Ethereum (ETH) and Ethereum Classic (ETC) are two cryptocurrencies that share the same origin but have grown into very different blockchains (with distinctly diverging futures).
Both networks allow users to build decentralized applications (dApps) and execute smart contracts, but their philosophies and long-term goals diverged after the infamous 2016 DAO hack.
After the hack and subsequent fork, Ethereum has become the second-largest cryptocurrency after Bitcoin, powering the majority of decentralized finance (DeFi), NFTs, and Web3 applications. Ethereum Classic, on the other hand, represents the original chain that refused to alter its transaction history, appealing more to those who value immutability and a capped token supply.
In this guide, we break down the history of the 2016 fork, explore the similarities and differences between ETH and ETC, and highlight what each network means for users.
History of Ethereum: Before the Fork
Before diving into a comparative analysis, it is important to understand why two separate blockchains with very similar names exist. To explain that, we need to revisit one of the most important and controversial events in Ethereum's history.
A brief glimpse into the history of the Ethereum protocol will help highlight the implications of the 2016 DAO hack:
2013: Vitalik Buterin first proposed the idea of a programming language for automating on-chain tasks and building applications on the blockchain.
2014: Vitalik published the original Ethereum blockchain whitepaper, bootstrapping $17 million for the network.
2015: The original version of the Ethereum network went live and everything ran smoothly for a year.

The DAO Hack and Ethereum’s Hard Fork
In 2016, the launch of the decentralized autonomous organization known as “The DAO”, however, changed things for the new blockchain. The DAO was a decentralized venture capital fund enabling retail investor accounts to crowdfund projects on the Ethereum network. It successfully raised $150 million by selling DAO tokens. Retail clients could use the coins to vote and pledge their support for decentralized apps (dApps) on the network.
Unfortunately, DAO's smart contract code had a security vulnerability known as the ‘Split Function'. Originally, the smart contract included this feature to enable investors to withdraw their investment if they weren't satisfied with a project. If someone invoked the function, users would get their ETH back, and the smart contracts would update the public ledger accordingly.
Due to this security flaw, malicious hackers could receive money without updating the transaction history. On June 17, 2016, hackers exploited the code and drained $50 million from the project. This was a big blow to the nascent Ethereum network and the original ETH token owners had to do something about their stolen funds.
Consequences of the DAO Hack
After the hack, Vitalik Buterin and other project developers felt that regaining the confidence of the Ethereum community was necessary. Users could only trust the Ethereum ecosystem again if they retrieved their money.
Ethereum developers initially proposed a soft fork so that the current and updated versions are mutually compatible. But this didn't materialize due to legal and technical issues. Instead, the network arrived at a consensus to hard fork Ethereum, which meant the creation of a new and backward-incompatible blockchain.
Ethereum vs. Ethereum Classic thus became an either / or choice.
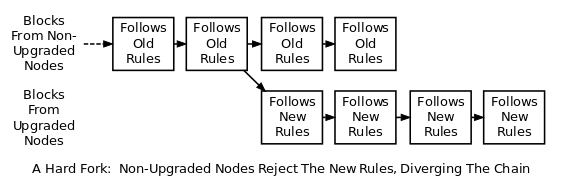
The decision to hard fork the original Ethereum blockchain led to an ideological debate within the cryptocurrency community. Some argued that “code is law” and the immutability of the blockchain is sacrosanct. The hack should therefore remain part of the transaction history.
The counterargument was that retrieving the money is of paramount importance and transactions should be altered if necessary.
After a heated debate, the decision was put to a vote. The community voted in favor of the hard fork and the developers implemented it on July 20, 2016, after the 192,000th block.
Thus, a single blockchain forked to become two distinct networks:
The pre-forked version of the blockchain came to be known as the Ethereum Classic Network, which contained the record of the hack. The Ethereum blockchain reversed the hack and returned the money to its users.
What is Ethereum Classic (ETC)?
Ethereum Classic (ETC) emerged as the unaltered version of Ethereum (ETH) and derived its name after forking the network. Anonymous developers vehemently upheld the immutability of blockchain technology and convinced others to maintain the transaction record of the old Ethereum.

The open-source and decentralized Ethereum Classic interface supports decentralized applications and runs on the Proof of Work consensus mechanism. Ethereum Classic users rely on the native ETC cryptocurrency to power transactions on the platform.
What is Ethereum (ETH)?
Ethereum compromised on the immutability principle to return money to its users after forking the blockchain. Vitalik Buterin and the Ethereum Foundation garnered support for the platform, which eventually became famous in the crypto community.
The popular cryptocurrency Ether (ETH) powers the Ethereum platform. Ethereum has distinguished itself from other blockchains through its compatibility with dApps that run on smart contracts, and has since become the main hub for decentralized finance (DeFi).

After using a Proof of Work consensus protocol for most of its existence, Ethereum completed the process of migrating to a Proof of Stake (PoS) system on September 15, 2022.
Also known as Ethereum 2.0, the new PoS version of ETH includes a roadmap with several upgrades to the network, mostly in the name of greater scalability, faster transactions, and lower gas fees.
Here’s a quick snapshot of the main differences between Ethereum (ETH) and Ethereum Classic (ETC) at a glance:
Key Difference | Ethereum (ETH) | Ethereum Classic (ETC) |
Consensus Method | Proof of Stake | Proof of Work |
Supply | Unlimited (≈4.5% yearly growth) | Capped at 230M |
Market Value | $500B + | $4B + |
Security | Strong validator network | History of 51% attacks |
Adoption | Leading DeFi, NFT, dApp ecosystem | Smaller ecosystem, niche community |
Similarities Between Ethereum and Ethereum Classic
Both Ethereum and Ethereum Classic function as a medium of exchange, facilitating trades and exchanges with other cryptocurrencies. Here are some other similarities between them:
Decentralized blockchain technology
Ethereum continues to be a decentralized protocol similar to Ethereum Classic with its globally distributed blockchain nodes that eliminate single points of failure and process transactions 24/7.
Smart contract functionality
Both Ethereum and Ethereum Classic automate decentralized applications and financial decisions using smart contracts. A smart contract is essentially self-executing code that can perform actions based on predefined conditions.
Privacy protection
Ethereum and Ethereum Classic both put great emphasis on protecting the privacy of their users. While public keys are open for everyone, private keys remain under the user's exclusive control. Users are also free to use aliases instead of their name and other details, preserving their anonymity while carrying out transactions.
Differences Between Ethereum and Ethereum Classic
The main difference between Ethereum and Ethereum Classic comes down to factors like minting limit, price, market cap, and consensus protocol.
Minting limit
According to the monetary policy of Ethereum, there is no hard cap on its supply, which can increase indefinitely. However, developers have programmed the supply of Ethereum to increase by 4.5% only every year.
The monetary policy of Ethereum Classic, on the other hand, stipulates a fixed supply of its tokens. There can only ever be 230 million Ethereum Classic tokens, which is meant to ensure a fair price.
Market value and price
ETH price
Throughout 2025, Ethereum price has oscillated between lows of $1,500 and highs exceeding $4,900 (remember that cryptocurrency prices are subject to constant change).
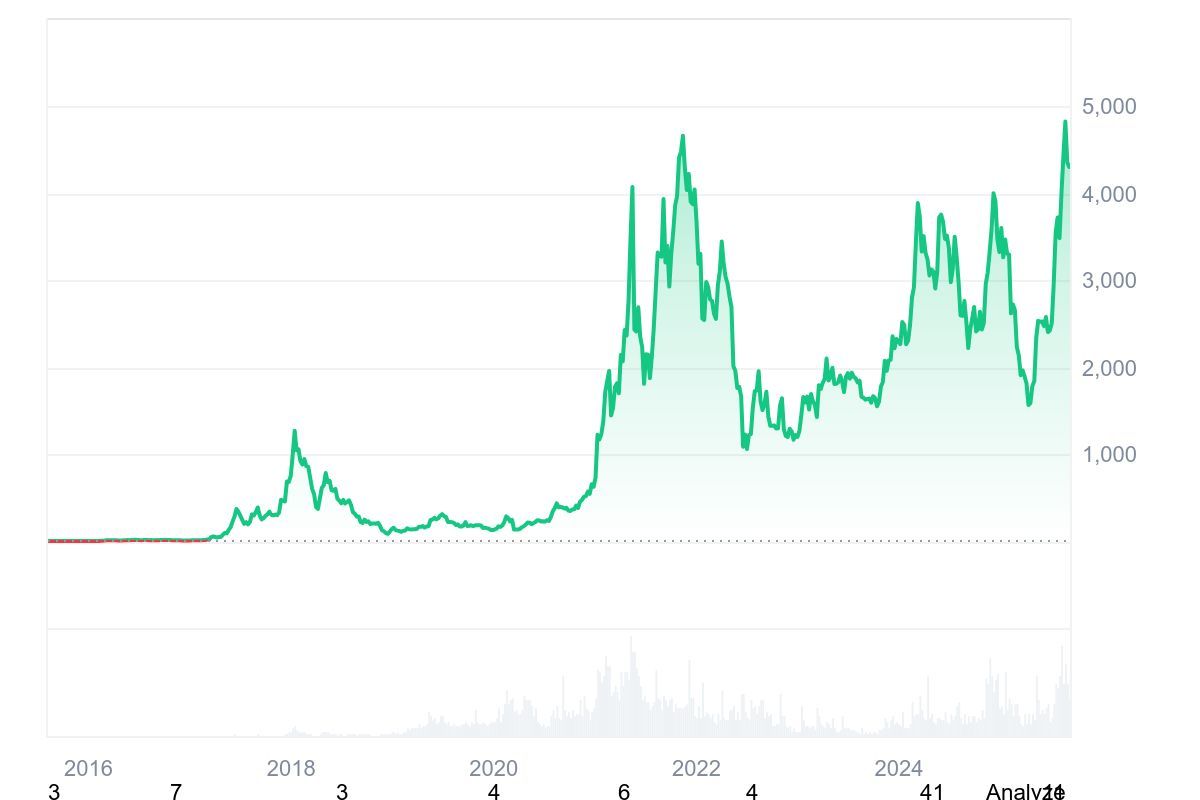
ETH is the second-largest cryptocurrency (after Bitcoin) with a market capitalization above $500 billion and a circulating supply of over 120.7 million tokens. Ethereum reached an initial all-time high of $4,891.70 on November 16, 2021, before breaking its own record again in August, 2025.
For live Ethereum price and market metrics, view our Ethereum Price page
ETC price
Ethereum Classic has a price of nearly $29 at the time of writing (nearly 120x lower than ETH).
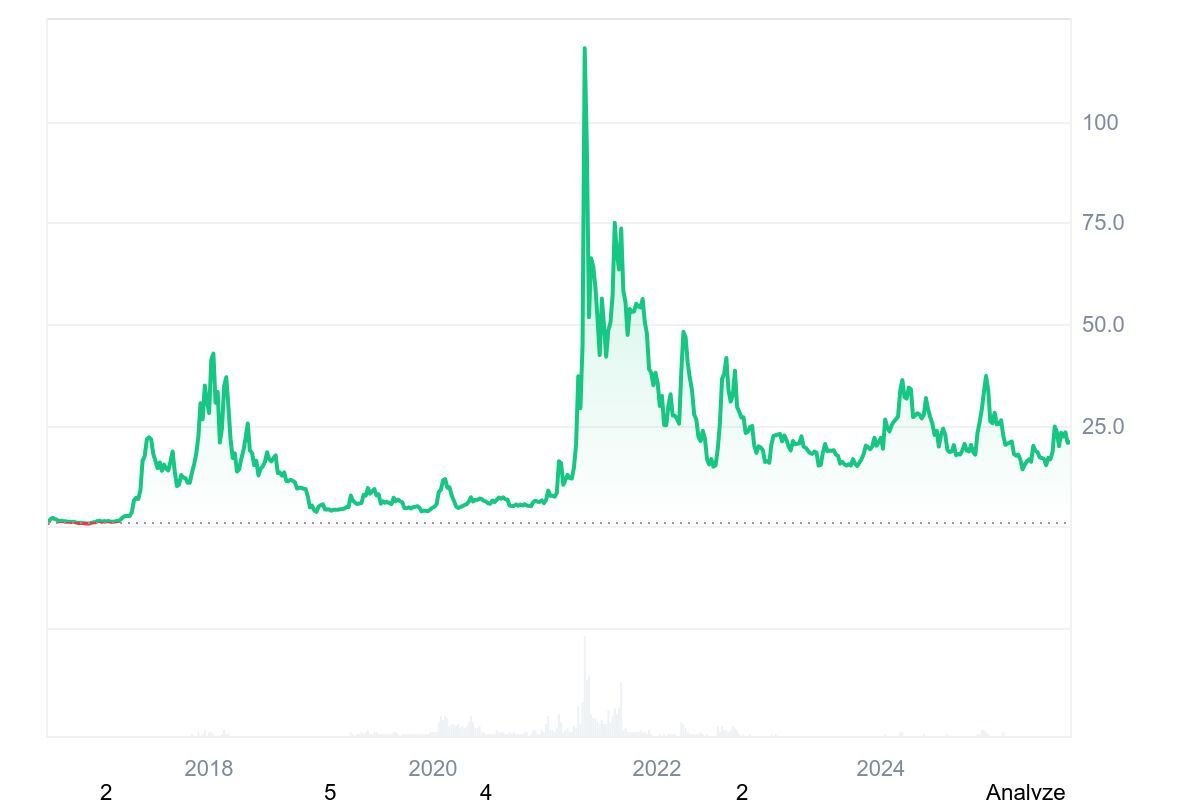
ETC has a top 40 market cap of all cryptocurrencies at above $3 billion, with a circulating supply of over 153 million tokens. Ethereum Classic reached its all-time high of $176 on May 6, 2021.
Consensus protocol
Ethereum Classic runs on the Proof of Work consensus mechanism. Through this process, miners solve complex mathematical problems using energy-intensive equipment to gain rights for validating transactions on the blockchain. By successfully validating and adding new blocks, they get ETC tokens as rewards.
Ethereum used to run on the Proof of Work consensus model, but made the shift toward the Proof of Stake mechanism where nodes must stake Ether tokens to become validators. Staking ensures that validators won't add any dubious transaction to a block. This shift from PoW to PoS is known as the Merge and took place in September of 2022.
Recommended reading: Proof of Work vs Proof of Stake
Earn interest in Ethereum and Ethereum Classic
One way to earn interest is to deposit your Ethereum and Ethereum Classic tokens in yield farming protocols, liquidity pools, and other lending platforms. These platforms use the funds for loans, offering you a competitive interest rate for your deposit. Despite relative stability, however, interest rates may fluctuate depending on the supply-demand ratio.
Ethereum users can also stake ETH to earn interest. You can choose to stake Ethereum independently using an Ethereum wallet or do so on a crypto exchange. You will need a minimum of 32 ETH to independently participate in staking, but for exchanges there is no fixed staking amount since they aggregate the funds from multiple investors.
Recommended reading: What is crypto staking?
The following side-by-side comparison highlights the key differences between Ethereum and Ethereum Classic across consensus, supply, price, security, and adoption:
Feature | Ethereum (ETH) | Ethereum Classic (ETC) |
Origin | Forked after DAO hack in July 2016 | Original unaltered chain |
Philosophy | Community reversed the hack to refund investors | “Code is law” = immutability above all |
Consensus Mechanism | Proof of Stake (since 2022 ETH Merge) | Proof of Work (mining) |
Token Supply | No hard cap (≈4.5% annual issuance) | Hard cap of 230 million ETC |
Market Rank | Top 2 by market cap | Top 40 by market cap |
Price (2025) | $4,950 + ATH (Aug '25) | $29 + |
Ecosystem | Leads DeFi, NFTs, Layer-2 scaling | Smaller ecosystem, fewer dApps, miner-focused |
Security History | Strong validator network, institutional adoption | Multiple 51% attacks (notably in 2020) |
Staking | Yes (32 ETH minimum) | No (mining only) |
Future Outlook | Scalability upgrades, mainstream adoption | Niche PoW chain with loyal community |
Ethereum vs Ethereum Classic: Concluding Thoughts
Ethereum is not the only network to have undergone forking. The Bitcoin community also faced a similar dilemma in 2017 when it forked and Bitcoin Cash was born. The forking of the Ethereum blockchain is therefore not an exceptional incident in cryptocurrency history, and it didn't permanently solve Ethereum's problems.
For instance, despite its transition to ETH 2.0, Ethereum suffers from scalability issues and causes environmental damage. In recent years, Ethereum Classic has been subject to three 51% attacks in a month, significantly hurting its reputation. Nevertheless, both blockchains have adopted measures to rectify these flaws.
With a better understanding of ‘immutability politics', Ethereum Classic implemented the Atlantis hard fork in 2019 to improve its compatibility with Ethereum. Soon after, it also implemented the Agharta hard fork to ensure complete compatibility between ETH and ETC.
Similarly, the Ethereum 2.0 upgrade was completed in 2022, giving the Ethereum blockchain network enhanced scalability, speed, low ETH gas fees, and lower carbon emissions. With these modifications, Ethereum will continue to become far more efficient than it has ever been.
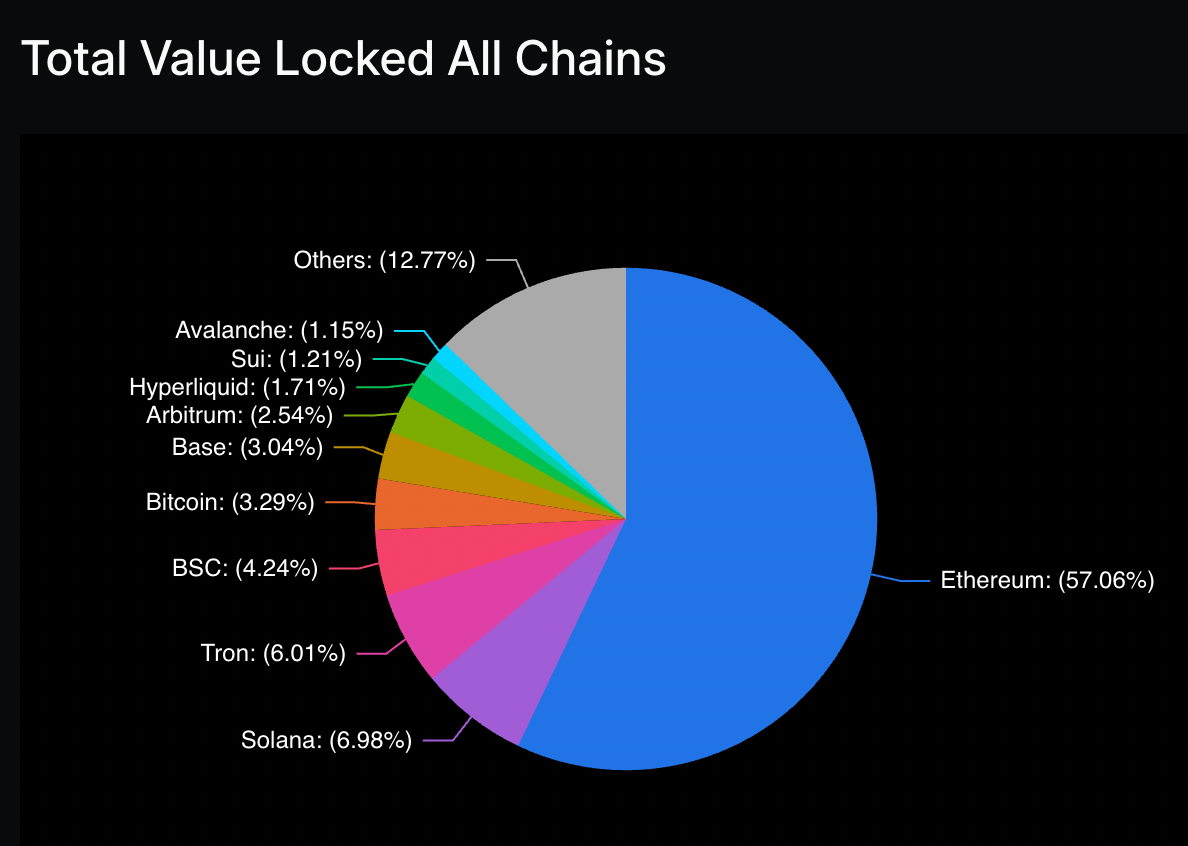
At the time of writing, the total value locked (TVL) in DeFi sits at $133 billion, with Ethereum dominating the market at over $70 billion. Although this is down from its 2022 high of $125 billion, Ethereum has consistently controlled well over 50% of the DeFi TVL, with additional billions TVL in Ethereum cross-chain bridges.
Overall, we can expect better communication and interaction between Ethereum and Ethereum Classic, with both chains contributing to the crypto industry's future.
FAQs: Ethereum vs Ethereum Classic
Which is better, Ethereum or Ethereum Classic?
While, no token can truly be deemed "better", there are qualities that each possesses that makes it appeal to different users. Ethereum (ETH) has more adoption, stronger security, and higher market cap, while Ethereum Classic (ETC) sticks to the principle of immutability with a capped supply.
The choice between ETH and ETC ultimately depends on whether you prioritize ecosystem growth and usability or ideological principles and scarcity.
Why did Ethereum split into two?
Ethereum split in 2016 after the DAO hack. ETH chose to reverse the hack and refund investors, while ETC preserved the original chain.
Is Ethereum Classic the original Ethereum?
Yes, Ethereum Classic represents the original unaltered blockchain, while Ethereum is the fork that altered history after the DAO hack.
Can you stake Ethereum Classic?
No, ETC uses a Proof of Work consensus mechanism, so it can’t be staked. Only Ethereum (ETH) supports staking on its Proof of Stake network.
What is the long term outlook for Ethereum Classic?
ETC has a dedicated community but limited adoption compared to ETH. Like any cryptocurrency, its survival depends on continued developer support and security upgrades.
How to Buy Ethereum (ETH) and Ethereum Classic (ETC)
Now that you have a good understanding of Ethereum vs Ethereum Classic, you might want to buy these tokens for yourself.
You can buy Ethereum (ETH) and Ethereum Classic (ETC) via MoonPay or through any of our partner wallet applications with a credit card, bank transfer, Apple Pay, Google Pay, and many other payment methods.
Users can also top up in euros, pounds, or dollars and use MoonPay Balance for buying cryptocurrencies like ETH and ETC. Once funded, use your balance for faster, cheaper transactions and higher approval rates. When you're ready to withdraw, enjoy zero-fee transfers straight to your bank account.
How to Sell Ethereum (ETH)
MoonPay makes it easy to sell Ethereum when you decide it's time to cash out your crypto.
Simply enter the amount of ETH you'd like to sell and enter the details where you want to receive your funds.
We're always adding more cryptocurrencies like Ethereum Classic (ETC) to sell, so check back soon.
Swap Ethereum Today
Want to exchange Ethereum for other cryptocurrencies like Ethereum Classic and Bitcoin? MoonPay allows you to swap crypto cross-chain with competitive rates, directly from your non-custodial wallet.