To understand Bitcoin hashrate we must first review "Bitcoin mining".
A crash course in Bitcoin mining
While banks validate transactions by controlling the books, blockchains rely on something called a consensus mechanism: a set of rules to ensure all transactions are legitimate.
Bitcoin’s consensus mechanism works like this:
- New transactions are bundled together and encrypted with a secret 64-digit number. This is called a “hash”.
- Powerful computers, also known as “miners”, race to discover this number by making billions of random guesses.
- Once the correct guess is made, transactions are recorded on the blockchain with the hash as its unique identifier.
This process, known as Bitcoin mining, can be difficult to understand, which is why MoonPay put together a primer: What is Bitcoin mining and how does it work?
Suffice it to say, Bitcoin runs on math.

Sign up to our weekly MoonPay Minute newsletter
So what is the “hashrate”?
The mathematics of Bitcoin revolves entirely around that 64-digit hash. The puzzle that miners solve to identify the hash, called the “hash function”, takes an enormous amount of computing power. This leads us to “hashrate”, which is simply the total computing power of all the miners in the Bitcoin network combined.
The greater the hashrate, the more secure the Bitcoin network.
Why? In blockchain networks, one of the main security concerns is something called a 51% attack, which is when a bad actor gets control of more than half the network's total hashrate. The higher Bitcoin’s hashrate, the more difficult and costly it is for an attacker to get to 51%. It’s been estimated that the mining equipment alone for a 51% attack on Bitcoin’s network would cost nearly $8 billion.
Common terms for hashrate include: hash power, hashing power, and mining power.
Calculating the hashrate
Hashrate is typically measured in hashes per second (H/s) or its multiples: kilohashes per second (kH/s), megahashes per second (MH/s), gigahashes per second (GH/s), and so on. Bitcoin is measured in exahashes per second (EH/s), which is equivalent to one quintillion (!) hashes. That’s 1 followed by 18 zeros, or
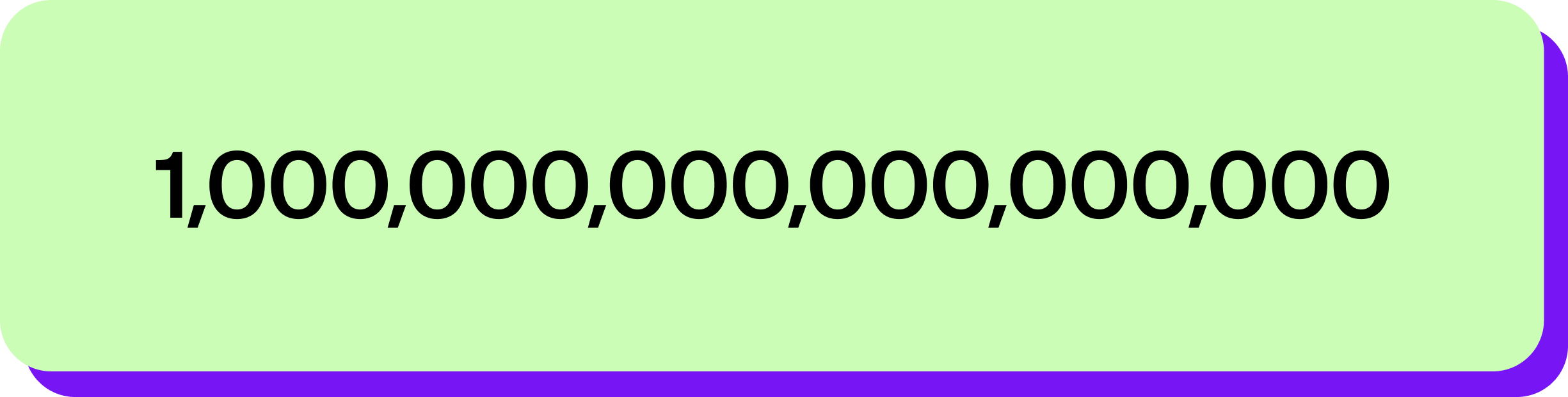
That means the Bitcoin network can process quintillions of hashes per second. At the time of writing, the Bitcoin hashrate’s all-time high is 716.21 EH/s.
Subscribe to our newsletter!
Did you like this article? Sign up to our weekly MoonPay Minute newsletter to get similar content delivered directly to your inbox.