If no single entity can control a decentralized network like Bitcoin, how do new cryptocurrency tokens come into circulation? And how can it be ensured that bad actors do not sabotage the network by producing more or fewer tokens than what is proportionate?
The answers lie in a process known as cryptocurrency mining, which may be confusing to newcomers to the space.
In this guide, we'll walk through the basics of cryptocurrency mining and how it works.
What is crypto mining?
Cryptocurrency mining is the process of verifying and adding transactions to a Proof-of-Work (PoW) blockchain by solving complex mathematical problems that become progressively more difficult as the blockchain grows.
Mining is how new units of cryptocurrency on PoW blockchains are created. It's also how the network prevents double spending and secures itself from attack. A miner, therefore, is a device that verifies the legitimacy of blockchain transactions.
The first miner to verify a transaction and add it to the blockchain is rewarded with cryptocurrency in the form of a transaction fee and/or a newly minted coin. In a figurative way, then, they “mined” the new units of crypto.
Mining requires special hardware and software to solve complex mathematical problems in order to confirm transactions on the blockchain.
The more miners participate in the network, the harder it becomes to mine new tokens. This helps ensure that only valid transactions are added to the blockchain and that fraudulent activity is reduced.
It is essential to note that "cryptocurrency mining" is not synonymous with "Bitcoin mining." The latter is a subset of the former.
To learn more about Bitcoin mining, see our article What is Bitcoin mining?
How does cryptocurrency mining work?
Cryptocurrency mining requires two key things: a blockchain and mining equipment.
A blockchain is a digital ledger of all cryptocurrency transactions. It is constantly growing as new sets of recordings are appended to "completed" blocks.
Each block contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, a timestamp, and transaction data. The nodes use the blockchain to differentiate legitimate cryptocurrency transactions from attempts to re-spend already spent coins.
Mining rigs (or miners) are specialized computer hardware that use their processing power to verify cryptocurrency transactions and add them to the blockchain. In return for the services, the mining rigs are rewarded with cryptocurrency.
In a PoW-based blockchain, there are several miners. But only one miner, the one that solves the mathematical problem first, is rewarded.
Mining can therefore be seen as a race among the miners to solve the problem. But unlike common mathematical problems, no logic or formulae are involved here. The answer results from trial and error–it has to be guessed. The first miner to “guess” the correct answer is rewarded.
This means that the likelihood of a miner guessing the correct answer largely depends on how many answers or combinations a miner can put forward per second, otherwise known as "hash rate" or "hash power."
Hash power is a unit used to measure a blockchain network's processing power. It is calculated by multiplying the number of hashes per second by the number of watts consumed.
Why do cryptocurrencies need miners?
Miners are needed to prevent fraud and maintain the security of blockchains and the cryptocurrencies on those blockchains.
Proof-of-Work cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin are based on a public ledger maintained by a network of miners. These miners use their computing power to verify transactions on the blockchain and to add new blocks of data.
In order for this system to work, it's vital that there is a sufficient number of miners verifying transactions and adding new blocks. If there were no miners, it would be easy for someone to tamper with the blockchain and fraudulent transactions would go undetected.
Mining is also essential for maintaining the security of cryptocurrencies. Because all transactions are verified by miners, it is very difficult for anyone to sabotage the chain by creating fraudulent transactions.
How to start mining cryptocurrencies
Mining can be a great way to earn passive income and contribute to a blockchain network.
In this section, we will look at three ways to mine cryptocurrencies:
- Individual mining
- Joining a mining pool
- Cloud mining
Before we jump in, there are some things to keep in mind:
- You can only mine Proof-of-Work cryptocurrencies
- You cannot mine ETH as the Ethereum network has moved to Proof of Stake
- Mining cryptocurrencies can have detrimental environmental impacts
To learn more about the difference between Proof of Work and Proof of Stake, see our article Proof of Work vs Proof of Stake
Individual mining
If you’re doing it yourself, here are two main types of cryptocurrency mining:
- GPU mining
- ASIC mining
GPU mining
GPU mining is the process of using a graphics processing unit (GPU) to mine cryptocurrency.

It’s the easiest way to start mining cryptocurrencies because it uses the same components you'd find in a standard PC.
The better the performance of the GPU, the more coins you can mine. But due to high demand, it can be difficult to find some of these graphics cards.
The downside of GPU mining is that it is slower since the network demands a high hash power.
Checklist for GPU mining:
- High-end GPU (graphics card)
- Cooling mechanism (air-cooled, liquid-cooled, etc.)
- Mining software, which must be installed
Profitability Calculator by NiceHash can help you figure out whether or not it is worth it to mine cryptocurrencies based on the hardware you have and the cost of power in your region. Note that this does not factor in the price of buying the GPU.
ASIC mining
ASIC mining is the process of using a purpose-built computer to mine cryptocurrency. ASIC stands for Application Specific Integrated Circuit, and it’s designed to do one thing and one thing only: mine cryptocurrency.

ASIC miners are more expensive than GPU miners but are also much more powerful. They can mine cryptocurrency much faster and are therefore more profitable.
But ASIC miners have a few downsides.
First, they can be very expensive. Second, they can only mine one specific cryptocurrency. So if you want to mine multiple cryptocurrencies, you'll need to buy multiple ASIC miners.
Checklist for ASIC mining:
- ASIC miner
- High voltage power supply (usually at least 220V)
- Noise-insulated and well-ventilated location
- Cooling mechanism (air-cooled, liquid-cooled, etc.)
- Ethernet connection
Joining a mining pool
Mining pools are groups of miners that combine their hash power to mine cryptocurrencies.
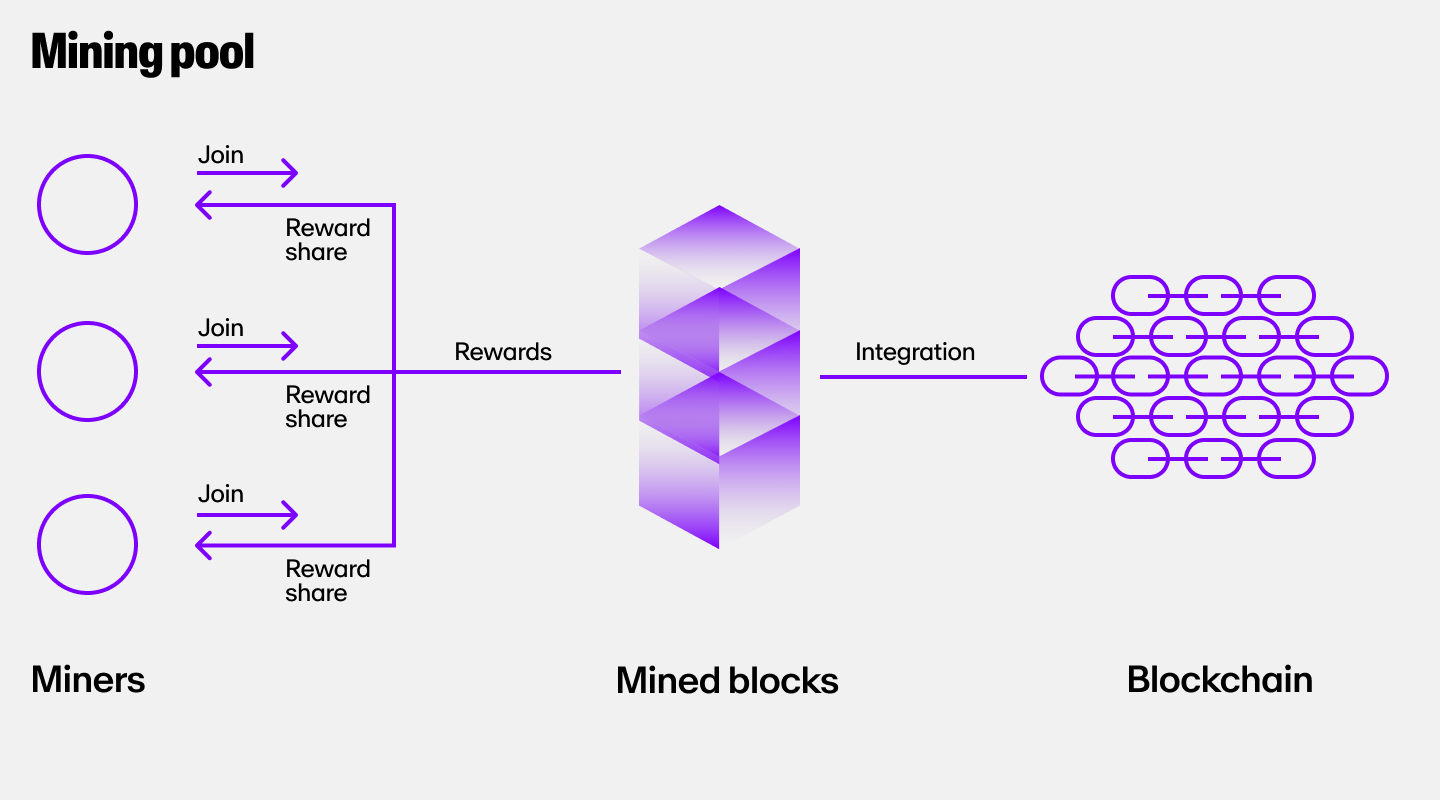
The main benefit of mining pools is that they increase your chances of finding a block and receiving a reward. When you mine alone, there is a very small chance you will verify a block because of your low hash rate. But when you join a mining pool, your hash rate is combined with the other miners in the pool.
The downside to mining pools is that they will take a small percentage of your rewards as a fee.
Checklist for joining a mining pool:
- Create a cryptocurrency wallet
- Download, install and run mining software
- Join a mining pool
The first thing you'd have to do to get started is to choose a mining pool. There are hundreds of mining pools, and choosing one is very difficult if you try to do a manual search.
MiningPoolStats is a website that helps you cut down your research time. It aggregates information on all the cryptocurrencies that can be mined, their corresponding mining pools, and essential metrics like pool fees, hash rate, and more.
The payout you'd receive from a pool depends on your contribution, which is determined by your miner's hash rate.
There are three standard payout methods:
Pay Per Share (PPS)
You are paid a fixed amount for each share you contribute. This does not include transaction fees.
Pay Per Last N Shares (PPLNS)
Similar to PPS, but the payout is based on the last ‘N’ shares instead of each share.
PPS+
This is a combination of PPS and PPLNS where you are paid per share, but the transaction fee is paid per last N shares.
Cloud mining
Cloud mining is the process of mining cryptocurrencies in the cloud. This means you can mine cryptocurrencies without having to buy, build, or maintain your own mining rigs.
This type of crypto mining is much cheaper than traditional mining. You don't have to worry about the cost of power, cooling, or maintenance.
Cloud mining combines the best of cloud computing and cryptocurrency mining.
With cloud computing, users are able to access computational power greater than their home desktop through the internet. Cryptocurrency mining, on the other hand, is very resource-intensive. It requires expensive hardware and a lot of electricity to power those rigs.
The combination of the two allows users to get all the benefits of cryptocurrency mining without the hassle.
On the flip side, it is much riskier than traditional mining. There have been many scams in the cloud mining space.
Cloud mining is made possible when companies with sufficient resources set up large mining rigs, which is impractical for any one person to do. Once everything is functional, users are offered to purchase a fraction of the hash power for a specified period. This is also called "leased hash power mining."
For instance, instead of buying a 14 terra-hash Bitcoin ASIC miner, setting it up, and starting to mine crypto, you could simply rent the same amount of hash power from the cloud mining company. All charges (electricity, coolant, maintenance, housing, etc.) are typically included in the rent.
Alternatively, you could purchase your own miner and host it elsewhere. The company housing, running, and maintaining your miner would simply take a cut of the cryptocurrency mined and give you your share. This type of cloud mining is called "hosted mining."
Another thing to keep in mind is that cloud mining contracts are usually sold for 1-3 years. During that time, the mining difficulty could increase significantly, which would decrease your earnings proportionally.
What are the risks of crypto mining?
While mining cryptocurrencies can be profitable, there are also many risks and potential downsides.
Environmental impact
Crypto mining is a very energy-intensive process. It has been estimated that Bitcoin mining uses as much electricity as the entire country of Denmark.
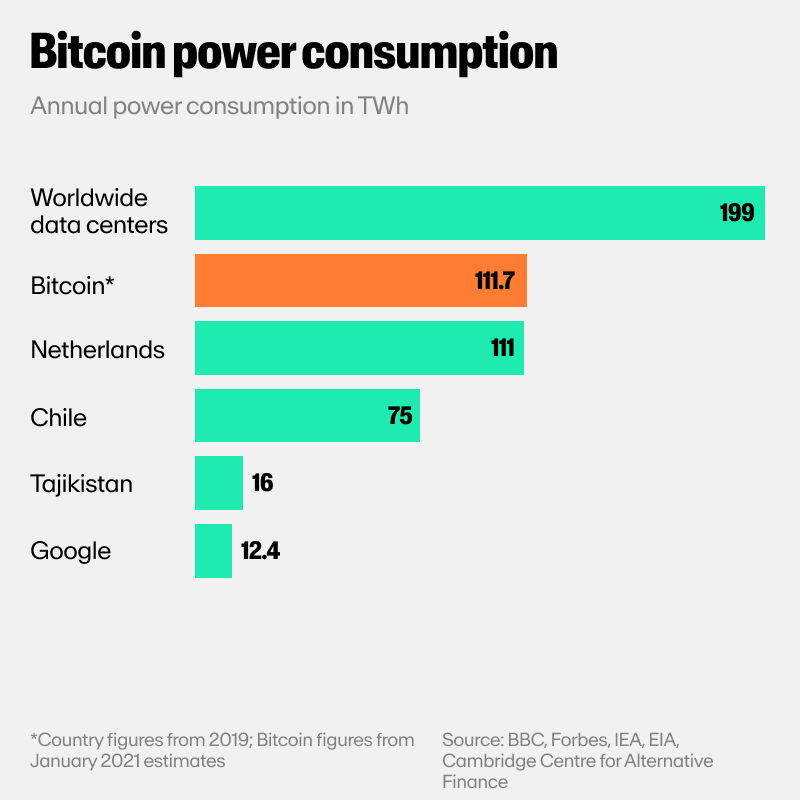
You can think of mining as a race in which there is only one winner who takes home the prize, and all other participants get nothing.
In a network that has thousands of miners competing to validate transactions, only one miner is rewarded per validation. The net energy consumption per transaction therefore continues to climb regardless of network throughput.
For perspective, the world's most popular cryptocurrency to be mined, Bitcoin (BTC), consumes more energy per transaction than over 47 US households combined, according to Digiconomist.
By shifting from a PoW consensus model to a PoS consensus model, blockchains like Ethereum can lower their energy consumption by over 99.99%. In this case, however, mining would not be possible.
Price volatility
The cryptocurrency market is known for its volatility. The price of Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies can go up and down by hundreds, even thousands of dollars in a matter of hours.
This makes it difficult to predict how much money you can make from mining. If the price of the coin you are mining goes down, your earnings will go down, and it will take longer for you to break even, especially if you have invested in expensive mining rigs.
The price below which a miner is no longer profitable is referred to as the "shutdown price."
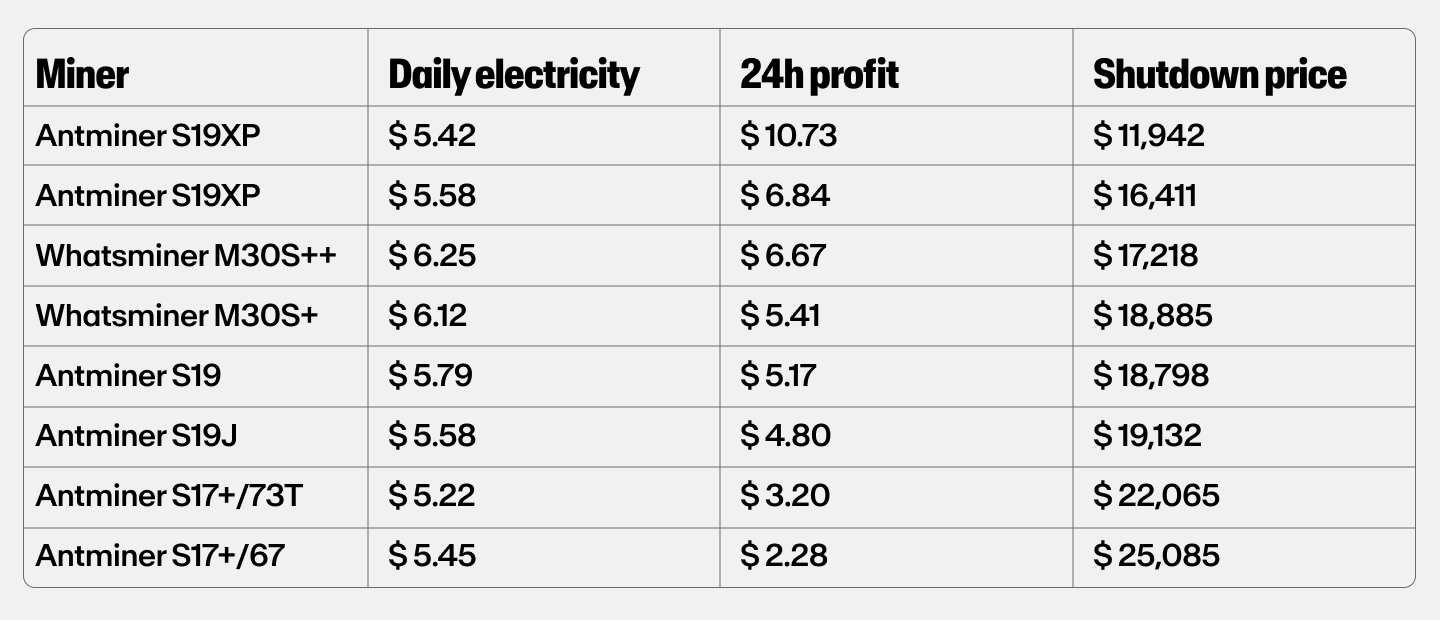
It's essential to keep in mind that just because the price of a cryptocurrency is rising doesn't mean that it's a good investment. The price of cryptocurrencies are often based on speculation and can be extremely volatile.
View our Bitcoin Price and Ethereum Price pages for live price and market data for these leading cryptocurrencies.
Fraud
Another considerable risk when it comes to mining cryptocurrencies is fraudulent activity. There have been cases in which companies have set up mining operations only to vanish with people's money.
This is more common in the case of cloud mining.Make sure you do your due diligence before investing in any cloud mining operation. Some things to look out for include:
Lack of transparency
Does the company provide detailed information about its mining rigs, locations, and processes? If not, it may be a sign that they are trying to hide something.
No contact information
A company that doesn't provide any contact information is likely a scam.
Exaggerated claims
Be wary of companies that guarantee high returns or make other unrealistic promises.
Lack of customer reviews
If there are no customer reviews, it may be because the company is new or it could be a sign that they are trying to hide something.
Tax implications and regulatory issues
Since crypto mining can be considered a business activity, there may be tax implications depending on your country's laws.
In the US, for example, crypto miners are required to pay tax on the currencies they mined as per their fair market value.
It's also important to be aware of any regulatory issues that could impact your ability to mine cryptocurrencies. For example, China recently cracked down on crypto mining operations, which led to a decrease in hash power on the Bitcoin network.
Is crypto mining worth it?
The answer to this question depends on a number of factors, including the cost of electricity, the price of the coin you are mining, and the value of the cryptocurrency market.
While crypto mining can be used to earn passive income, it's important to do your research before investing in any operation.
Buy crypto via MoonPay
Of course, mining is not the only way to get crypto.
MoonPay makes it easy to buy cryptocurrency like Bitcoin using your credit card or any other preferred payment method.





.png?w=3840&q=90)