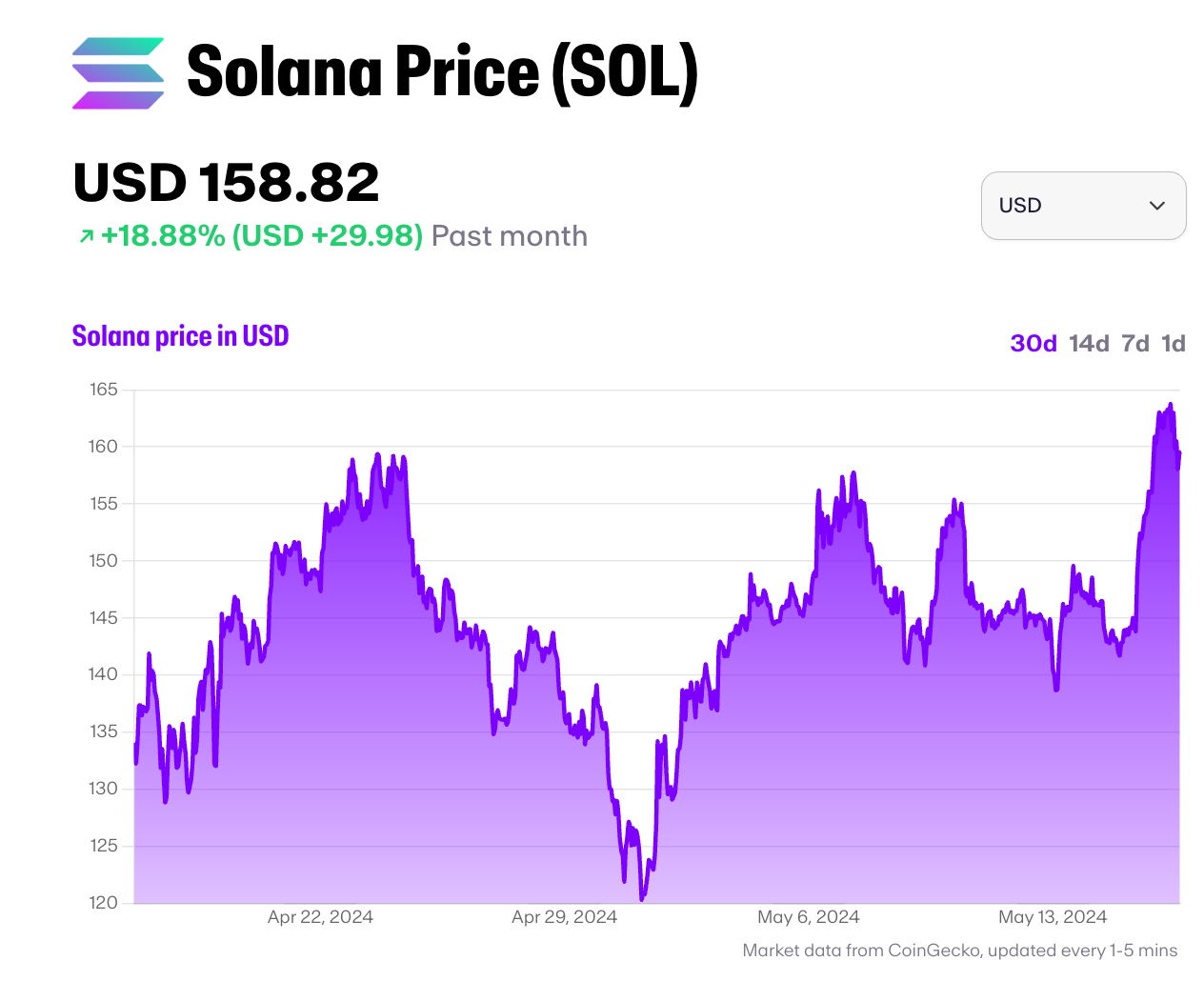
However, Solana's rapid growth has not come without challenges. The network has faced technical issues, including occasional outages and network congestion, which have impacted its reputation. These issues have contributed to Solana price volatility, causing periods of uncertainty among users and potential investors.
Community and governance of Solana and Bitcoin
The communities surrounding Bitcoin and Solana play a crucial role in shaping the direction and governance of their respective networks.
Bitcoin governance
Bitcoin's community is known for its diversity and strong emphasis on decentralization, with no central authority or leadership controlling Bitcoin's development or governance.
Instead, Bitcoin relies on a consensus-based approach where changes to the protocol require broad agreement among developers, miners, and other stakeholders. This decentralized structure contributes to Bitcoin's stability and resistance to centralized control, ensuring that no single entity can dictate the network's future.
Solana governance
Solana's community is more developer-centric, with a strong focus on innovation and building new applications. This community has contributed to Solana's rapid growth, creating a vibrant ecosystem of decentralized applications (dApps), non-fungible tokens (NFTs), and decentralized finance (DeFi) projects. Solana's approach fosters active engagement among developers and entrepreneurs, driving its expansion.
Although Solana is a popular platform for DAOs (decentralized autonomous organizations), Solana's governance model is more centralized compared to Bitcoin's. This allows for quicker decision-making and adaptability to changing market conditions and technological advancements. However, this centralization can also lead to concerns about transparency and potential central points of failure.
Regulatory considerations of Bitcoin and Solana
Regulation plays a critical role in the adoption and growth of blockchain networks, which are subject to various legal and regulatory frameworks worldwide.
Bitcoin regulatory status
The most common regulatory differences revolve around Bitcoin's classification: whether it is a currency, a commodity, or something else. This ambiguity in classification creates varying approaches to regulation, taxation, and compliance in different jurisdictions around the world.
In some countries, like El Salvador, Bitcoin is recognized as a legal tender, allowing individuals and businesses to transact with it. In others, it is treated as a commodity or a virtual currency, subject to capital gains taxes and other financial regulations.
Regulators are also concerned about Bitcoin's use in illegal activities, such as money laundering, tax evasion, and financing illicit operations. As a result, many countries implement Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Know Your Customer (KYC) requirements for businesses that deal with Bitcoin, such as cryptocurrency exchanges, payment processors, and on-ramps like MoonPay.
Solana regulations
Solana faces similar regulatory scrutiny, especially as it expands into various applications and markets. Given Solana's focus on decentralized applications (dApps), the regulatory landscape encompasses not only the core network but also the projects built on top of it, such as decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms and non-fungible token (NFT) marketplaces.
Regulators are concerned about the rapid growth and innovation of DeFi in blockchain platforms like Solana and Ethereum, where there is a high risk of fraud and hacking. This scrutiny has led to increased regulatory attention, with agencies focusing on consumer protection, financial stability, and compliance with existing laws and regulations in certain countries and regions.
Where to buy Bitcoin and Solana
Now that you've learned about the differences of Bitcoin vs Solana, you may wish to explore their ecosystems firsthand.
You can buy Bitcoin (BTC) and Solana (SOL) via MoonPay with a credit card, bank transfer, Apple Pay, Google Pay, and many other payment methods. Send your newly purchased crypto directly to your preferred Solana or Bitcoin wallet, like Ledger, Phantom, Trust Wallet, Exodus, and more. Just enter the amount of BTC or SOL you wish to purchase and follow the steps to complete your order.
Users can also top up in euros, pounds, or dollars and use MoonPay Balance for buying cryptocurrencies like BTC and SOL. Once funded, use your balance for faster, cheaper transactions and higher approval rates. When you're ready to withdraw, enjoy zero-fee transfers straight to your bank account.
How to sell BTC and SOL
MoonPay also makes it easy to sell Bitcoin and Solana when you decide it's time to cash out your crypto.
Simply enter the amount of SOL or BTC to sell in the MoonPay widget and enter the details where you want to receive your funds.



.png?w=3840&q=90)


