“Gwei” is one of those terms that pops up constantly when using the Ethereum network. Whether you're sending ETH, swapping tokens, or interacting with decentralized applications (dApps), you'll often come across Gwei in wallet confirmation screens and gas fee estimators.
While it might seem like just another intimidating bit of crypto jargon, Gwei is actually quite a simple concept. It's also key to understanding how Ethereum works, especially when it comes to gas fees.
In this guide, we’ll break down what Gwei is, how it's used to calculate gas fees, and how you can better navigate Ethereum’s occasionally costly transaction fees.
What is Gwei?
Gwei is the fundamental unit used to measure gas fees on the Ethereum blockchain. Short for gigawei, it represents the cost required to process transactions, and helps users estimate the fees they'll pay when sending ETH, interacting with Ethereum dApps, and executing smart contracts.
You can think of Gwei like cents to a dollar, but in much smaller fractions. Since Ethereum gas fees are often fractions of ETH tokens, Gwei provides a more practical unit for displaying them—similar to how Satoshis subdivide Bitcoin.
- 1 ETH = 1,000,000,000 Gwei (1 billion Gwei)
- 1 Gwei = 0.000000001 ETH (one billionth of an ETH)

For example, instead of saying a transaction fee is “0.000000025 ETH,” it’s much easier to say it costs 25 Gwei.
How Gas Fees Work on Ethereum
Gas fees are necessary to use the Ethereum network, but how they work can be confusing at first. Here are the basics to help you understand what you’re really paying for.
What is “gas” on Ethereum?
On Ethereum, gas refers to the computational power needed to perform operations, like sending ETH, executing smart contracts, or interacting with dApps. Every action on the blockchain requires gas. The more complex the action, the higher gas prices will be.
How gas prices are measured in Gwei
As we've established, gas prices on the Ethereum network are measured in Gwei per unit of gas. When you initiate a transaction, the total cost is calculated by multiplying the gas limit (the maximum amount of gas allowed for the transaction) by the gas price (the cost of each gas unit in Gwei).
The formula for calculating the total fee is:
Total Gas Fee = Gas Limit × Gas Price (in Gwei)

- The gas limit can vary depending on the type of transaction, with more complex actions requiring a higher gas limit.
- The gas price is determined by network demand and can fluctuate, especially during periods of high congestion.
Curious to see how much gas prices can vary by transaction? We'll cover that with real examples below.
Factors that influence gas fees
Several things affect how much gas (and Gwei) you’ll pay:
Network congestion
When more users are active on the network, such as during periods of high demand or popular events like NFT mints, gas prices can increase. The more transactions that are happening, the more competition there is for limited block space, leading to higher fees.
Transaction complexity
Simple actions like sending ETH are relatively inexpensive, as they require minimal computational effort and resources. However, more complex actions like minting an NFT, swapping tokens, or interacting with decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols involve more computations and data storage, increasing gas fees.

Priority fee (tip)
Ethereum allows users to include an optional “tip” or priority fee to speed up their transaction. The higher the tip, the faster your transaction is likely to be processed by miners, especially during high-traffic times.
Real-World Examples: Gwei in Action
From sending ETH to minting NFTs, there are multiple ways for Gwei to come into play in everyday Ethereum activities.
Example of a standard ETH transaction and Gwei cost
When you send ETH to someone, it’s considered a standard transaction. A typical ETH transfer on the Ethereum blockchain uses a gas limit of 21,000 units, which is the amount of computational effort required to execute the transaction.
Let’s say the current gas price is 30 Gwei. To calculate the cost of the transaction:
- Gas limit: 21,000 units
- Gas price: 30 Gwei (0.000000030 ETH per unit)
The total gas fee would be: 21,000 × 30 = 630,000 Gwei, or 0.00063 ETH.
At an ETH price of $2000, the transaction fee would be: 0.00063 ETH × $2000 = $1.26
So, a simple ETH transfer could cost you around $1.26 in gas fees, depending on network congestion and the current Gwei price. It should be noted that this is a basic example, and actual costs can vary greatly based on factors like network demand, transaction speed, and whether you're willing to pay more for it to go through faster.
Gwei ranges for different actions
Action | Typical Gwei Range |
ETH Transfer | 10–30 Gwei |
Token Swap (Uniswap) | 30–150+ Gwei |
NFT Mint | 100–300+ Gwei |
Complex Contract Calls | 200+ Gwei |
How to read Gwei values on wallet confirmations
In wallets like MetaMask, you’ll see the estimated gas fee displayed in:
- ETH
- Gwei
- USD (or local fiat currency) equivalent
You can also set the gas limit, priority fee, and max fee, to avoid overpaying for gas in the event that prices surge during peak hours.
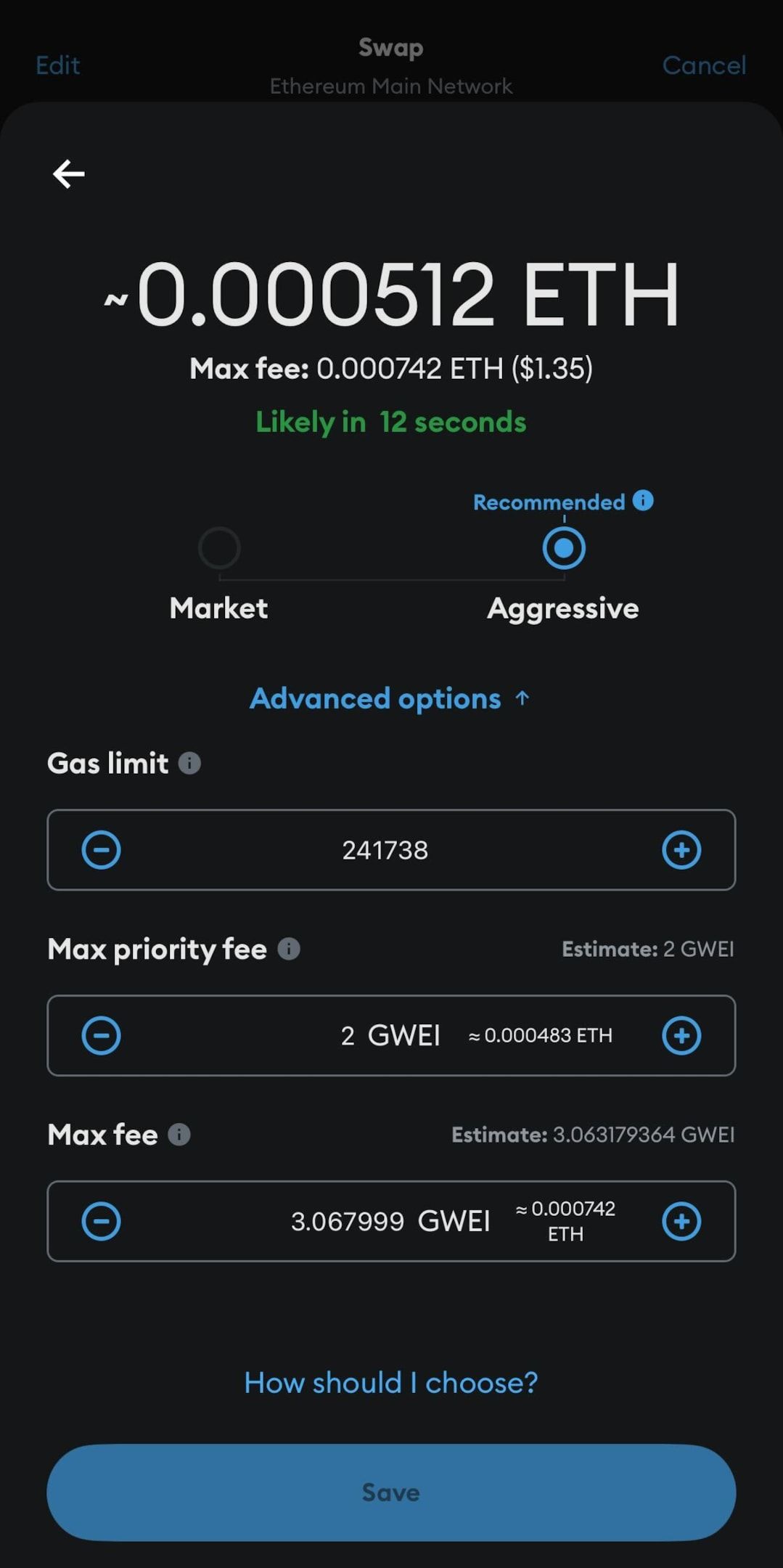
On the transaction preview screen, some crypto wallets may omit displaying the gas fees in Gwei, opting instead for the value in the user's local fiat currency. However, you can usually play around in settings to customize the Gwei amount if you want faster or slower confirmation speeds.
How to Check Current Gwei Prices
Knowing the current Gwei price can help you time your transactions for the best value. Let’s explore how to check real-time gas prices and understand what they mean for your Ethereum activities.
Top tools and websites for real-time gas tracker data
If you want to know if gas is low right now, you can check out popular tools like:
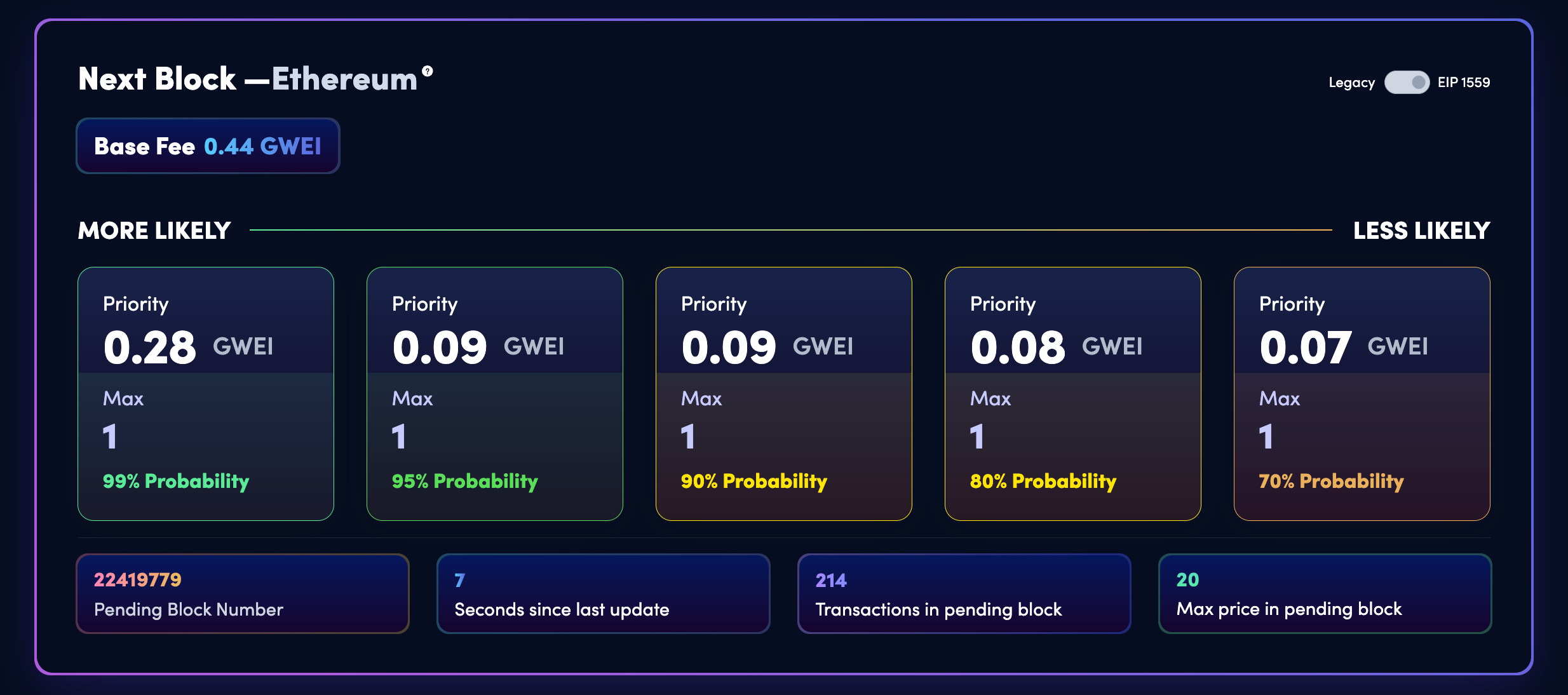
These tools show real-time Gwei prices, network congestion levels, and even give recommendations for whether you should wait or go ahead with a transaction at a given time. Previously, there were additional sites like ETH Gas Station, that have since shut down their services.
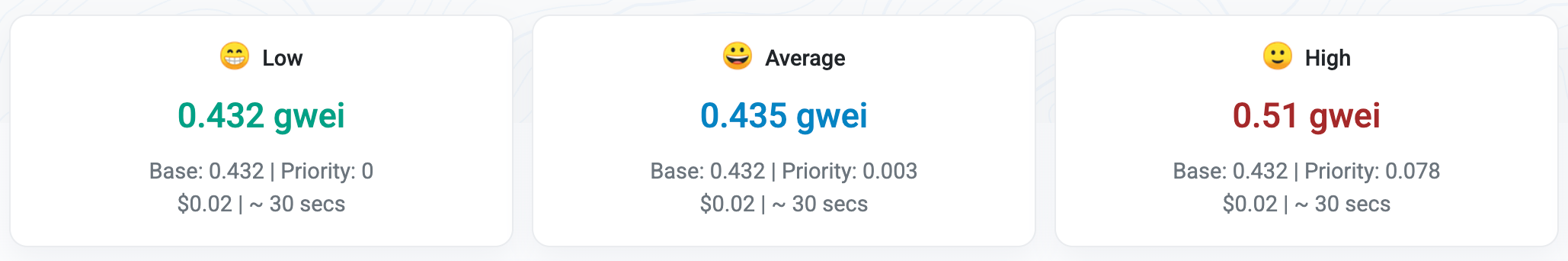
Understanding “low,” “average,” and “high” Gwei prices
These categories indicate how fast your transaction will be processed. Simply:
- Low: Cheapest, but slowest.
- Average: Balanced option for most users.
- High: Fastest, but costs more.
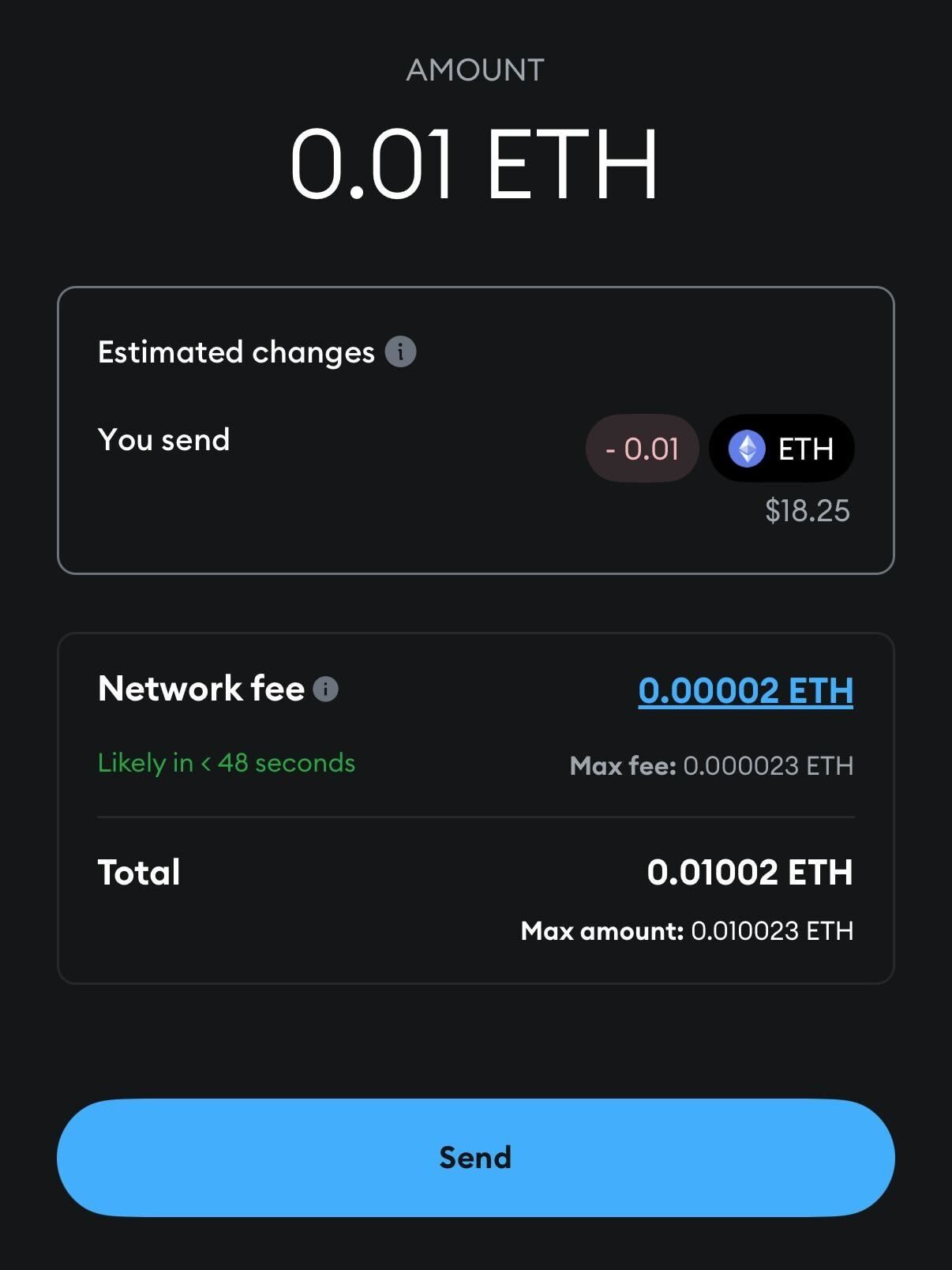
Gas estimation features in popular crypto wallets
Ethereum wallets like MetaMask, Rainbow, and Trust Wallet include built-in gas estimators. These tools allow users to choose preset speeds (slow, average, fast), set a custom Gwei amount, and see live estimates before confirming the transaction.
Tips to Reduce Gas Fees Paid in Gwei
Gas fees can add up quickly on Ethereum, but there are a few smart ways to reduce the amount of Gwei you spend on transactions:
1) Timing your transactions for lower network demand
Ethereum gas prices fluctuate throughout the day. To get the timing right, you can:
- Avoid high-traffic times (like weekday afternoons UTC during market hours)
- Instead, schedule important actions during off-peak hours (late nights or weekends)
- Use tools like Etherscan to view Ethereum network activity
2) Using Layer-2 solutions
Layer-2 solutions allow you to interact with Ethereum at a fraction of the gas cost. Instead of sending a transaction on the mainnet, you can use rollups like Arbitrum or Optimism. These solutions offer faster speeds and cheaper fees by batching transactions off-chain and submitting them to the main blockchain as a single transaction.
3) Choosing slower transaction speeds to save on fees
If you're not in a rush, opt for a “Low” gas fee option in your wallet. You’ll save on gas and still get your transactions confirmed, albeit just a tad slower. Most wallets like MetaMask let you manually select slower speeds or set a custom Gwei amount for even greater control.
Gwei and EIP-1559: Base Fee + Tip Explained
To better understand how Gwei works today, it helps to know how Ethereum gas fees were structured before and after EIP-1559.
The Ethereum EIP-1559 upgrade
In August 2021, the Ethereum blockchain introduced EIP-1559 (Ethereum Improvement Proposal), a significant upgrade designed to make gas fees more predictable and efficient. Prior to this update, gas fees were based on an auction system, leading to fluctuating and sometimes unpredictable costs.
Upon its approval, EIP-1559 implemented a base fee + tip system:
- Base fee: Gwei fee set algorithmically based on network demand and is automatically burned to reduce supply.
- Priority fee (tip): Optional Gwei tip users can add to speed things up and incentivize miners to prioritize their transaction.
For example: If base fee = 40 Gwei and Tip = 10 Gwei, the total amount = 50 Gwei
Since the EIP-1559 upgrade, ETH gas fees have stabilized somewhat, while also benefiting from a deflationary mechanism that burns a portion of the ETH used for gas. Over time, this reduces Ethereum’s circulating supply and supports its shift toward becoming a more deflationary asset.
Pay Lower Gas Fees on ETH Today
Tired of getting hit with high Gwei and gas fees?
Platforms like MoonPay can help you optimize your ETH transactions with cost-effective fiat-to-crypto payment options, Layer-2 token support, and real-time fee transparency at checkout. Plus, you can buy Ethereum using recurring purchases to take advantage of optimal pricing over time.
.png)





.png?w=3840&q=90)